Si el cambio climático anula el ciclo estacional de hielo y deshielo, se desencadenaría un ciclo de retroalimentación de derretimiento del hielo marino en algunas partes del Ártico canadiense.
surface waves & tides
Accurate Ocean Tides for Earth System Models
Accurate tide models require self-attraction and loading terms, but can this calculation be done accurately and efficiently for use in global tide and Earth system models?
Can Anelastic Attenuation of Oceanic Mantle be Reliably Measured?
A new study demonstrates that robust anelastic attenuation measurements can be made across ocean bottom seismic arrays at different locations using surface wave array analysis.
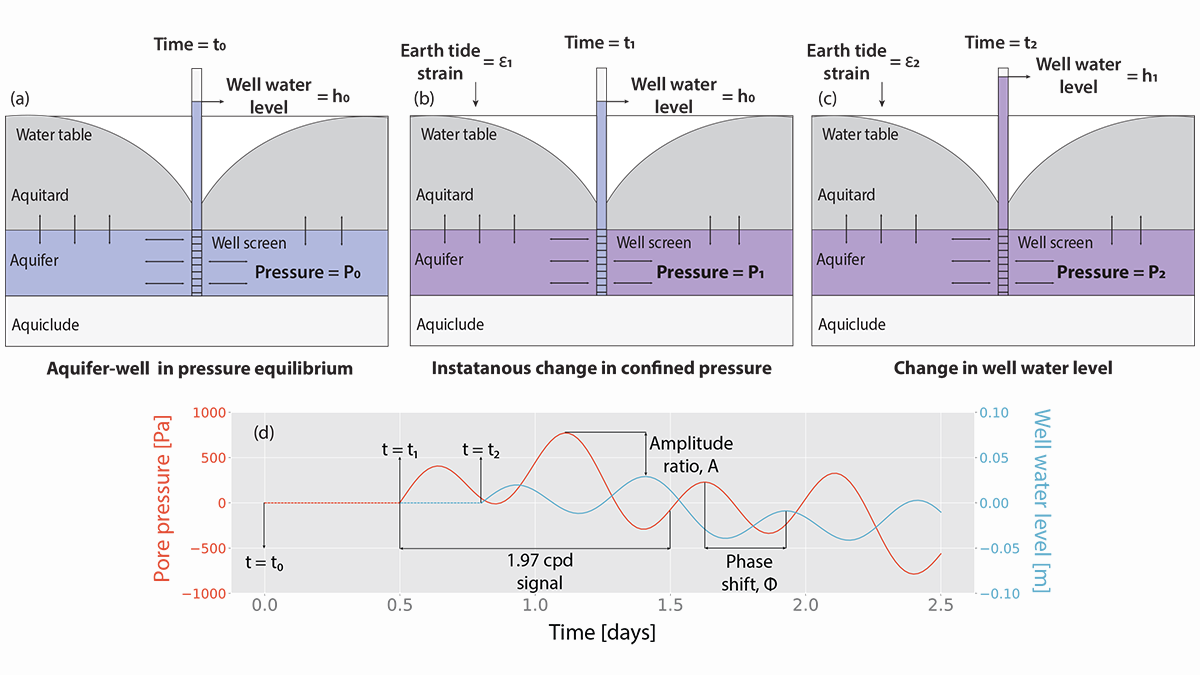
Modeling Groundwater Responses to Earth Tides
Tidal fluctuations in water well levels can reveal characteristics of the subsurface, and a new model based on coupled physics delineates the limitations of inherently simplistic analytical solutions.
Ocean Waves Cause Drag Coefficient Asymmetry Within Typhoons
Observations show that, due to ocean waves, the drag coefficients for surface wind stresses have spatial asymmetry within typhoons, which should be considered in weather and climate simulations.
River Floods Can Trigger Powerful Underwater Landslides
A record-length turbidity current triggered by river flooding has revealed a new link between the surface and the deep sea.
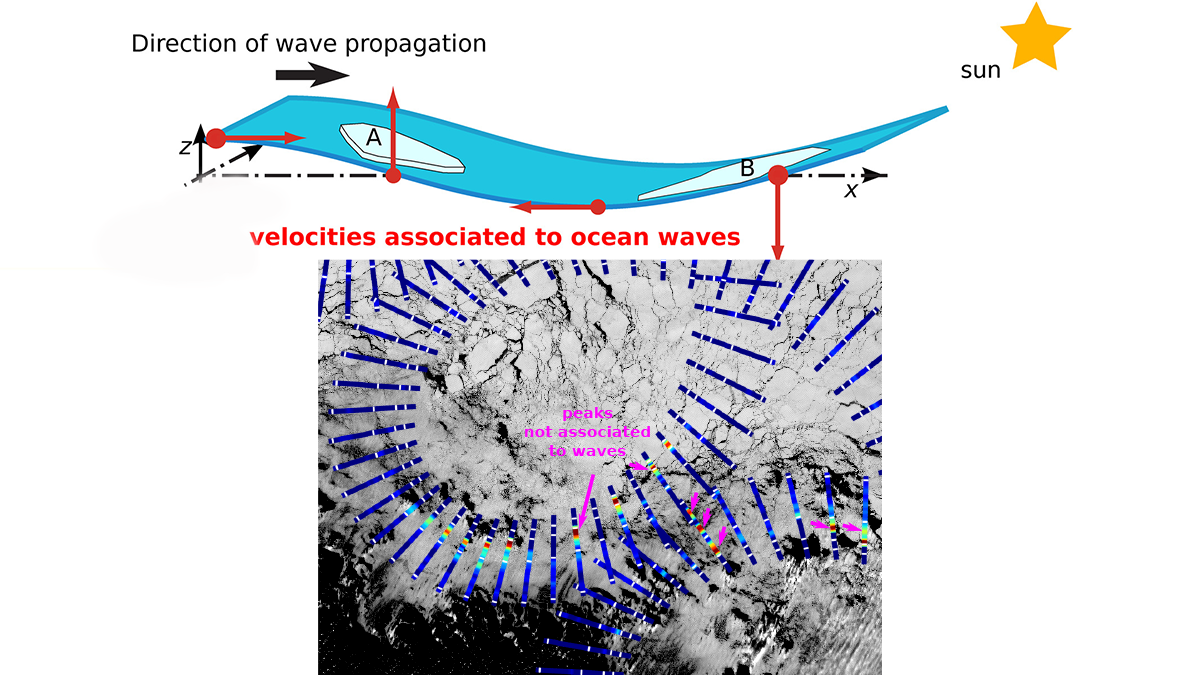
Satellites Remotely Measure Ocean Waves and Sea Ice Interactions
A new method for using satellite observations from multiple sensors improves measurements of ocean waves as they propagate through and interact with sea ice.
An Ocean Surface Layer with Potential
The depth of the ocean’s surface mixed layer is typically defined based on density thresholds. However, a more physically appealing definition can be constructed from potential energy considerations.
Muography Array Under Tokyo Bay Spots Meteotsunami Waves
A new study shows how muons can be used to study tide and wave phenomena, helping secure coastal communities.
Rising Seas Boost Tsunami Impacts on Distant Shorelines
Modeling suggests that rising sea levels will render Southern California ports increasingly vulnerable to waves from distant-source tsunamis.