As thunderstorm updrafts strengthen, electrification of clouds can heat the lower ionosphere, explaining prolonged disturbances to radio waves in the rarefied atmospheric layer.
Research Spotlights
Research spotlights are plain-language summaries of recent articles published in AGU’s suite of 24 journals.
A “Super” Solution for Modeling Clouds
Climate models struggle to accurately portray clouds because the models cannot resolve the scales at which clouds form. A new study demonstrates a potential fix for the problem.
Solving the Global Nitrogen Imbalance
Excess nitrogen causes serious environmental problems, but too little can lead to food insecurity and unrest. A team of researchers proposes a five-pronged solution to our planet’s nitrogen woes.
Theoretical Models Advance Knowledge of Ocean Circulation
A review of recent advancements highlights key insights into the Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation and what might be in store for future research.
How Land Use Affects Nutrient Pollution in a Changing Climate
As heavy rain falls more frequently, the land alongside a river has a greater effect on the waterway’s nutrient levels—for better or worse.
Revealing the Ocean’s Rare but Prolific Carbon Export Events
New findings suggest that rare events underlie a global inverse relationship between primary production of organic carbon in the upper ocean and the fraction that is exported to the deep sea.
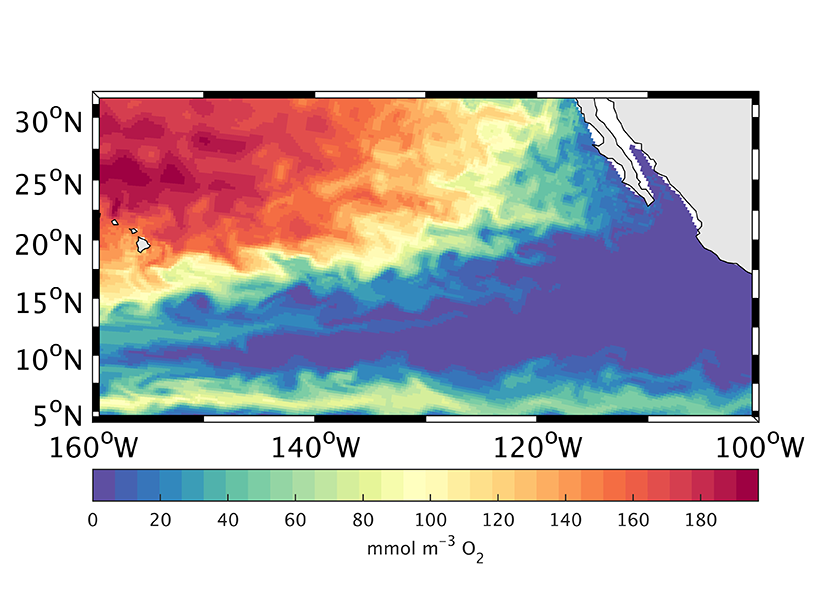
How the Ocean’s “Shadow Zone” Breathes
A new study uses Argo floats and an ocean circulation model to track the sources supplying pulses of oxygen to the deep North Pacific.
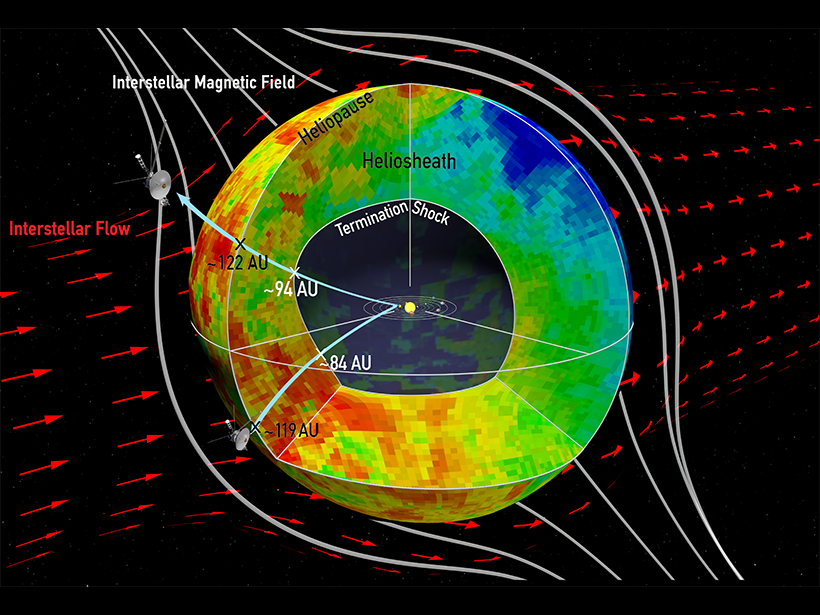
Sampling the Space Between the Stars
Data from the Cassini and Voyager spacecraft reveal new information about the Sun’s magnetic bubble.
Past Climate Sensitivity Not Always Key to the Future
New research suggests that changes in continental configuration, solar brightness, and background atmospheric carbon dioxide levels all conspire to drive Earth’s climate sensitivity over geologic time.
Capturing Snowmelt Patterns from Cloudy Satellite Images
A new modeling strategy could improve streamflow predictions in places where mountain snow is a critical source of water.