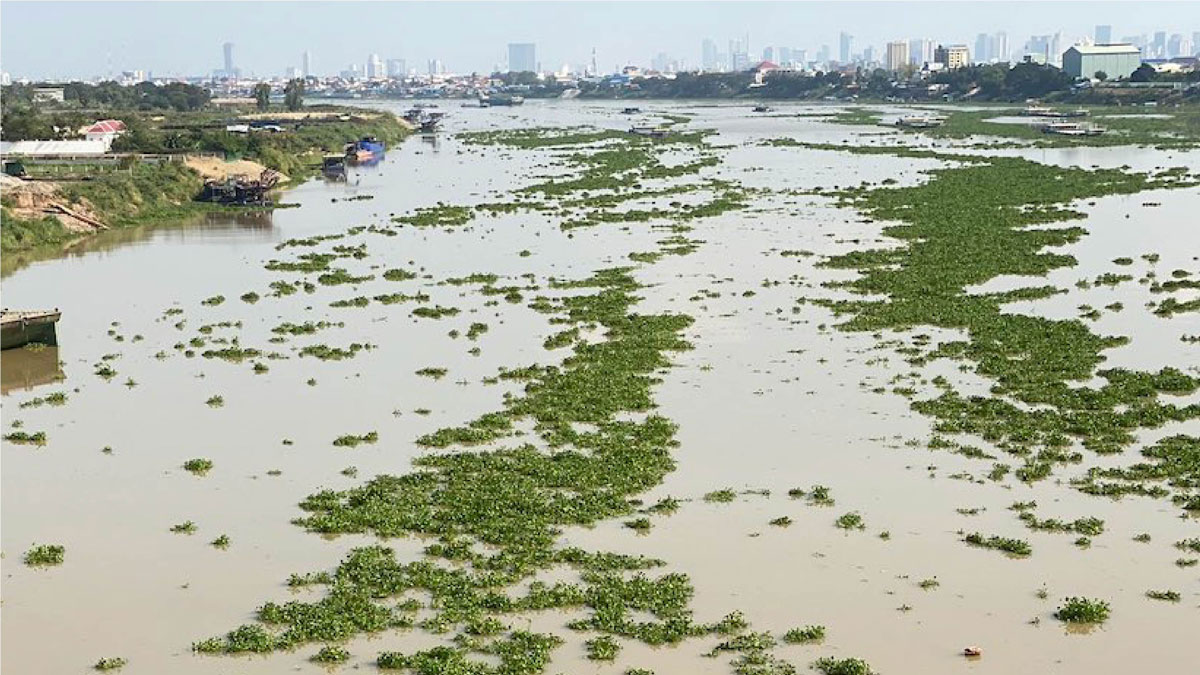
Researchers are using remote sensing to track floating mats of plastic trapped in water hyacinth plants.
rivers
Why Do Rivers Jump Off the Beaten Path?
Researchers sifted through 50 years of satellite imagery and came up with new clues to where and why rivers avulse, suddenly changing their course.
Algorithm Detects Thousands of Missing Levees from U.S. Database
An existing levee database accounts for just one fifth of the country’s actual total levee count, limiting the study of how these embankments affect riparian ecosystem health in the United States.
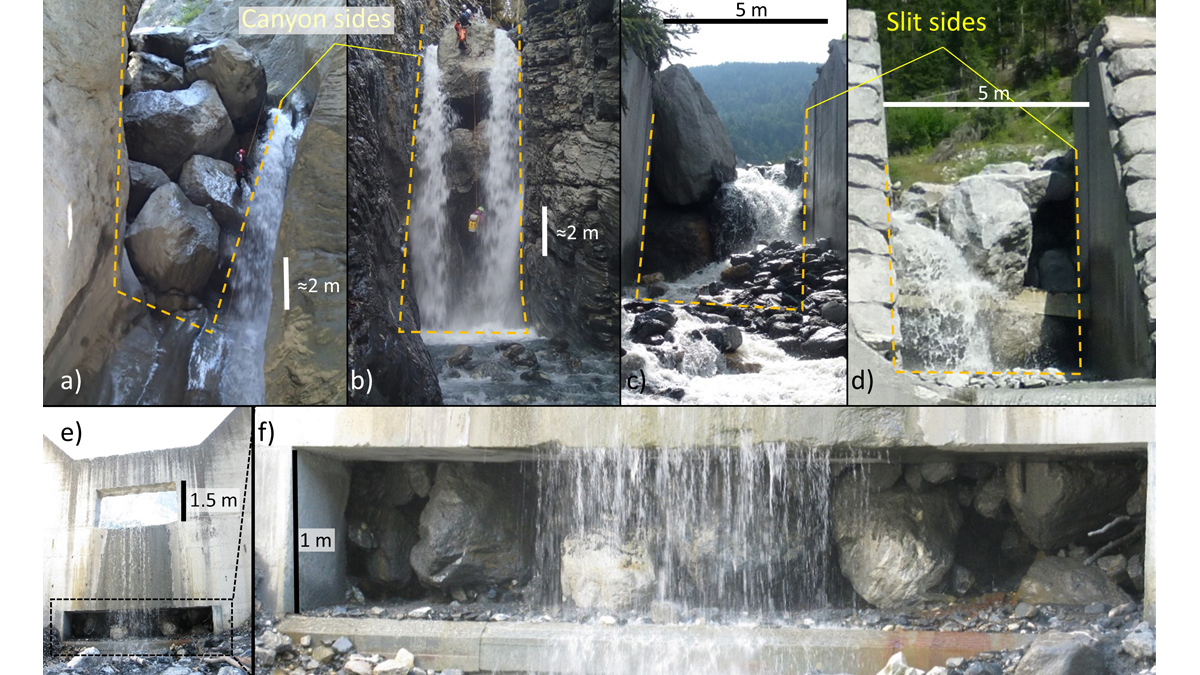
Good or Bad Jam? Modeling Boulders’ Fate at Constrictions
A new modeling framework to assess the likelihood of jamming at constrictions can be used to support the design of effective mitigation measures and reduce risk in debris flow prone areas.
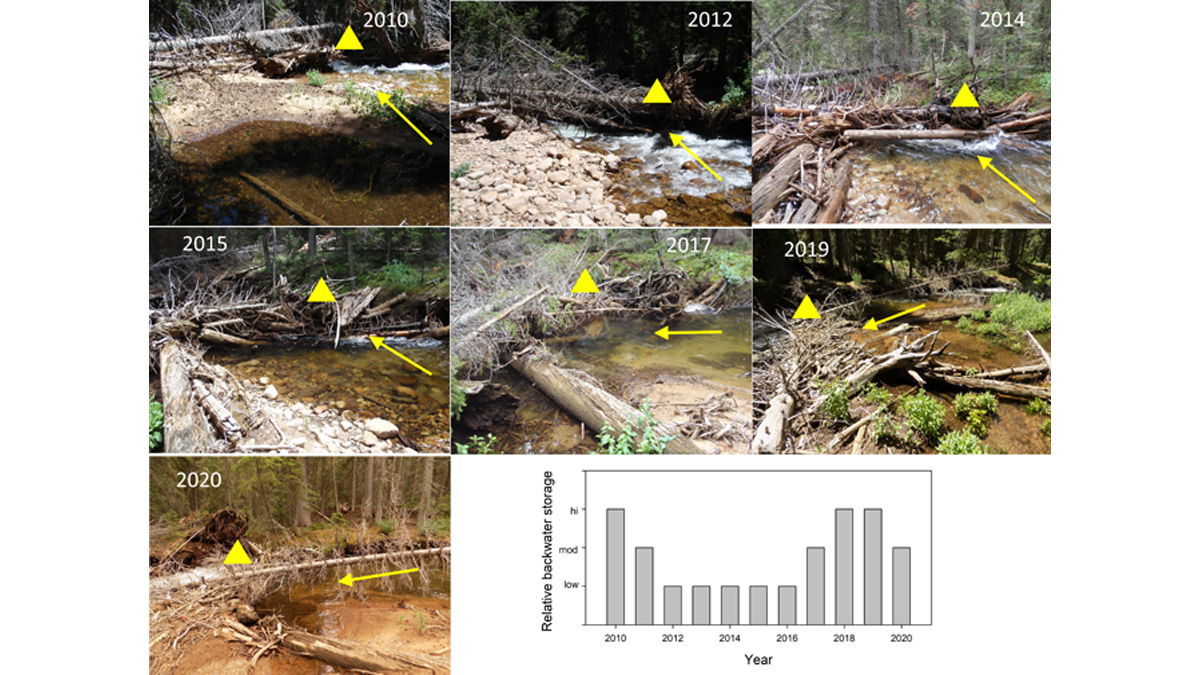
Logjams May Be Transient but Their Effect is Long Lasting
Even though natural logjams in rivers continuously change and maybe short-lived, their effects in terms of geomorphic diversity and habitat can be surprisingly long-lasting.
Charting Paths to New Knowledge
In our June issue of Eos, we home in on the unique ways researchers are using maps to better understand Earth and beyond.
A Probabilistic Model for Classifying Temporary Rivers
The model relies on measurable broad-scale attributes, increasing its flexibility for use in diverse environments.
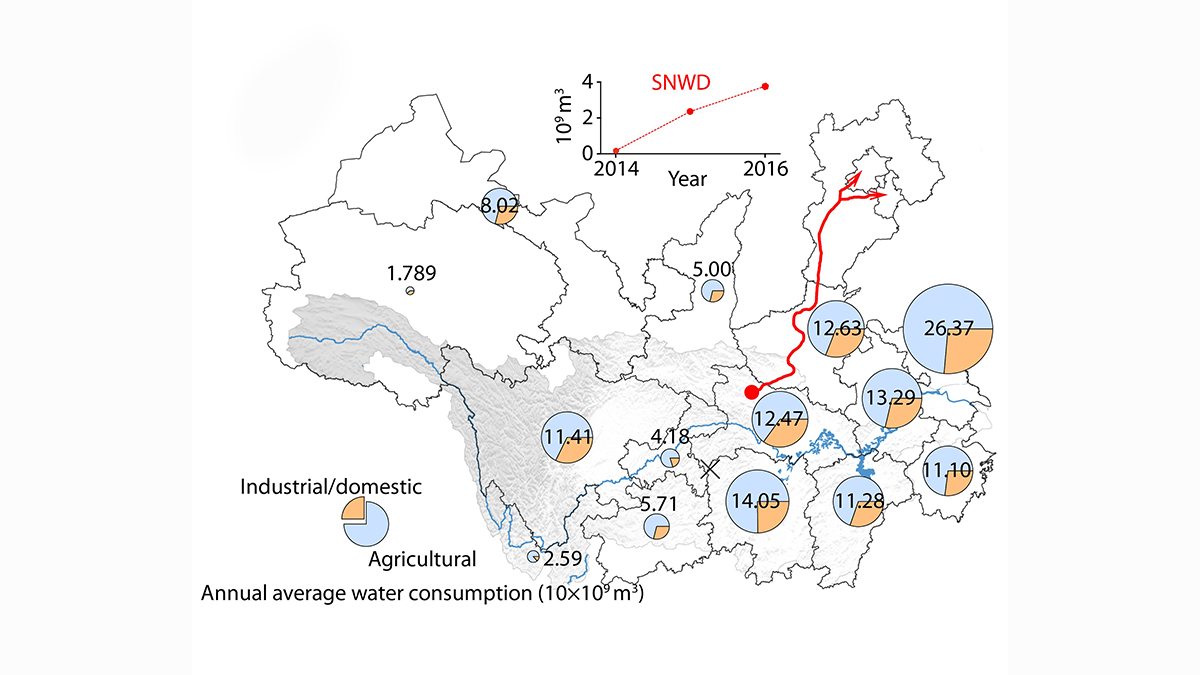
Improved Understanding of Runoff Dynamics in the Yangtze River Basin
Satellite data combined with in-situ observations on terrestrial water storage change and human water consumption provides a more accurate picture of runoff dynamics at sub-basin scale.
A New Index to Quantify River Fragmentation
Researchers have developed a new analysis based on a river’s catchment area as opposed its length.
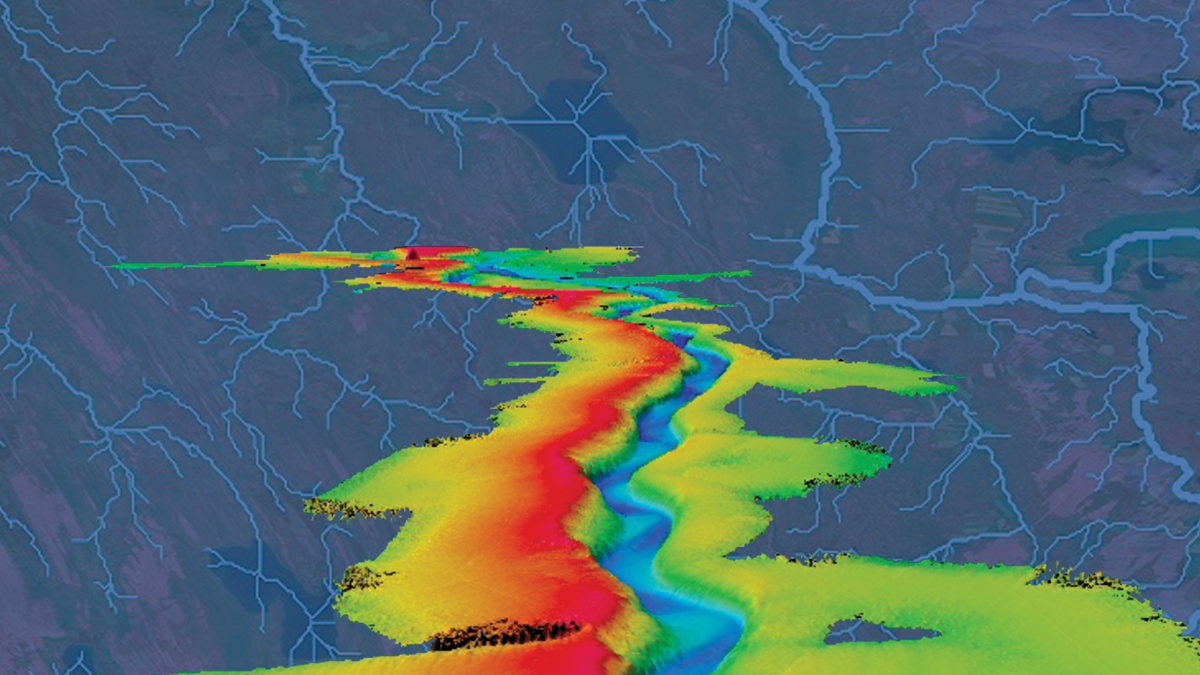
Running Water on Topographic Data to Better Delineate Channels
Two-dimensional hydraulic simulations are a powerful tool to identify process domains such as channels, hillslopes, and floodplains in high-resolution topographic data.