Tidal heating may have raised the surface temperature of early Earth and triggered global volcanism, a new study says.
surface waves & tides
Atmospheric Rivers Spur High-Tide Floods on U.S. West Coast
Researchers analyzed 36 years of data to understand how atmospheric rivers and other factors drive chronic coastal flooding.
Melting Arctic Sea Ice Strengthens Tides
If climate change throws off the seasonal freeze-thaw cycle of Arctic sea ice, it could trigger a reinforcing cycle of sea ice melt in parts of the Canadian Arctic.
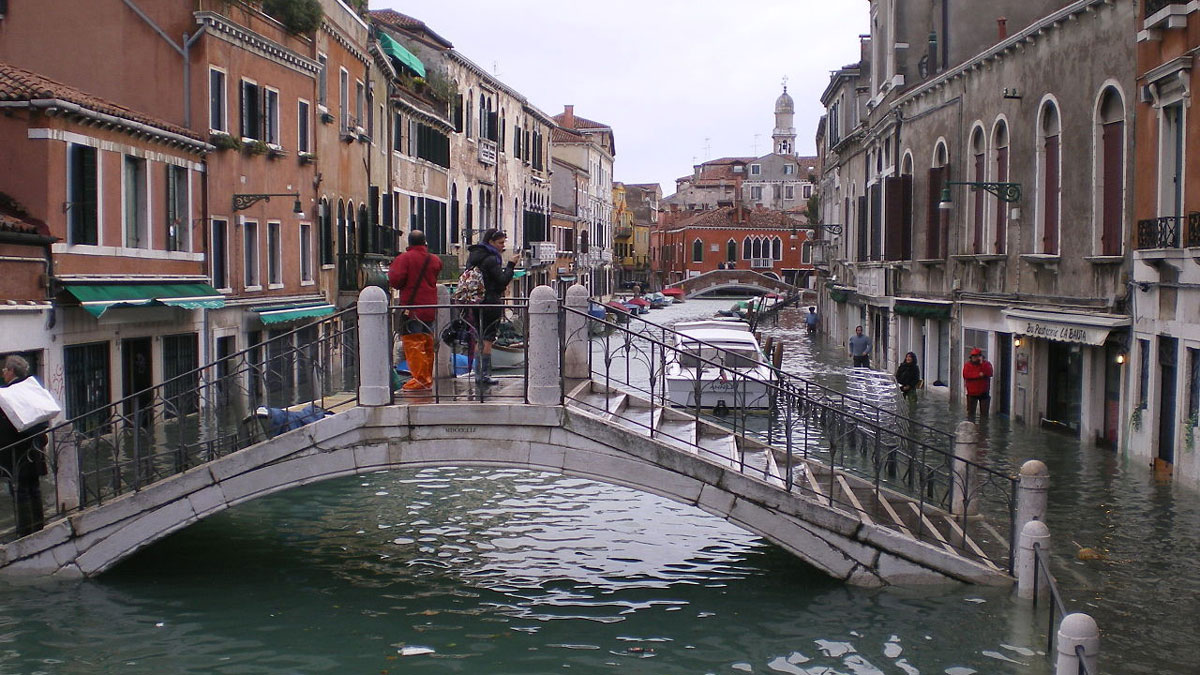
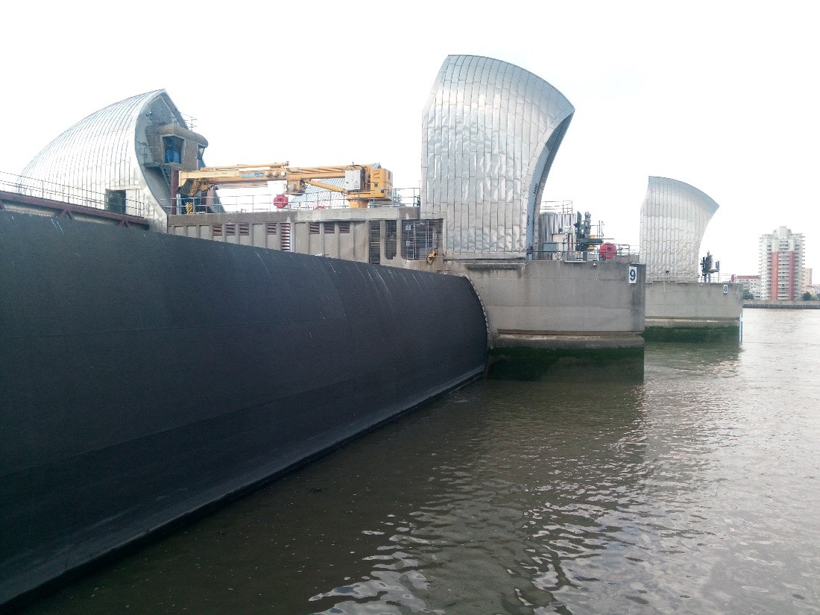
For Venice’s Floodgates to Work, Better Forecasts Are Needed
Climate change increases massive storm surges, which may be more than Venice’s flood-control system can handle.
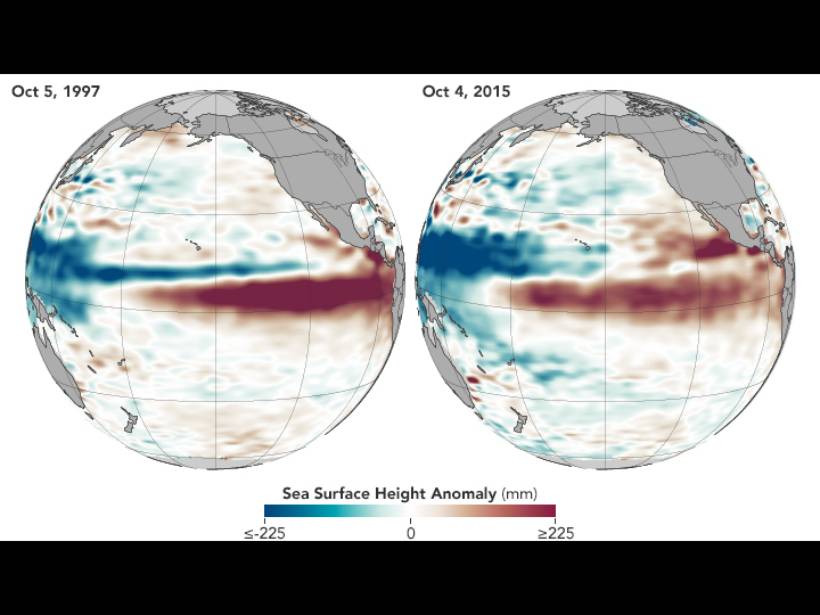
Explaining Thermal Tides in the Upper Atmosphere During the 2015 El Niño
Increased tropospheric heating and reduced dissipation combine to explain an anomalously large thermal tide.
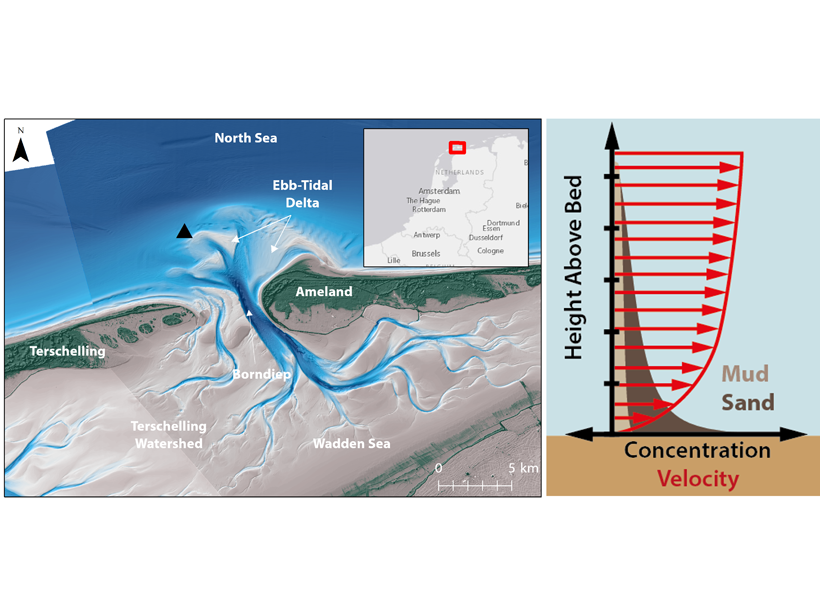
Unravelling Sands and Muds Suspended in Coastal Environments
A new study uses the response of optical and acoustic measurements to derive a sediment composition index for prediction of the relative fractions of mixed sediments in suspension.
Rastreando cómo se mueve el plástico en el océano costero
Investigadores utilizaron un tanque de olas para estudiar el movimiento de partículas de plástico de forma experimental y comprender el papel de la densidad de partículas en el comportamiento de deriva.
The Influence of Tidal Forces Extends to the Arctic’s Deep Sea
The Moon’s gravitational pull creates the tides, but its influence extends hundreds of meters below the sea surface too, influencing sensitive methane seeps in the seabed.
Jupiter’s Ocean Moons Raise Tidal Waves on One Another
New research considers the effect of Jupiter’s Galilean moons on each other’s oceans for the first time.
The Ups and Downs of Tides
The size of tides has changed in the past and will continue to change in the future due to natural and anthropogenic influences on estuaries, coastlines, and near shore regions.