For the first time, scientists have observed a deviation from the typical alternating pattern of easterly and westerly winds in the equatorial stratosphere.
Research Spotlights
Research spotlights are plain-language summaries of recent articles published in AGU’s suite of 24 journals.
The Role of Seafloor Methane in Ancient Global Warming
New research suggests that release of methane from seafloor hydrates was much slower than hypothesized during a period of rapid global warming about 56 million years ago.
Tremors Reveal the Structure of Deep Glacial Shafts
Seismic waves produced by free-falling meltwater could improve understanding of glacial drainage processes.
Incorporating 3-D Cloud Effects into Weather and Climate Models
Researchers explain how a new radiative scheme can be incorporated into global weather and climate models to better capture the effect of clouds on climate.
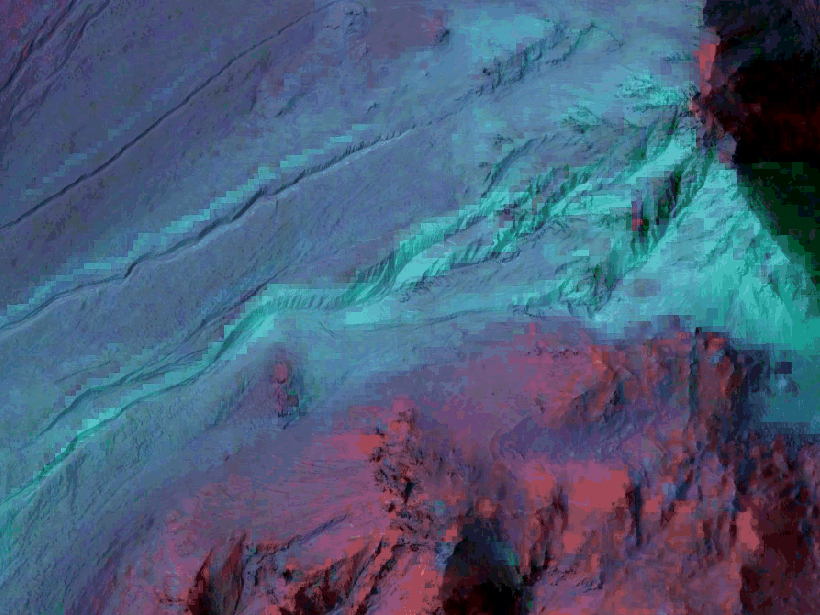
How Do Gullies Form on Mars?
New orbiter data support an important role for seasonal frost—not liquid water—in the formation of Martian gullies.
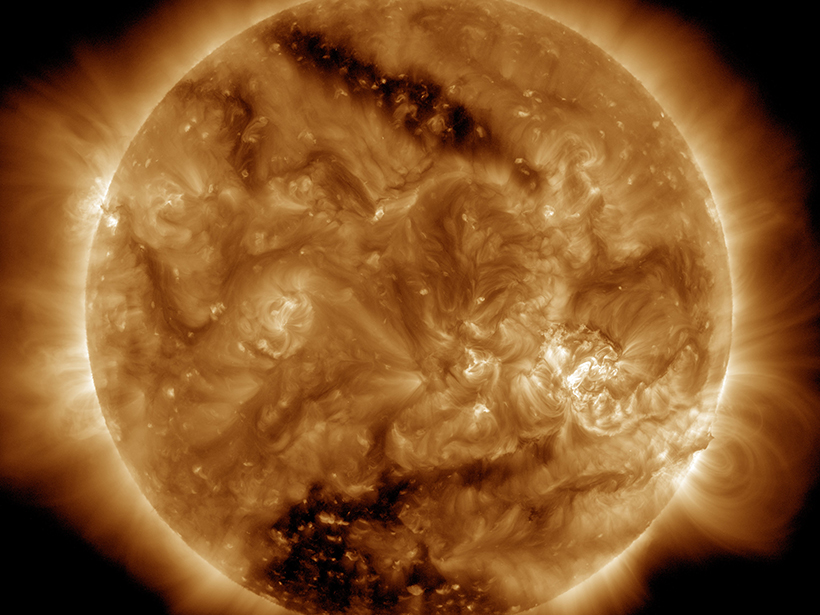
Spotting the Source of Slow Solar Wind
A new study suggests that magnetic reconnection may fuel slow solar winds, which top out at speeds below 500 kilometers per second.
How Sea Surface Temperatures Affect an Atmospheric Phenomenon
New research sheds light on the complex interplay between the atmosphere and the ocean and how both affect the Madden-Julian Oscillation.
Scientists Map Temperature and Density in Earth’s Exosphere
Data from multiple orbiters give a clearer picture of how density and temperature interact and what that could mean for future satellite missions.
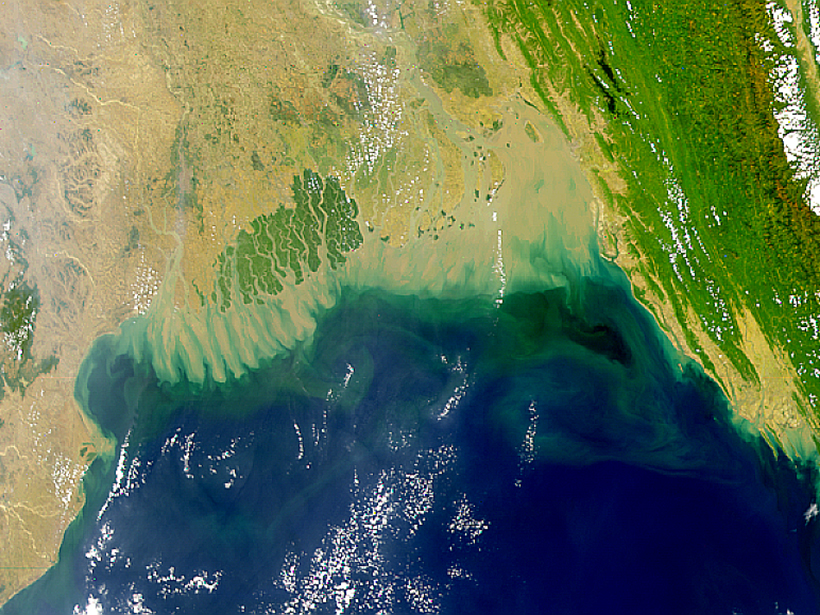
Deciphering the Bay of Bengal's Tectonic Origins
New magnetic and gravity data suggest that the boundary between continental and oceanic crust lies beneath northern Bangladesh, along the line of an Early Cretaceous spreading center.
Forecasting Space Weather Like Earth Weather
Researchers find that as with terrestrial weather, ensemble forecasting—which uses several different models simultaneously—is the best way to produce accurate and precise forecasts of space weather.