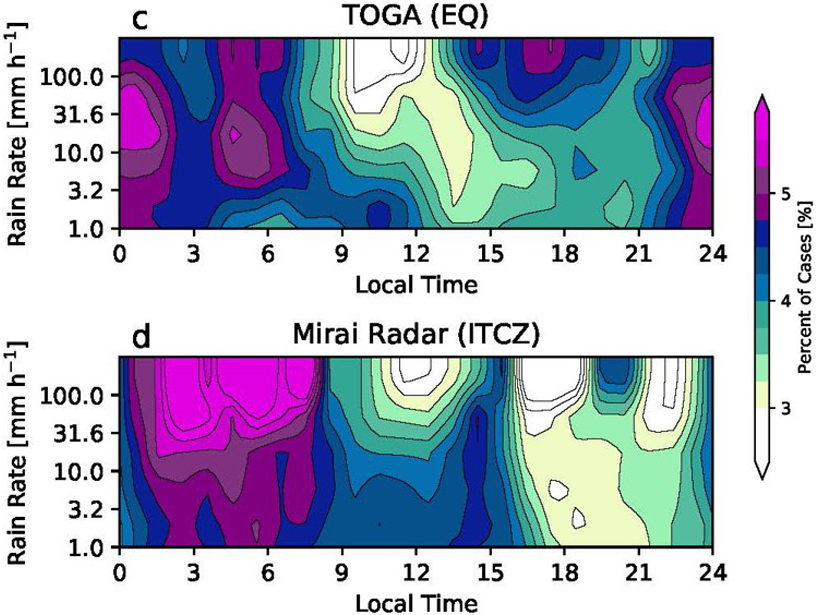
Radar data show an afternoon precipitation maximum in the equatorial Indian Ocean in addition to the nocturnal maximum; this occurs under light surface winds and suppressed large-scale convection.
tropics
Congress Throws Tropical Forest Research Program a Lifeline
Climate researchers and ecologists laud the continuation of effort to fuse data from tropical forests with modeling.
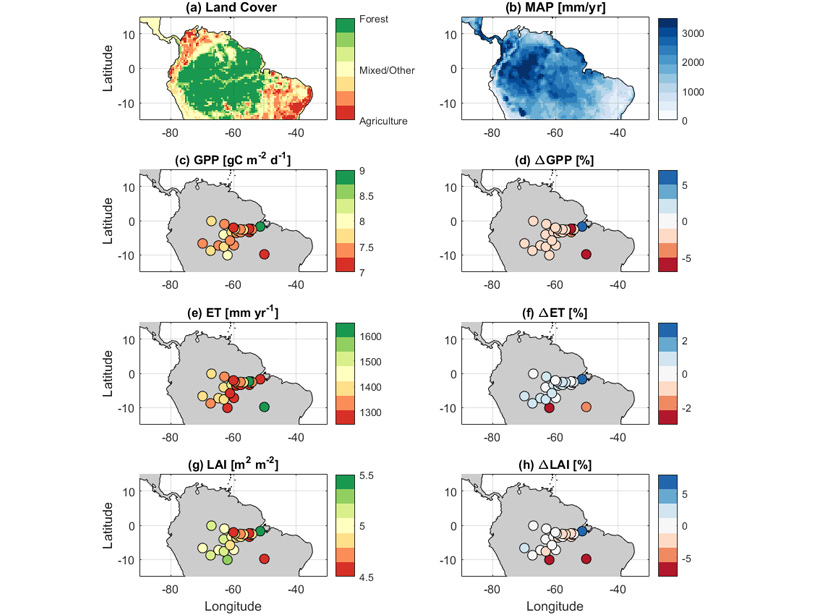
Seasonal Leaf Production Is Key Control on Amazon Carbon Balance
Characterizing leaf phenology in process-based models reconciles both “dry season green-up” and drought controls on Amazonian carbon balance.
The Stratosphere and Its Role in Tropical Teleconnections
Joint SPARC Dynamics and Observations Workshop; Kyoto, Japan, 9–14 October 2017
Reconstructing Climate and Environment from Coral Archives
Tropical Coral Archives—Reconstructions of Climate and Environment Beyond the Instrumental Record at Society-Relevant Timescales; Bremen, Germany, 28 September 2017
Monitoring Tropical Cyclones with Lightning and Satellite Data
A new storm-following tool continually watches for lightning over the open ocean. Combined with satellite microwave data, the new real-time observations will improve forecasts of tropical cyclones.
Rethinking How Water Circulates Between the Oceans and Land
A reexamination of the global water cycle shows that tropical coastlines exert a profound influence on atmospheric water circulation by wringing water vapor from the atmosphere.
Major Federal Tropical Research Project to Cease 7 Years Early
The Department of Energy shutters a project aimed at improving climate models less than halfway through the expected decade-long run.
Is Global Warming Suppressing Canonical El Niño?
A study explores the relationship between diverse El Niño events and the background state of the tropical Pacific.
Karnauskas Receives 2017 Ocean Sciences Early Career Award
Kristopher B. Karnauskas will receive the 2017 Ocean Sciences Early Career Award at the 2017 American Geophysical Union Fall Meeting, to be held 11–15 December in New Orleans, La. The award recognizes “significant contributions to and promise in the ocean sciences.”