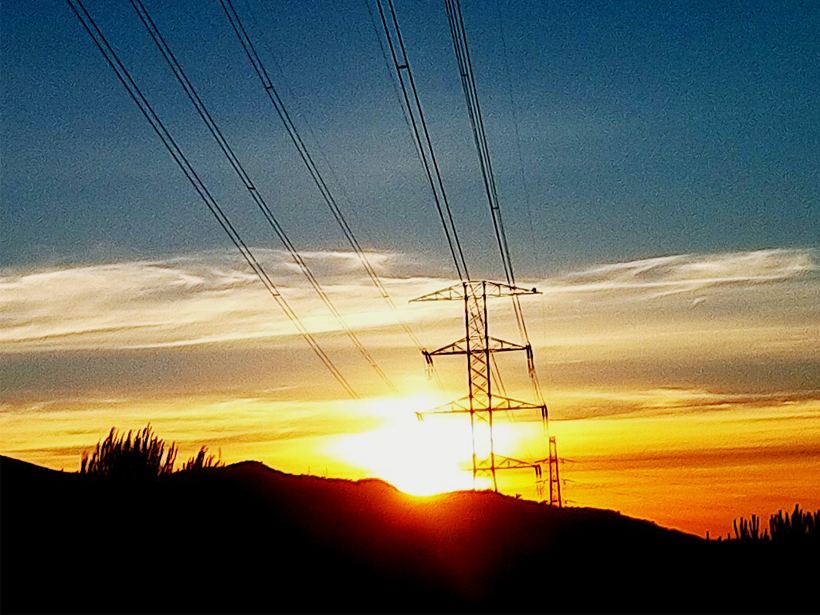
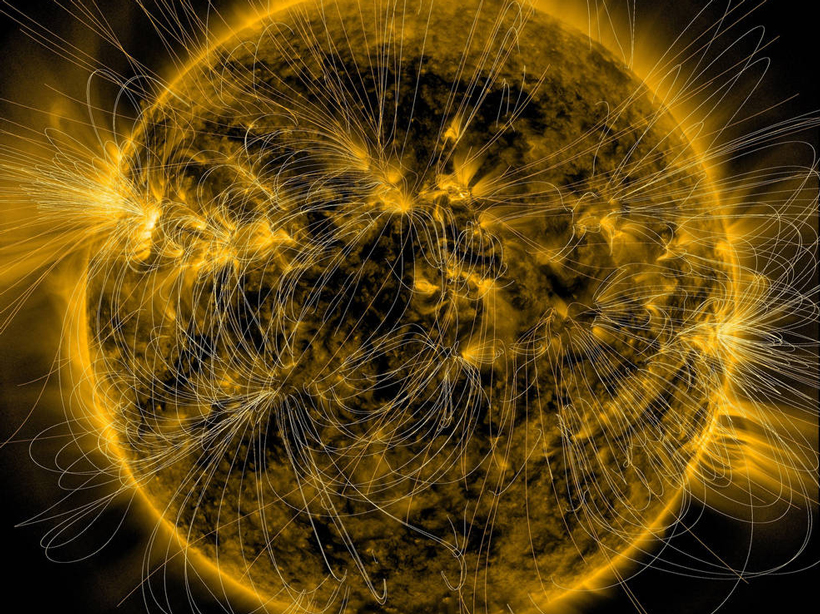
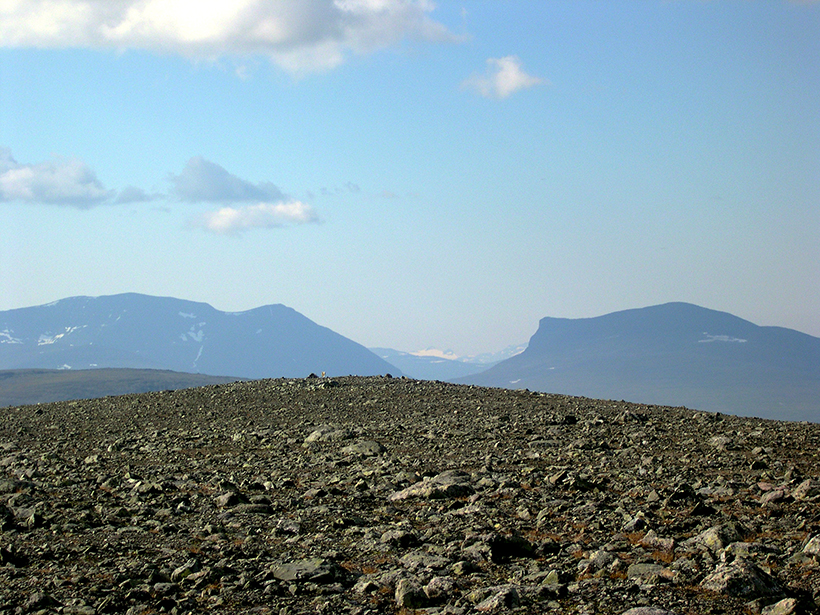
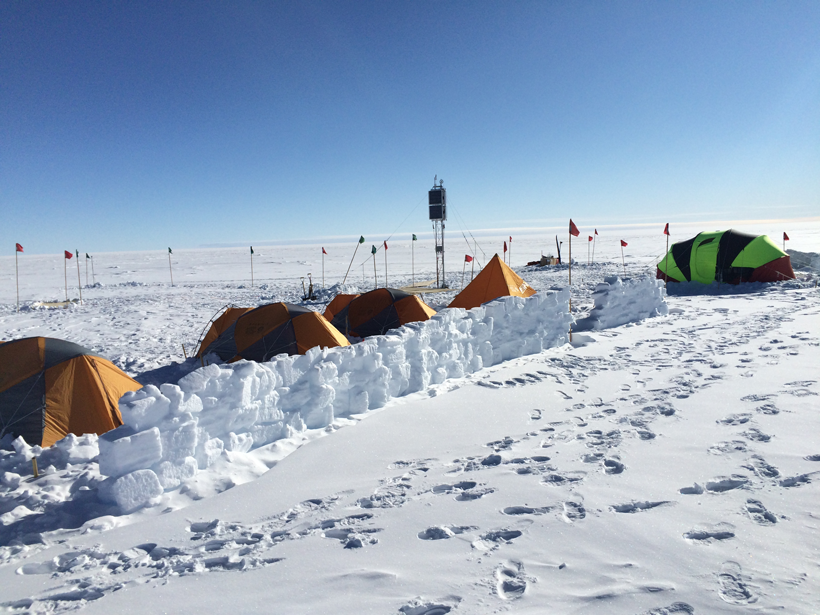
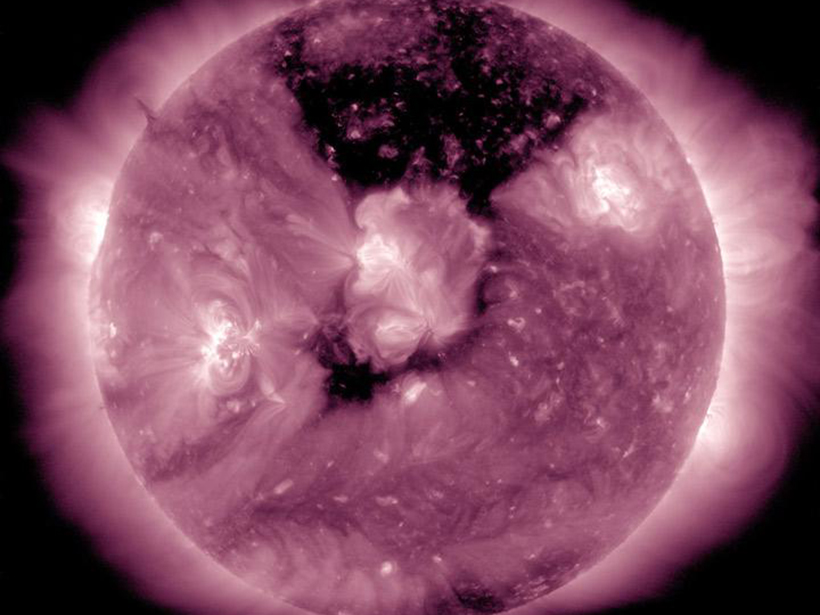
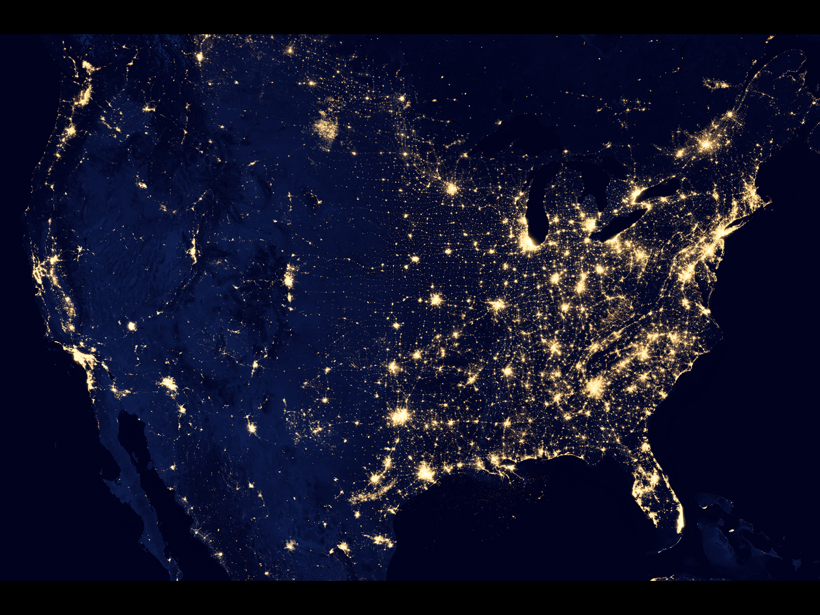
A survey of bedrock conductivity across Spain improves predictions of how vulnerable the nation’s power grid is to solar storms.
space weather (hazard)
Integrating Research of the Sun-Earth System
International Symposium on Recent Observations and Simulations of the Sun-Earth System III; 11–16 September 2016, Varna, Bulgaria
Predictive Capability for Extreme Space Weather Events
Workshop on Modeling and Prediction of Extreme Space Weather Events; College Park, Maryland, 22–24 August 2016
Explaining Unexpected Twists in the Sun's Magnetic Field
New research shows how the Sun's magnetic field can shift when it approaches Earth, which can throw off space weather forecasts.
Scientists Probe the Calm After Solar Storms
In forecasting the effects of solar storms, understanding how they subside—and not just how they arrive—will be crucial.
How Lightning Creates "Killer Electrons" in Earth's Radiation Belts
New calculations show that lightning-triggered plasma waves in Earth's magnetosphere absorb energy from slow particles and energize electrons to levels that can damage satellites severely.
When Lower-Atmosphere Waves Invade the Upper Atmosphere
A review of the literature shows that weather nearer Earth's surface could produce up to 35% of the ionosphere's variability.
Deciphering the Cosmogenic Code to Learn Earth's Surface History
Third Nordic Workshop on Cosmogenic Nuclide Techniques; Stockholm, Sweden, 8–10 June 2016
Space Weather from a Southern Point of View
A recently completed instrument array in Antarctica provides a more complete understanding of the near-Earth space environment.
Mapping Geoelectric Hazards Across the United States
Variations in Earth’s magnetic field can induce electric fields in the ground, driving damaging currents through our power grids.