A climate model with reversed rotation of Earth helps climatologists and oceanographers understand why our planet is the way it is and reveals how different it could have been.
Modeling
Piecing Together the Big Picture on Water and Climate
A new database brings together water isotope data from many sources, providing an integrated resource for studying changes in Earth’s hydroclimate over the past 2,000 years.
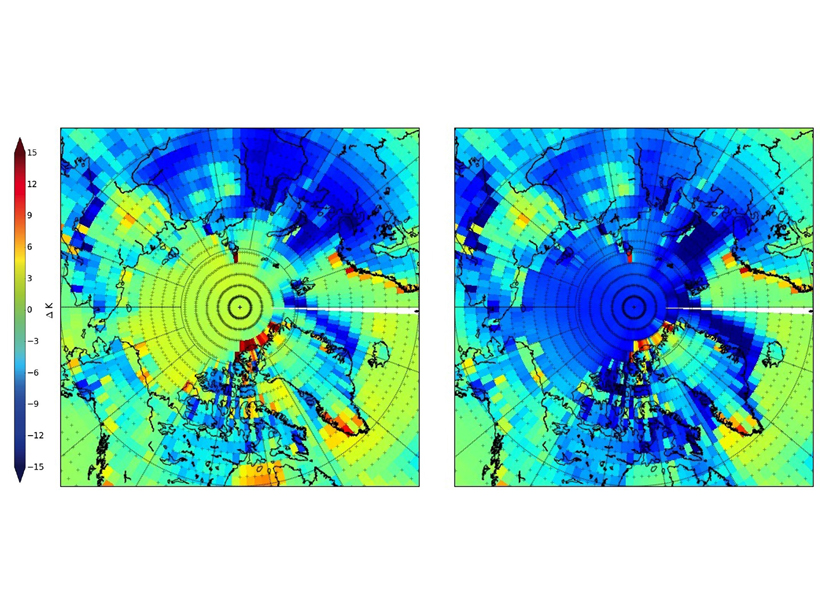
Spectral Surface Emissivity Improves Arctic Climate Simulation
Improving the representation of surface emissivity in the Community Earth System Model reduces its Arctic winter cold bias from 7 to 1 Kelvin degree.
Coupled from the Start
Atmosphere and land model development has historically been segregated but coupled processes crucial to prediction and extremes can be properly represented only with a holistic approach.
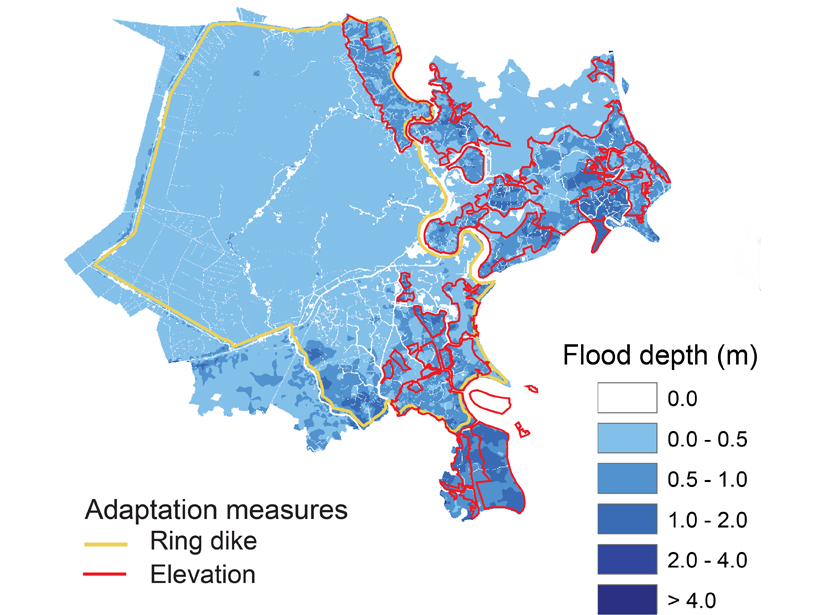
A City’s Challenge of Dealing with Sea Level Rise
A well-developed case study in Ho-Chi Min City, Vietnam, exemplifies how other mega-cities located on deltas could face the major challenge of adapting to rising sea-level.
New Model Simulates Faults and Folds Shaping Each Other
A new model simulates how faulting and folding deep in Earth’s crust shape the way rocks fold and cause earthquakes.
Next-Generation Climate Models Could Learn, Improve on the Fly
Scientists propose development of new models that use machine learning techniques to reduce uncertainties in climate predictions.
Improving Temperature Forecasts in the Upper Atmosphere
Scientists are blending output from multi-year model runs to improve temperature forecasts in regions where satellites experience “drag,” in the hopes of avoiding future spacecraft collisions.
Modeling Global Change Ecology in a High–Carbon Dioxide World
Ignite-style Session, Ecological Society of America Annual Meeting; Portland, Oregon, 11 August 2017
Modeling Storm Evolution
A “moist shell” makes all the difference in how some storms evolve.