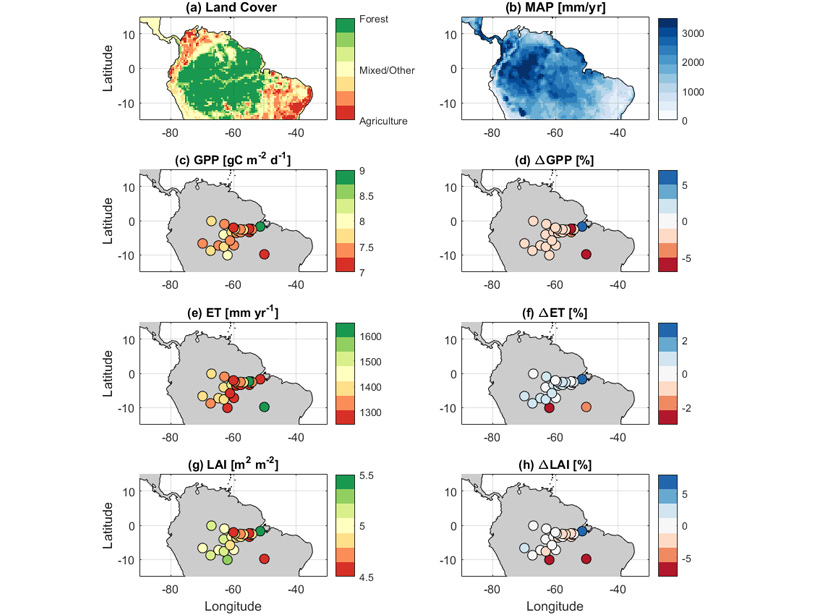
Characterizing leaf phenology in process-based models reconciles both “dry season green-up” and drought controls on Amazonian carbon balance.
Modeling
The Challenges of Global Flood Hazard Mapping and Prediction
A new book presents the latest tools in remote sensing technologies and modeling approaches for addressing challenges and meeting future needs in global flood hazard mapping and prediction.
Toward Standardized Data Sets for Climate Model Experimentation
A new initiative collects, archives, and documents climate forcing data sets to support coordinated modeling activities that study past, present, and future climates.
New Version of Popular Climate Model Released
After spending months addressing a big glitch, researchers released the second version of the Community Earth System Model.
Can We Crack the Climate Code of the Southern Polar Region?
The #GreatAntarcticClimateHack; La Jolla, California, 9–12 October 2017
Life and Death in the Deepest Depths of the Seafloor
Lacking light and energy, under-seafloor microbes rely on ancient organic materials to survive.
New Paths for Plankton in Warming Arctic?
Water flowing from the Pacific to the Atlantic could find new shortcuts, enabling plankton to survive the trip through the cold polar region.
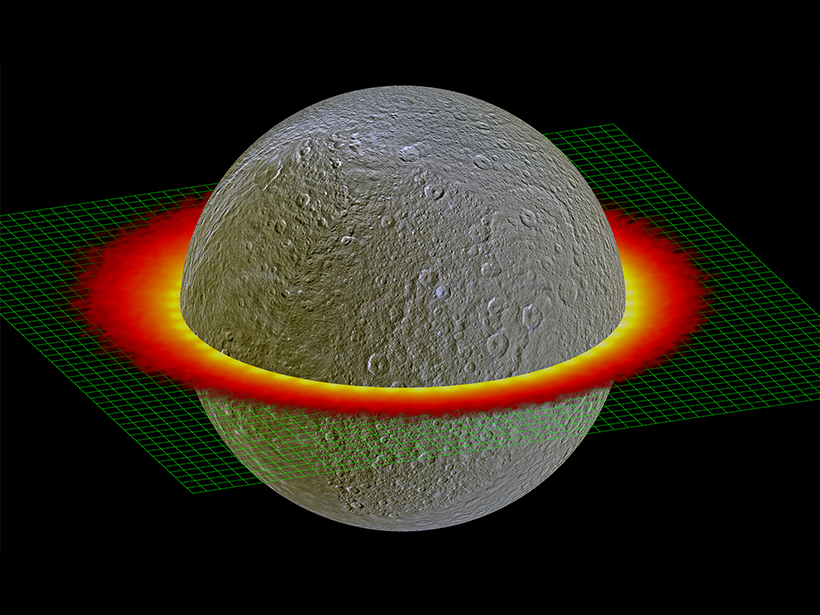
A Consistent Model of Ice Dissociation on Celestial Bodies
A model based on decades of experimental results can now quantify the products of water ice dissociation caused by radiation and predict the products expelled into an icy body’s outer atmosphere.
A Near-Real-Time Tool to Characterize Global Landslide Hazards
By fusing susceptibility information with precipitation data, a new model generates “nowcasts” to predict the potential for rainfall-triggered landslides in steep terrain between 50°N and 50°S.
A Better Way to Predict the Indian Monsoon
A new study finds that including Himalayan topography and land-atmosphere interactions improves climate models.