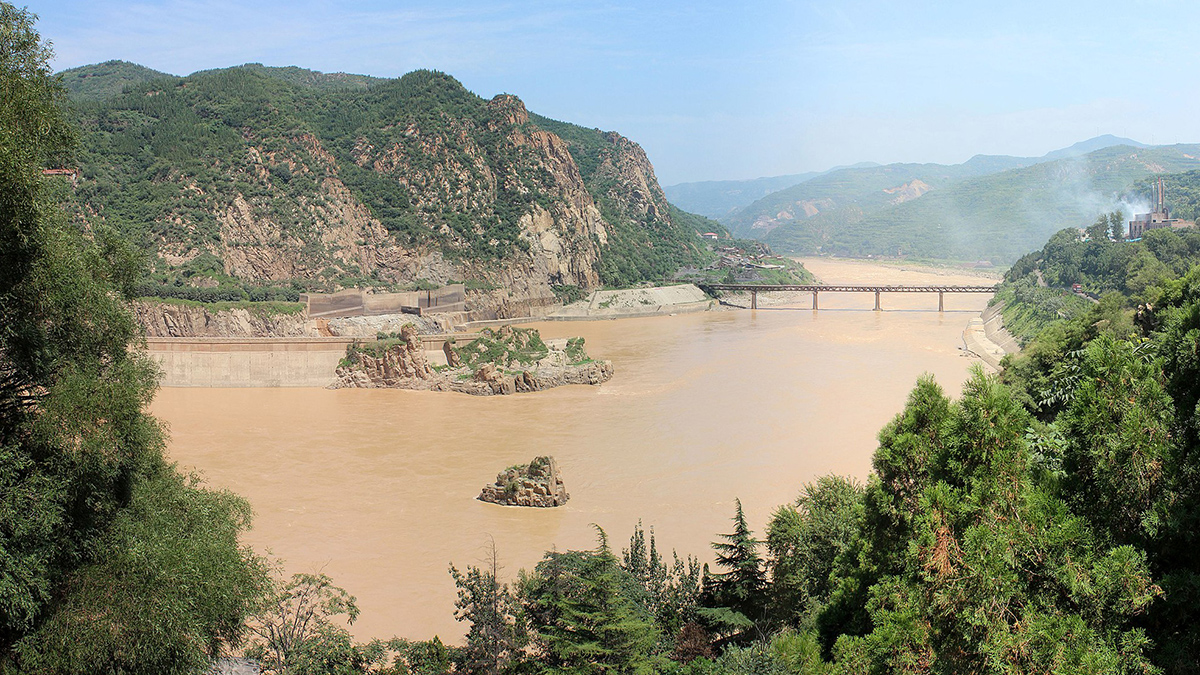
The mix of metals in China’s Yellow River stays relatively similar as it moves from the upper continental crust to biological life.
sediments
DNA in Lake Sediment Reveals the Impact of Introduced Fish
Non-native trout have altered the diversity of zooplankton that live in high-elevation lakes.
Geoscientists Demystify Baseball’s Magic Mud
Taking baseball’s mysterious Rubbing Mud into the lab revealed no magic ingredients—but plenty of useful natural properties from geomaterials.
Physics and Biology as Likely Stream Bedfellows
Streambeds are key sites for removal of nutrients and other contaminants through microbial processes, but are limited by diffusion, which can now be modeled from streambed physical properties.
Machine Learning Enhances Image Analysis in Biogeosciences
Machine learning can enhance our ability to identify communities of microorganisms and how they change in response to climate change over time.
Sedimentos Caribenhos Rastreados até o Terremoto e Tsunami Português de 1755
Arqueólogos escavando na Martinica encontraram por acaso o primeiro depósito de tsunami do terremoto encontrado no Novo Mundo. Ao que parece, o tsunami deixou um forte rastro, pois a onda passou por cima de um rio.
California Wildfires and Weather Are Changing Erosion Patterns
Sediment runoff from the state’s increasingly severe wildfires and heavy rain events may affect ecosystems and water resources downstream.
The Delicate Balance of Permafrost in Arctic River Floodplains
To evaluate the vulnerability of permafrost in Arctic floodplain landscapes to warming, scientists explore dynamics of its loss and reformation.
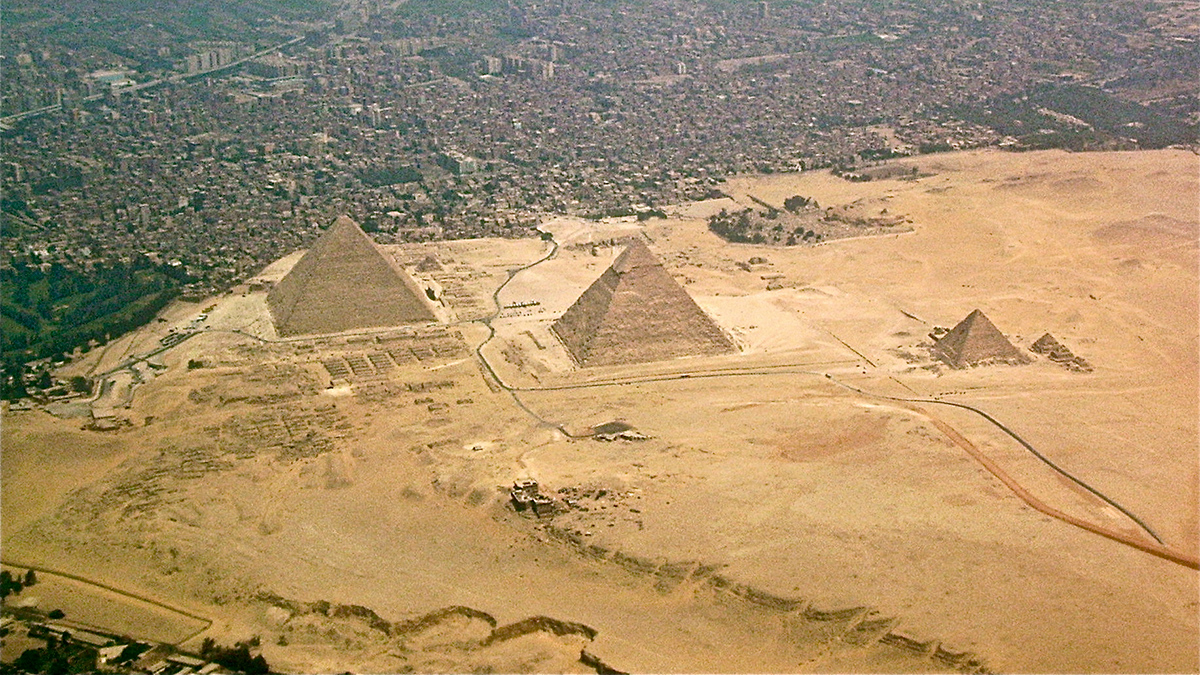
Encuentran contaminación por cobre de 5,000 años de antigüedad cerca de las pirámides
Una nueva investigación geoarqueológica demuestra que la metalurgia en el antiguo Egipto provocó una importante contaminación en un puerto cercano.