Scientists report the fastest rate of rift extension yet observed for an Antarctic floating ice shelf and explain why it is far slower than rates expected for brittle ice deformation.
Oceans
Researchers Compare Observations Versus Modeling of Coastal Carbon Cycle
While storing carbon dioxide, the coastal ocean also releases methane and nitrous oxide. New research shows that understanding the impact of coastal oceans on climate requires more research into these fluxes and how they counteract each other.
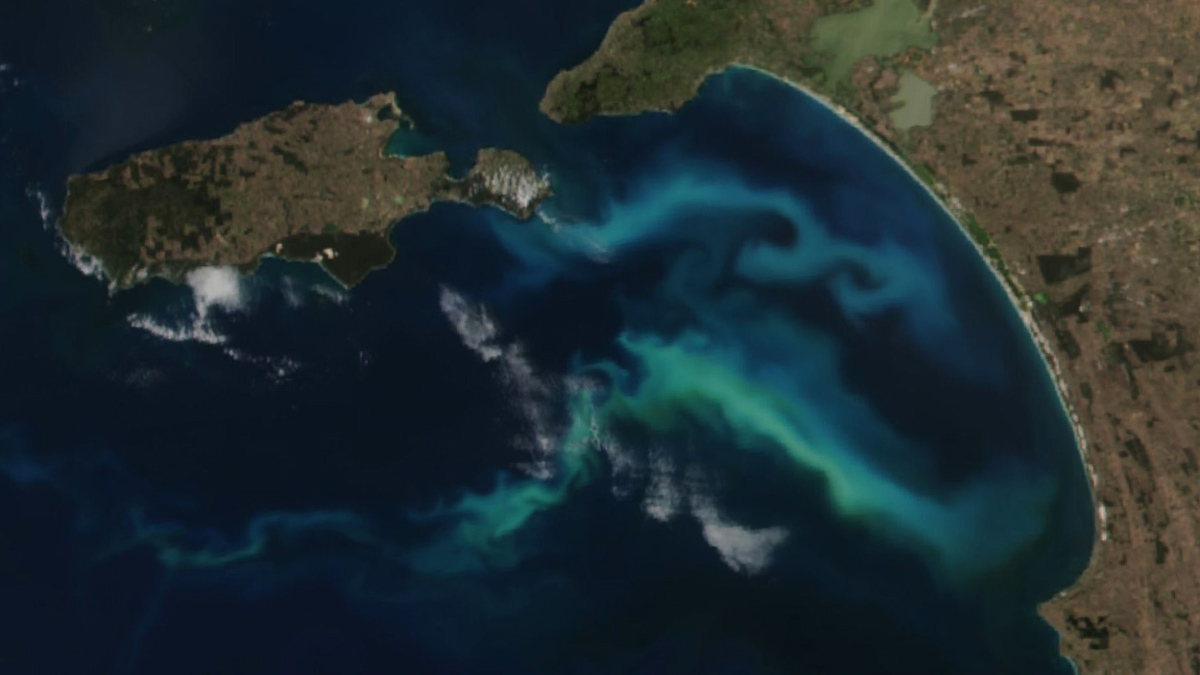
The Open Ocean, Aerosols, and Every Other Breath You Take
Phytoplankton and other marine plants produce half of Earth’s atmospheric oxygen and have big effects on food webs and climate. To do so, they rely on nutrients from the sky that are hard to quantify.
Record-Breaking Temperatures Likely as El Niño Persists
Global surface air temperatures will likely remain high through early summer because of a continuing El Niño event.
El Niño May Have Kicked Off Thwaites Glacier Retreat
Antarctica’s “Doomsday Glacier” started losing mass midcentury, around the same time as its neighboring glacier.
Step Aside, Internal Tides: Supercomputer Modeling Improves Satellite Altimetry Precision
New supercomputer models can provide valuable information about the ocean’s layers and movements, particularly slow moving features such as eddies and currents.
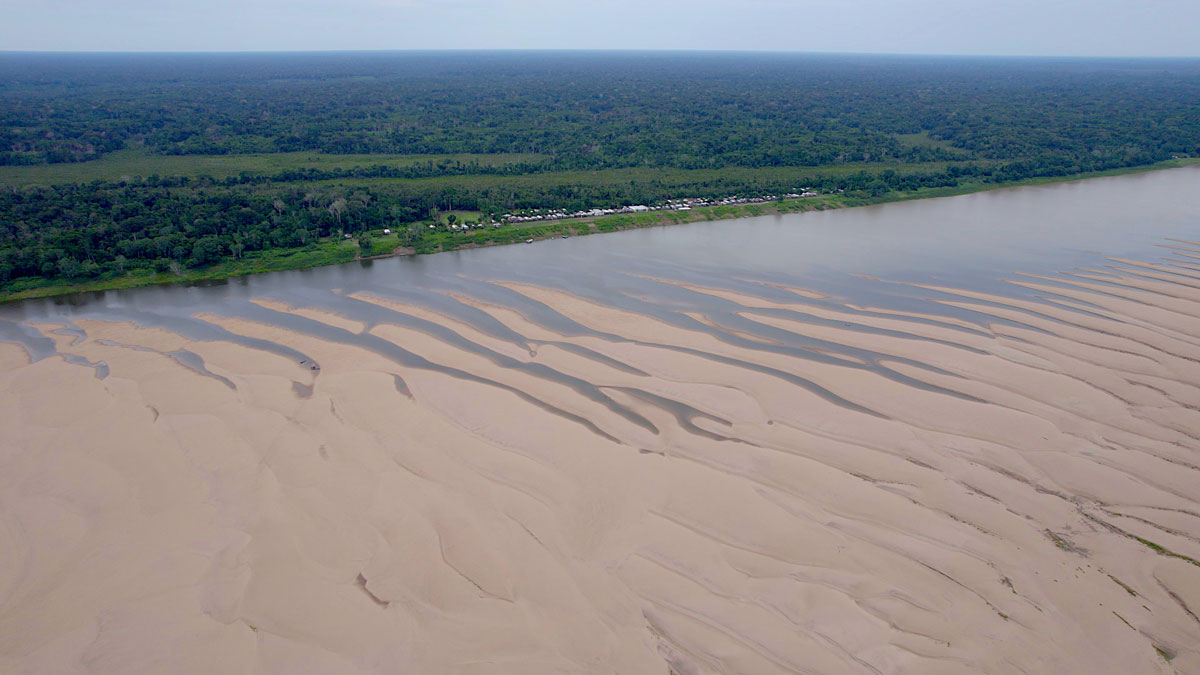
Almost a Year in, Drought in the Amazon Is Far from Over
Strengthened by climate change, northern Brazil’s dry spell might last longer than originally fore-cast, with lingering ecological and economic consequences.
Monitoring Polar Ice Change in the Twilight Zone
Landsat’s new extended data collection program is mapping Arctic and Antarctic regions year-round, even in polar twilight.
Mysterious Seafloor Pits May Be Made on Porpoise
Some shallow seafloor depressions off the coast of Germany that look like those associated with methane might instead be the work of porpoises.
Antarctica’s Ocean Acidity Set to Rise Rapidly by Century’s End
New research shows acidity levels could as much as double by 2100, imperiling fragile ecosystems in the frigid Southern Ocean.