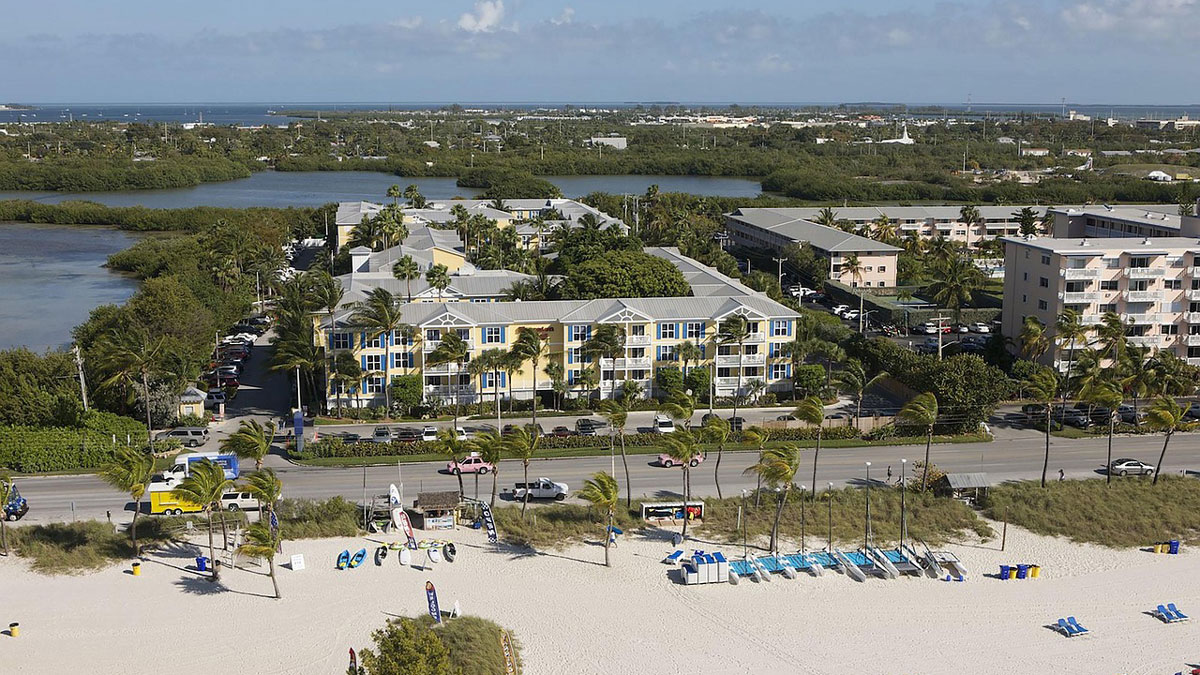
Injection of wastewater into shallow wells is meant to filter nutrients like nitrogen and phosphorus out of the wastewater. But a new study suggests that nutrients aren’t entirely eliminated—and may be polluting coastal waters.
phosphorus
Carbon-Nutrient Ratios Drive Nitrate Removal in Mediterranean Streams
The type of organic matter, and ratio of nutrients to carbon, impact the ability of heterotrophic bacteria to effectively remove certain forms of nitrogen pollution (nitrate) from streams.
Last Chance Lake Harbors the Highest Known Levels of Phosphate
Bodies of water such as this might have functioned as cradles of life, given their unique biogeochemistry.
Current Agriculture Adds More Phosphorus to Streams Than to Lakes
Improved agricultural nutrient management could improve stream water quality by reducing phosphorus levels, but rising temperatures and rainfall due to climate change might offset improvements.
Essential Ingredient for Life Found on Enceladus
Icy plumes from Saturn’s moon Enceladus contain phosphorus, part of the biochemistry of life—the first time the element has been found in a liquid environment beyond Earth.
Analyzing Sources of Pollution in the Great Lakes
Understanding how agriculture and land use affect nutrient flows and concentrations in the vast area of the Great Lakes is an essential step to developing sustainable management strategies.
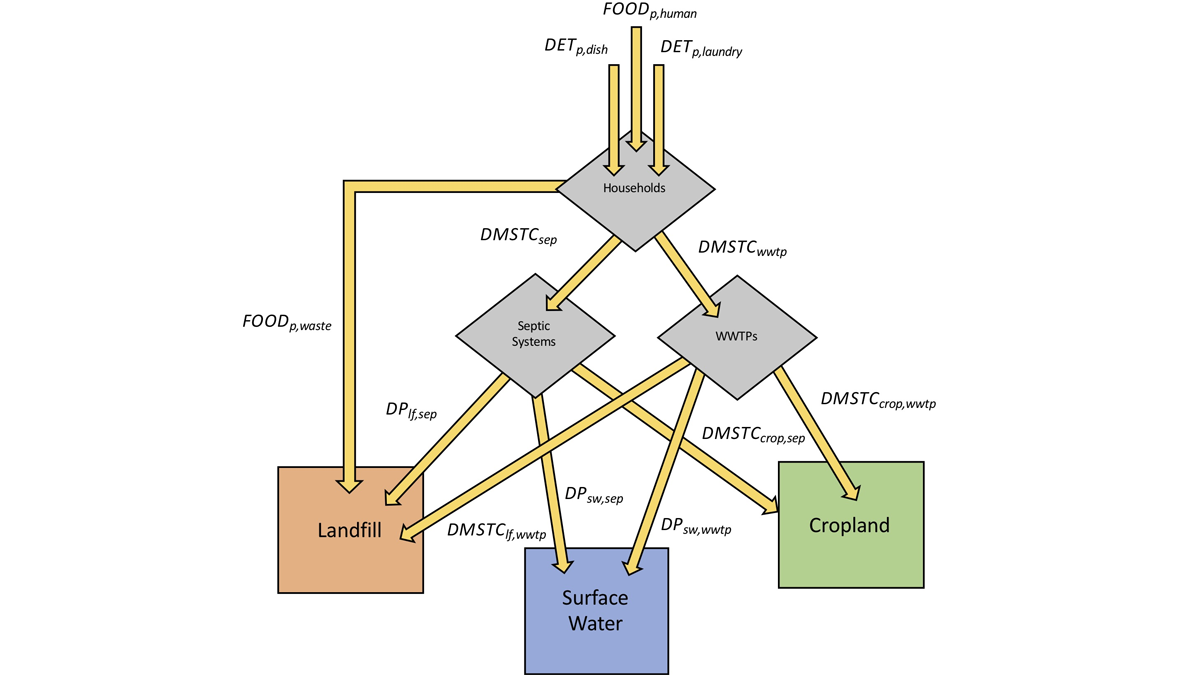
U.S. Public Water Supply Is a Local Source of Phosphorus Pollution
Excess phosphorus may reach U.S. rivers, lakes, and groundwater through water main leaks and outdoor water use.
If There Is Phosphine on Venus, There Isn’t Much
New observations of the Venusian atmosphere collected from an airborne observatory showed no sign of the potential biosignature gas, casting additional doubt on a previous report of its detection.
Water Quality Policy Must Consider Stored Watershed Phosphorous
Phosphorous stored in watersheds and affects water quality for decades. A new model predicts phosphorus accumulation and depletion, and the consequences for water quality conservation measures.
Cosmic Dust May Be Key Source of Phosphorus for Life on Earth
When tiny particles enter Earth’s atmosphere, a newly described series of chemical reactions may lead to production of phosphorus-containing molecules that are essential for biological processes.