The annual list of America’s Most Endangered Rivers includes practical calls to action to turn the tide on threatened U.S. waterways.
rivers
Incredible Journeys on the Crown of the Continent
Living in Geologic Time: The making, breaking, and backpacking of North America’s Continental Divide.
A Sharper Look at the World’s Rivers and Catchments
Digital hydrographic maps have transformed global environmental studies and resource management. A major database update will provide even clearer and more complete views of Earth’s waterways.
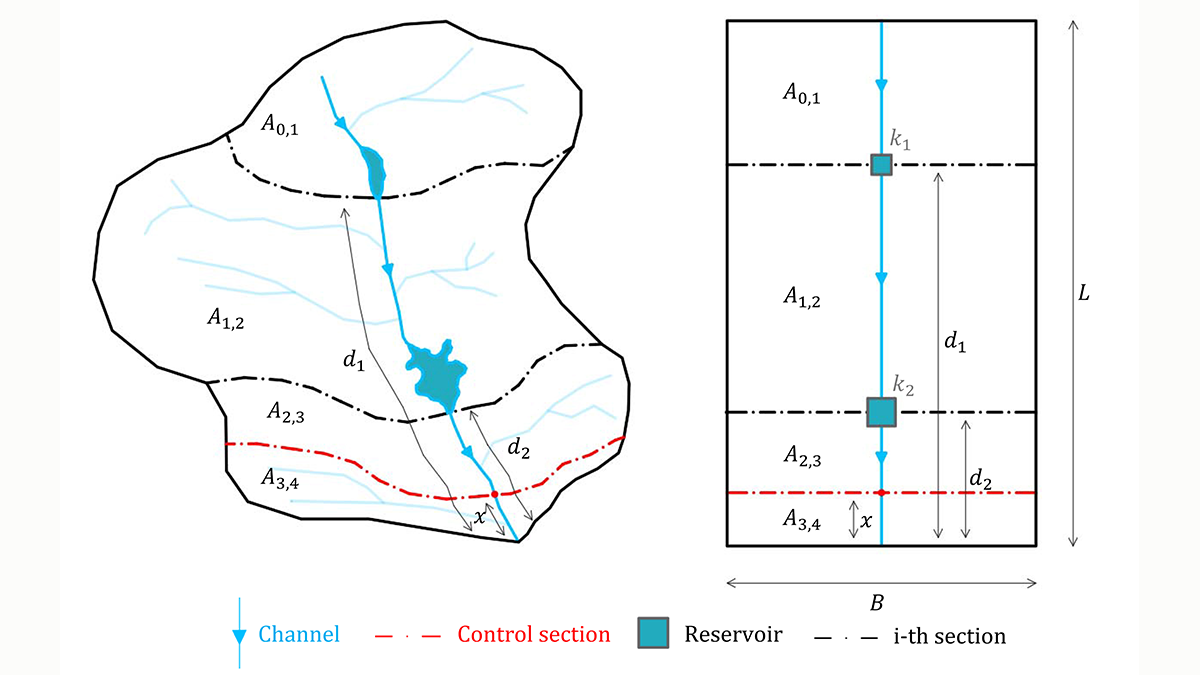
A New Index to Assess Multiple-Reservoir Effects on Peak Floods
A simple, yet quantitative, index is demonstrated to quantify reductions in the peak flood resulting from multiple reservoirs, arranged in series along the same river reach.
Pharmaceuticals Found in Rivers on All Continents
A quarter of 258 observed rivers had unsafe levels of at least one drug. The findings raise concerns about Earth’s aquatic life and the global threat of antimicrobial resistance.
Forest Fires Could Boost Western U.S. Water Supplies
Streamflow in the West has been below average since the early 2000s, but a new analysis shows that streams aren’t as dry as expected.
Lake Michigan’s Salinity Is on the Rise
Road salt is primarily to blame for the shift, though the water remains within safe levels for now.
How Climate Change Shaped the Amazon’s Land and Life
Ice Age climate swings shaped the equatorial basin’s terrain—and possibly its ecology—faster than previously thought.
From River to Sea: Estimating Wood Cascades
Dams and deforestation have chipped away at the millions of cubic meters of wood that flow through rivers and out to sea.
Recovering Mantle Memories from River Profiles
Researchers use a closed-loop modeling strategy to validate regional uplift patterns recorded in river profiles across the African continent.