A new analysis of cloud composition and behavior suggests that scientists have overestimated the ability of a type of mixed-phase ice-and-water cloud to mitigate climate change effects.
Climate Change
Expanding Use of Plant Trait Observations in Earth System Models
Workshop on Trait Methods for Representing Ecosystem Change; Rockville, Maryland, 18–19 November 2015
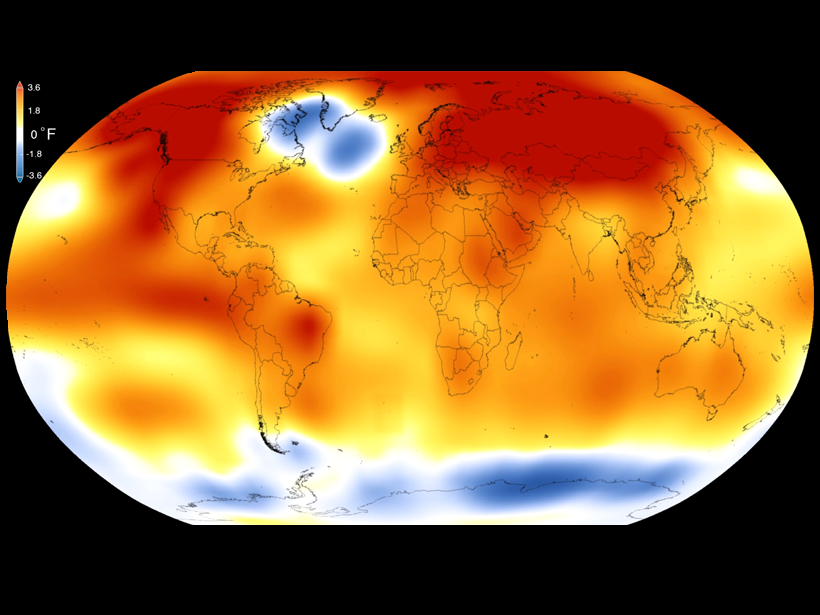
Researchers Attribute Human Influence on Climate Back to 1930s
A new study finds that humans likely have triggered the last 16 record-breaking hot years on Earth, up to 2014.
Salinity Monitoring Gives Insight into the Global Water Cycle
Salinity and Water Cycle over the Oceans: Recent Progress and Future Challenges; Hamburg, Germany, 12–15 October 2015
Insights on Climate Systems from Interglacials
Interglacials provide insights into the impacts of warmer than present conditions in certain regions of Earth.
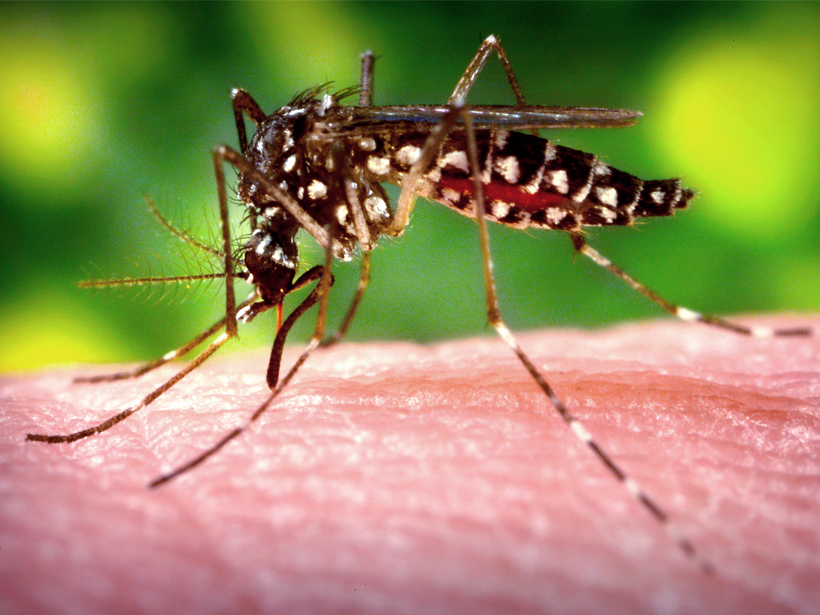
Seven Ways Climate Change Threatens U.S. Population's Health
A report by the U.S. Global Change Research Program finds health risks from global warming tied to heat, air quality, vector-borne diseases, water issues, extreme weather, nutrition, and mental stress.
Considering Atmospheric Electricity in Climate Models
Researchers create a new model of the electric currents circulating throughout the atmosphere that will improve the accuracy of global climate models.
How Do Climate Variations Affect the Width of the Tropics?
The Width of the Tropics: Climate Variations and Their Impacts; Santa Fe, New Mexico, 27–31 July 2015
Tide Pools Mimic Climate Change in Everyday Cycle
Researchers unexpectedly discovered that tiny shoreline ecosystems act as miniature laboratories in which ocean acidification and its effects play out nightly.
Forecasting India's Water Future
The NORINDIA project sheds light on how climate change could affect monsoons, droughts, and glaciers in northern India.