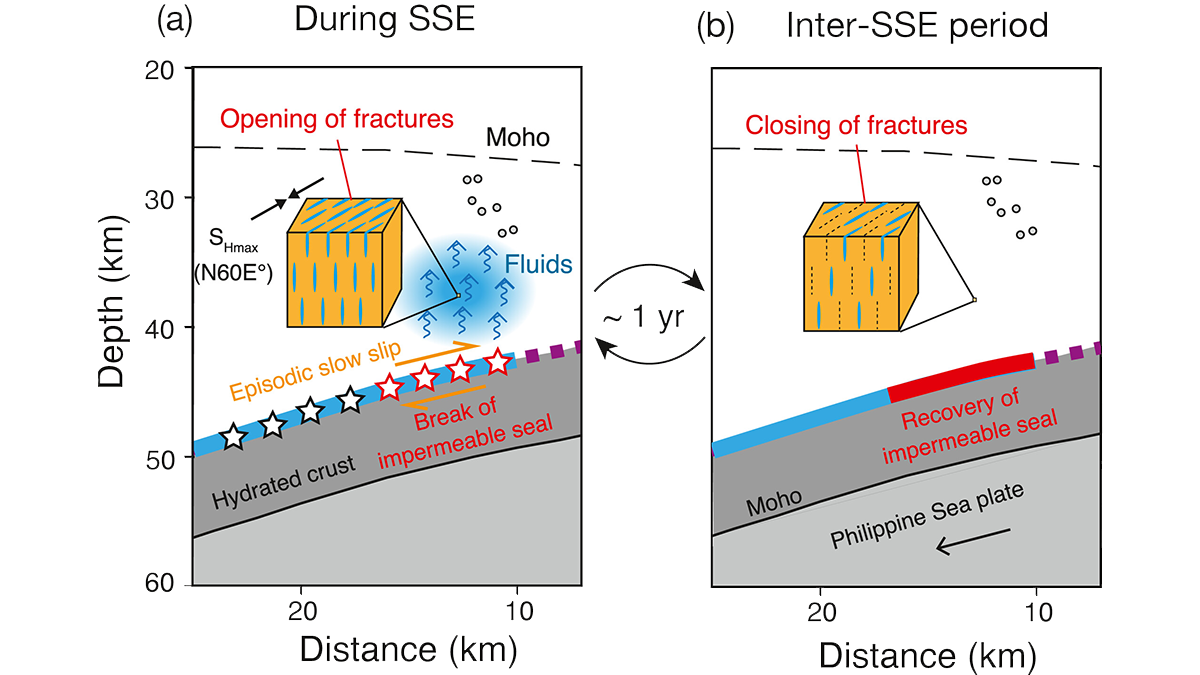
Seismic anisotropy changes through time suggest that cyclical opening of fluid-filled fractures is synchronized with subduction zone slow slip events.
seismology
Forecasting Caldera Collapse Using Deep Learning
A deep learning model trained with geophysical data recorded during the well-documented 2018 Kilauea volcano eruption, Hawaii, predicts recurrent caldera collapse events.
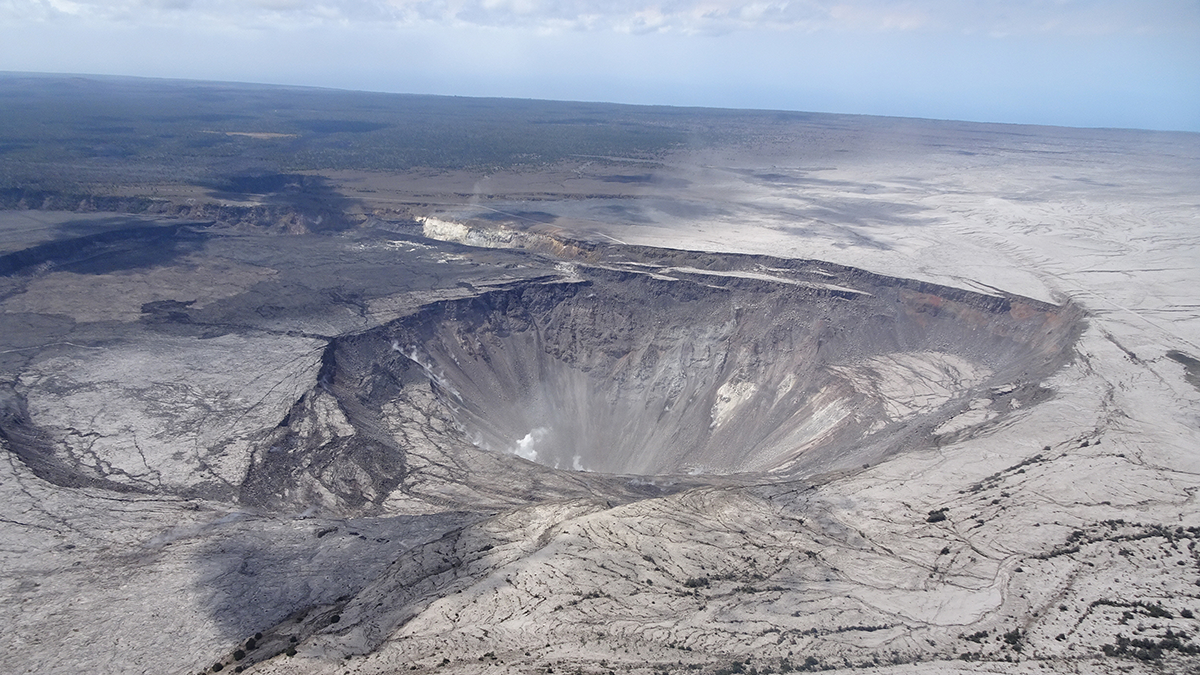
An Unprecedented Experiment to Map Kīlauea’s Summit Magma System
Dozens of researchers deployed nearly 2,000 seismic stations—and a T-Rex—to better illuminate subsurface structure and magma storage below the summit of the highly active volcano.
The 16 September 2023 landslide on the margin of Dickson Fjord in Greenland
The Landslide Blog is written by Dave Petley, who is widely recognized as a world leader in the study and management of landslides. There has been quite a stir over the last week regarding a remarkable paper (Svennevig et al. 2024) that was published in the journal Science, describing a series of events that occurred […]
Fiber-Optic Cables Used to Measure Changing Soil Moisture
Scientists are using seismic techniques to measure soil moisture. Their results show that recent droughts in California depleted water in the shallow subsurface.
U.S. Earthquake Early Warning System Gets a Major Upgrade
Satellite capabilities will improve the accuracy of ShakeAlert earthquake magnitude measurements.
New Moonquakes from Old Data
Almost 50 years after they were turned off, the Apollo seismometers still have secrets to reveal.
Seismologie: Ein vielversprechender Weg zur Überwachung von Permafrost
Passive seismische Daten von einer Messstation auf der Zugspitze zeichneten im Lauf der letzten 15 Jahre den Schwund von Permafrost auf. Somit eignet sich dieses Verfahren vermutlich auch für die langfristige Überwachung der Umwelt.
Imaging Below the Surface Reveals One of Los Angeles’s Webs of Faults
Damage zones extend to either side of many faults and can affect how future earthquakes behave.
Faults Along Salt Walls Are Less Stressed in the Paradox Basin
Based on an extended stress database, scientists observe systematic changes in the tectonic stress state and a reduction in fault reactivation potential near salt walls in the Paradox Basin.