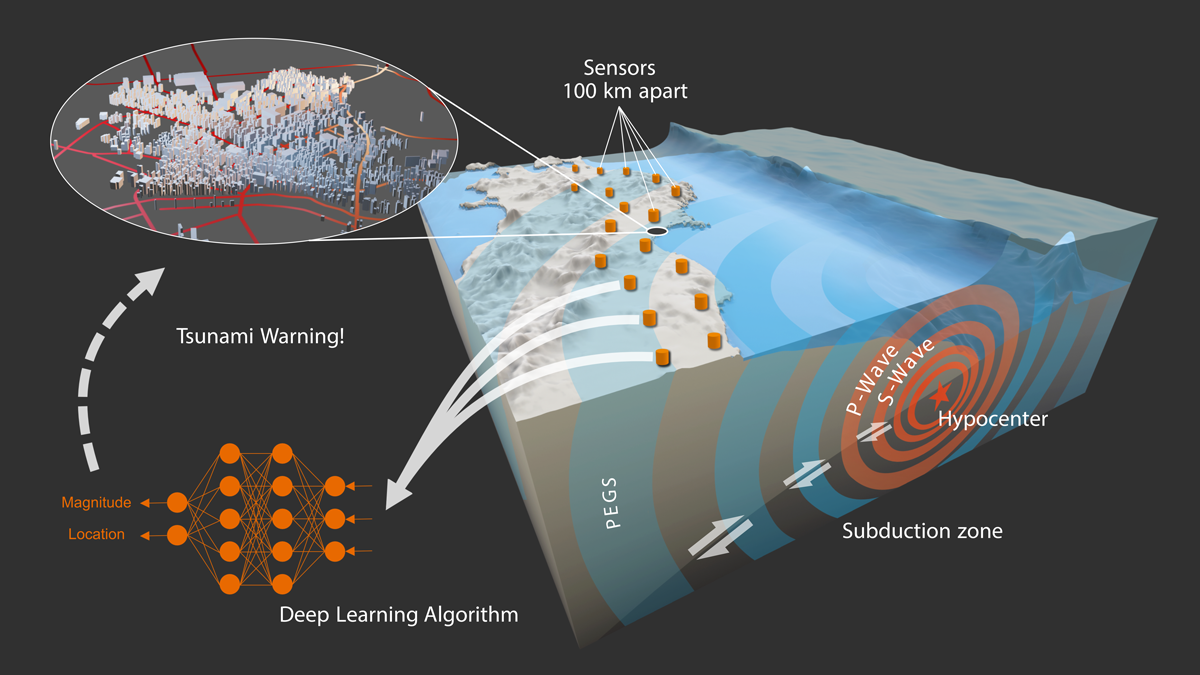
New research uses gravity and a machine learning model to instantaneously estimate the magnitude and location of large earthquakes.
disaster preparedness
Rock Music in Utah
Three-dimensional models could help forecast rock tower frequencies—and seismic impacts—around the globe.
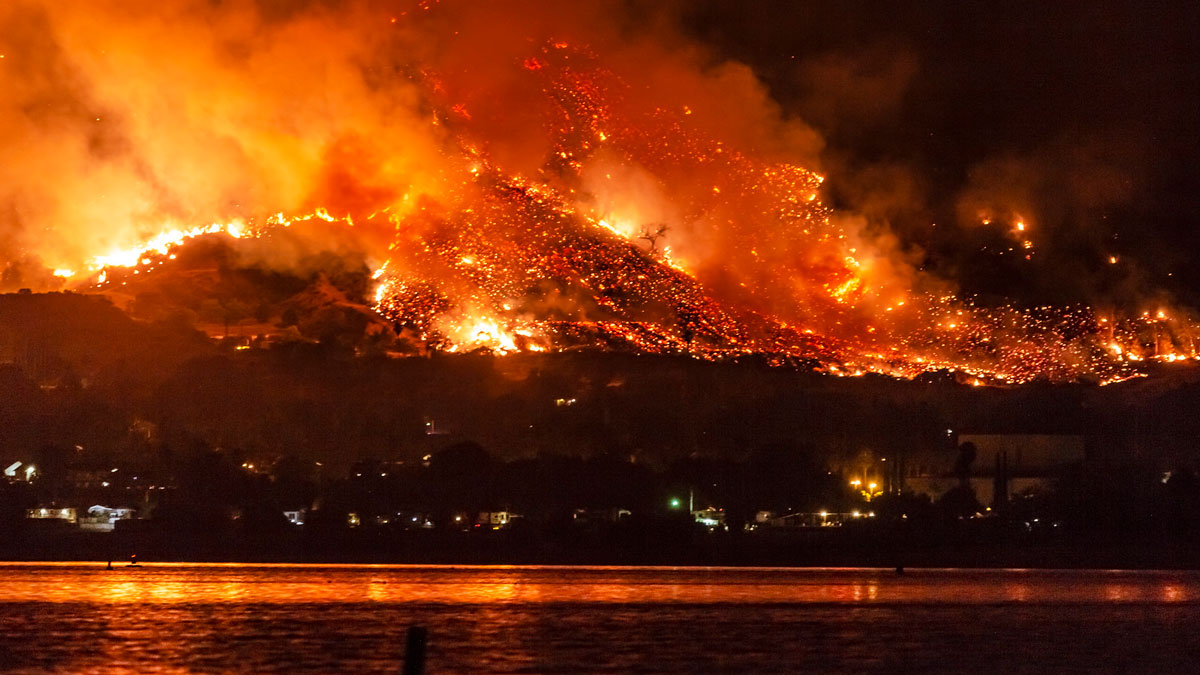
Los incendios forestales empeorarán, advierte informe de la ONU
Desde el ecuador hasta el Ártico, es probable que aumenten los incendios forestales y que el cambio climático los empeore, según un nuevo informe de las Naciones Unidas. La acción todavía es posible, dicen los autores.
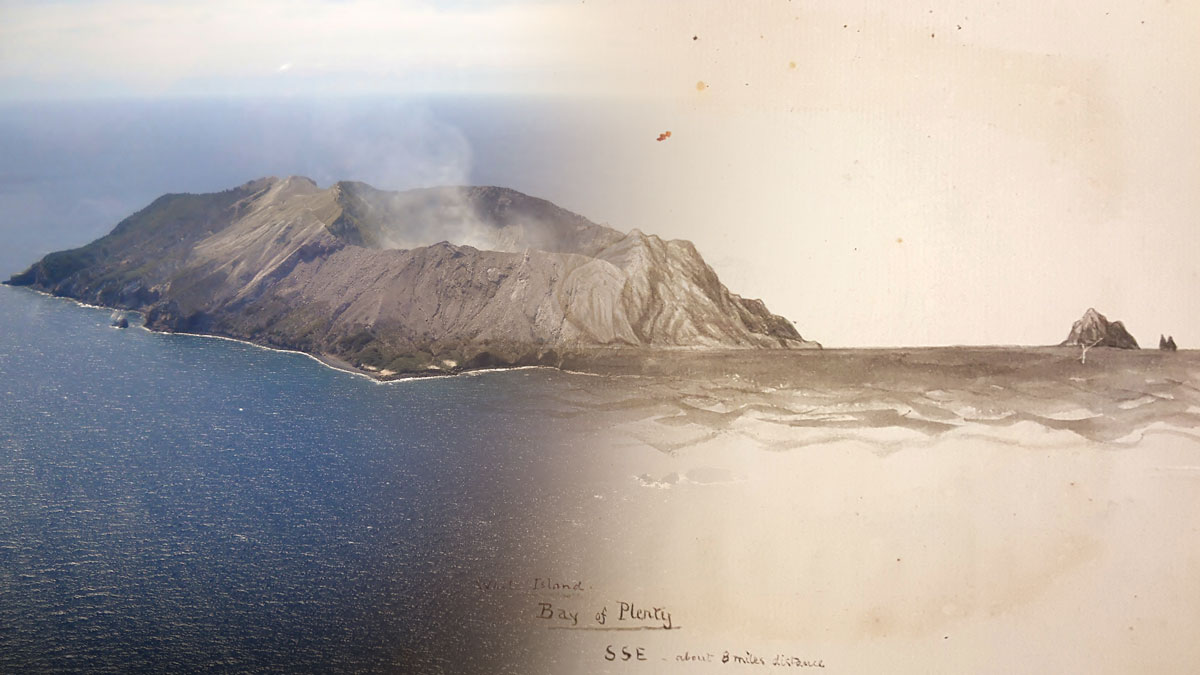
Studying Volcanoes through Myths, Legends, & Other Unconventional Data
Studying historic eruptions through a storytelling lens often improves our understanding of and ability to prepare for such events.
Estimando la frecuencia e intensidad las olas de calor: Un caso de estudio en Chicago
Modelado numérico mostró los impactos extendidos de la ola de calor del 2012 en Chicago, clarificando los impactos de la ola de calor y la isla de calor urbana en la temperatura de la ciudad.
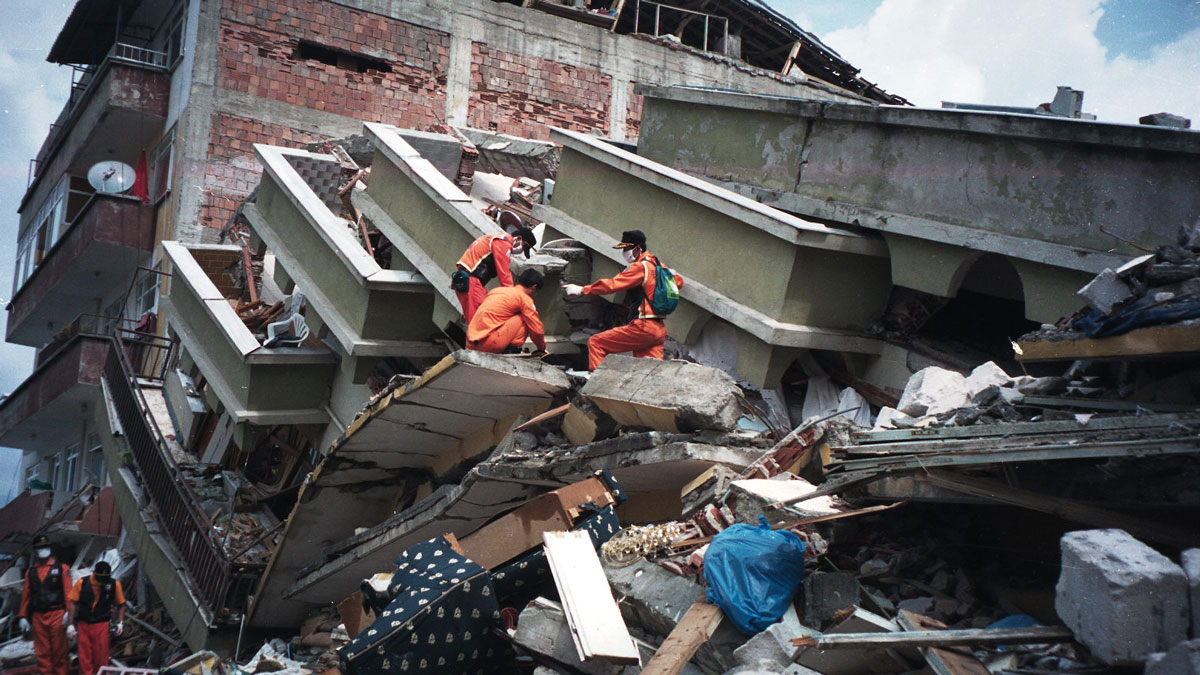
Do Earthquakes and Tectonic Plates Have a Two-Way Relationship?
A catastrophic earthquake in Turkey in 1999 changed the motion of the Anatolian plate, according to a study that could change the fundamentals of quake models.
After a Hurricane, Coastal Systems Draw a Line in the Sand
A new study finds nature can’t have it both ways: On the basis of thousands of case studies from dozens of hurricanes, there’s always a trade-off between resistance and resilience.
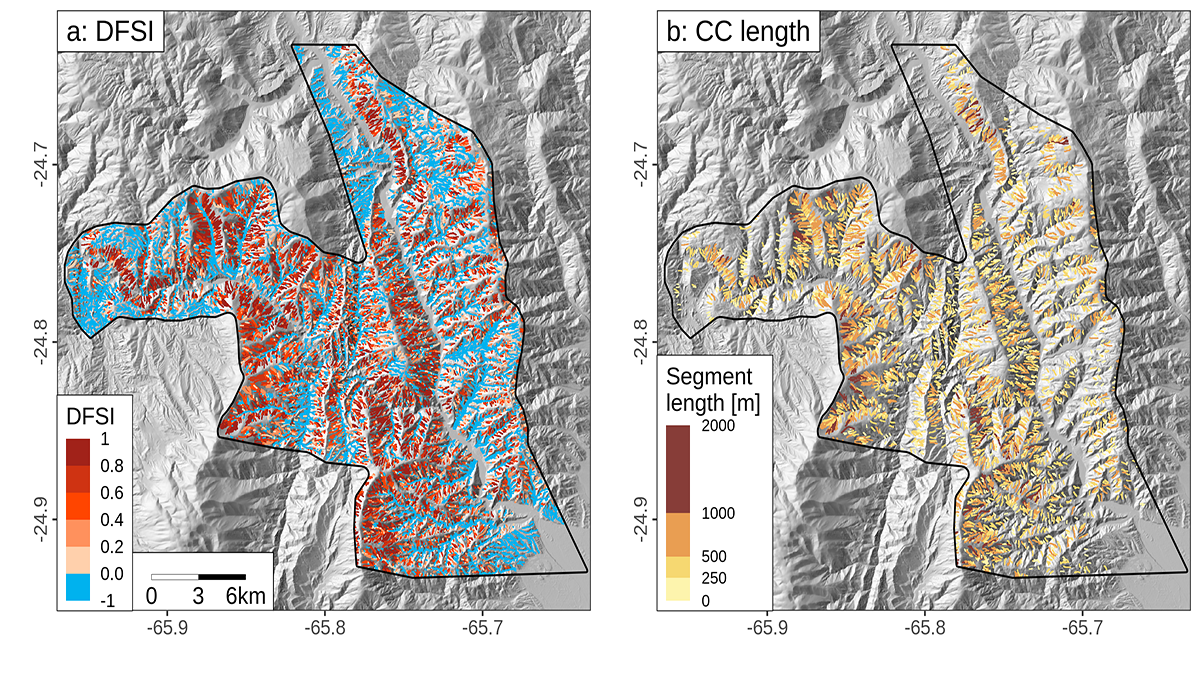
Debris Flows Keep the Landscape on the Straight and Narrow
New methods for identifying debris flow-shaped channels improve hazard quantification and highlight how high uplift rates and fractured bedrock facilitate debris flow-dominated landscape evolution.
Magma Lingers at Different Depths on the Basis of Its Water Content
The discovery, gleaned from observations of volcanoes on four continents, could help constrain models of volcanic eruptions.
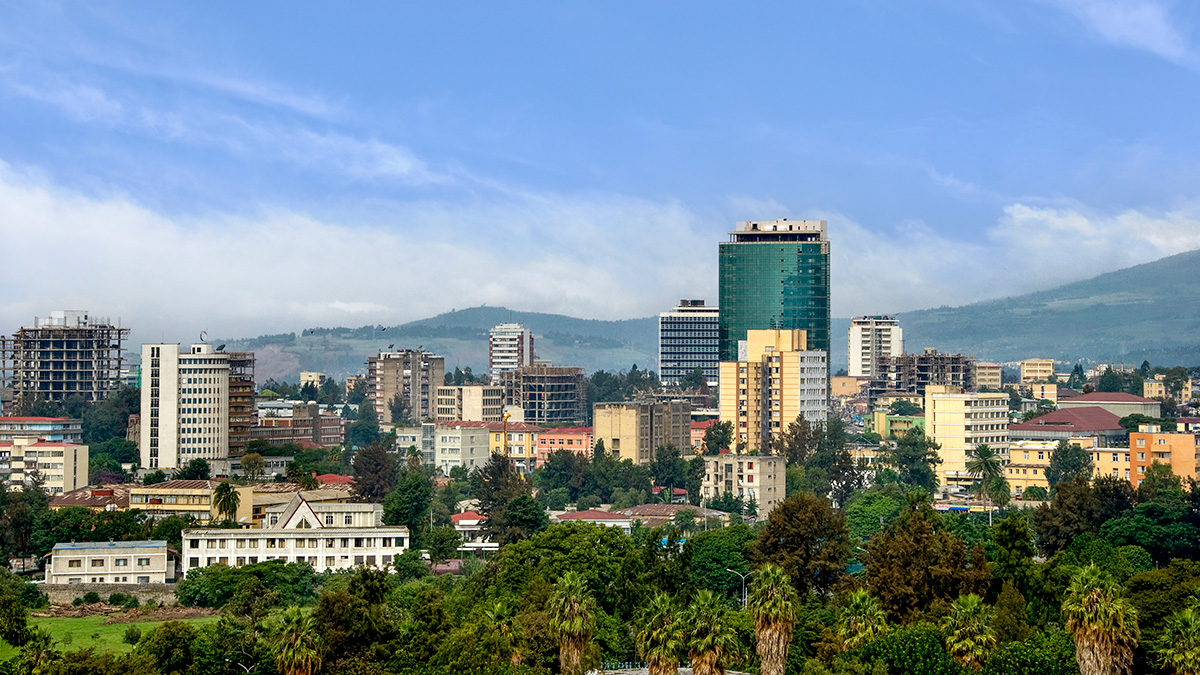
New Hazard Exposure Model for Africa
The rapid pace of urbanization could encroach on hazard-prone regions without adequate land management and building design regulations, a new modeling project shows.