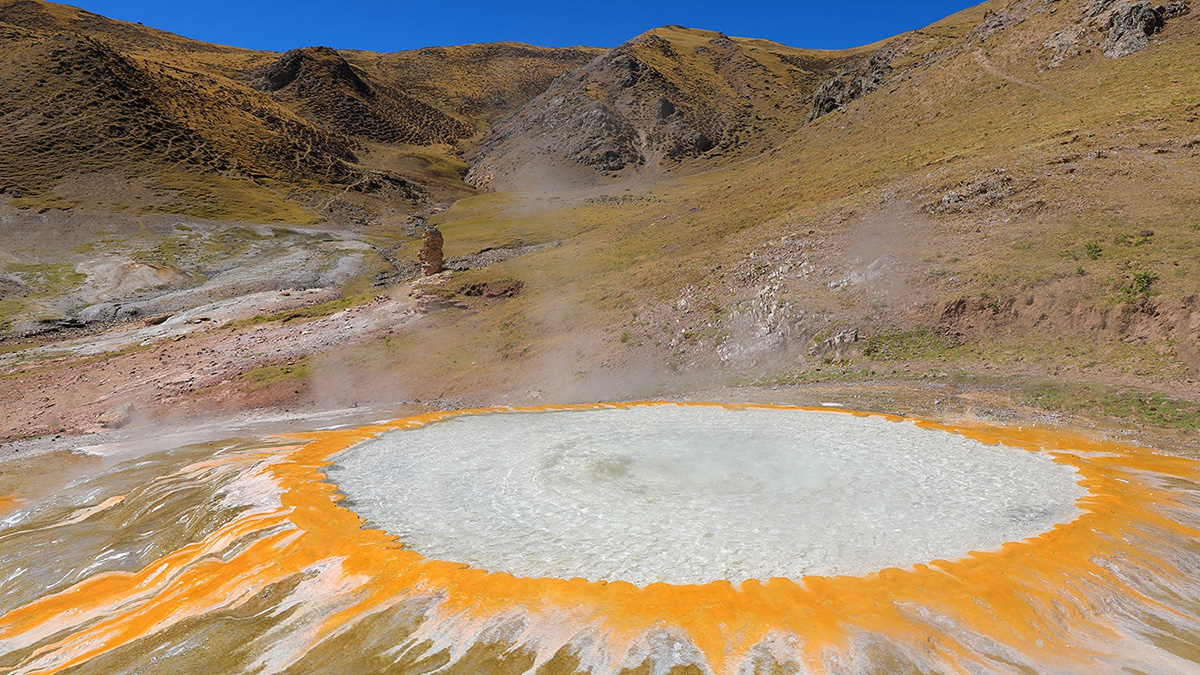
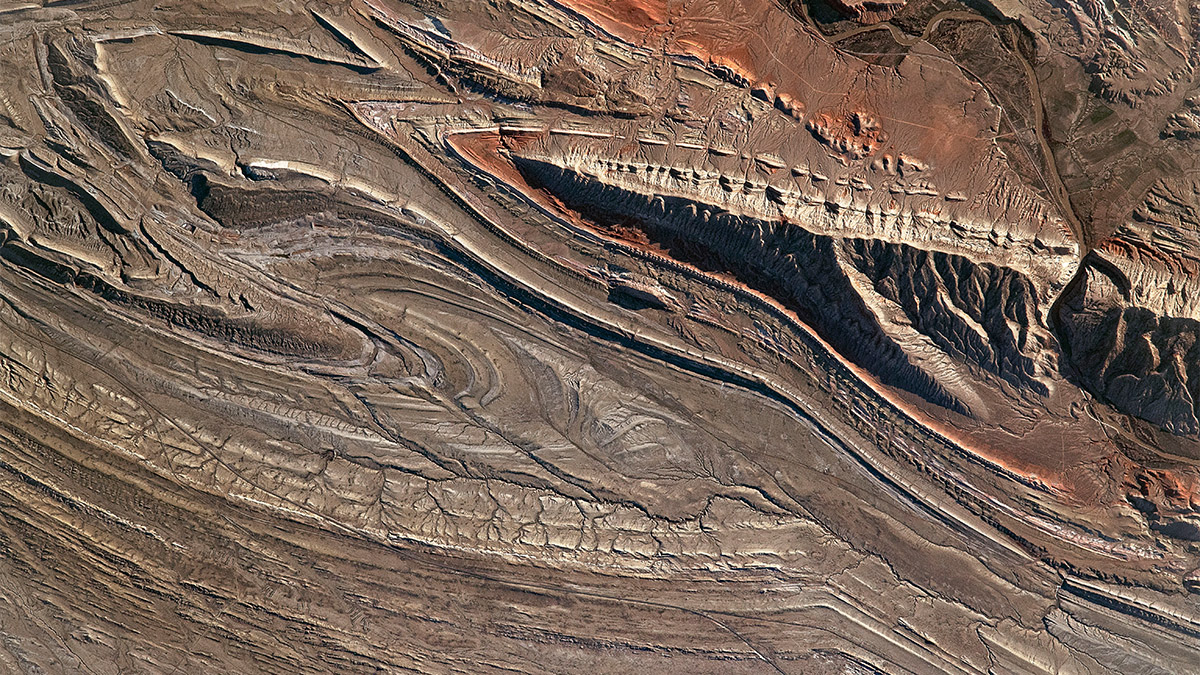
Helium isotopes found in water samples provide a snapshot of what lies beneath the plateau and stimulate debate within the geosciences community.
continents
Incredible Journeys on the Crown of the Continent
Living in Geologic Time: The making, breaking, and backpacking of North America’s Continental Divide.
The Birth, Growth, and Death of Continents
There are various explanations for how the Earth’s continents form, develop, and change but challenges remain in fully understanding the driving forces behind plate tectonics on our planet.
Cratons, Why Are You Still Here?
How have these continental relics from Earth’s early history survived the plate tectonic mixing machine?
Breaking Up Is Hard to Do, Especially for Continents
A decade-long research collaboration has revealed that the split between Africa and North America roughly 200 million years ago was more drawn out than previously thought.
Modeling the Creation of Cratons, Earth’s Secret Keepers
Geoscientists have long been trying to answer the complicated questions of how and why Earth’s continents formed. New research suggests a solution that surprised even the investigators themselves.
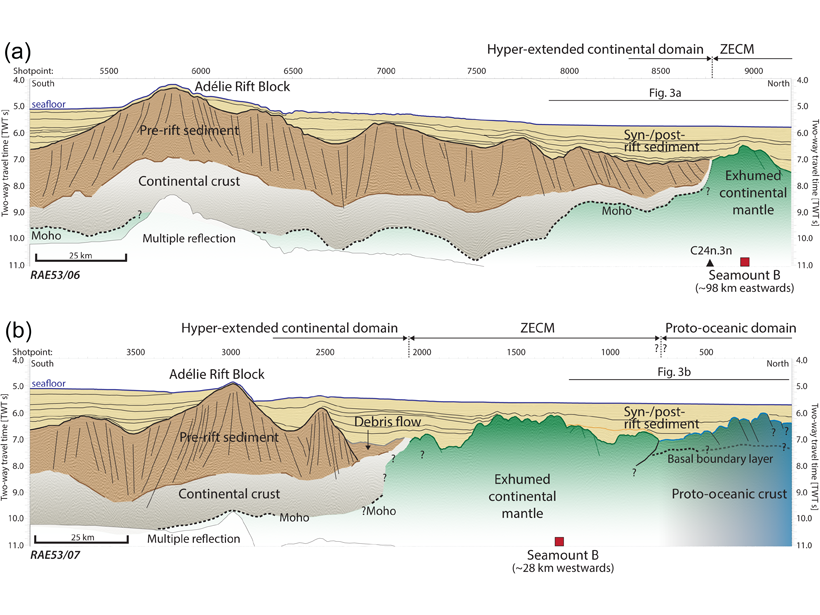
New Data from Earth’s Largest Non-Volcanic Rift Margin
Seismic reflection images combined with petrological data provide new constraints on the nature of the basement in the enigmatic Australia-Antarctic oceanic-continent transition zone.
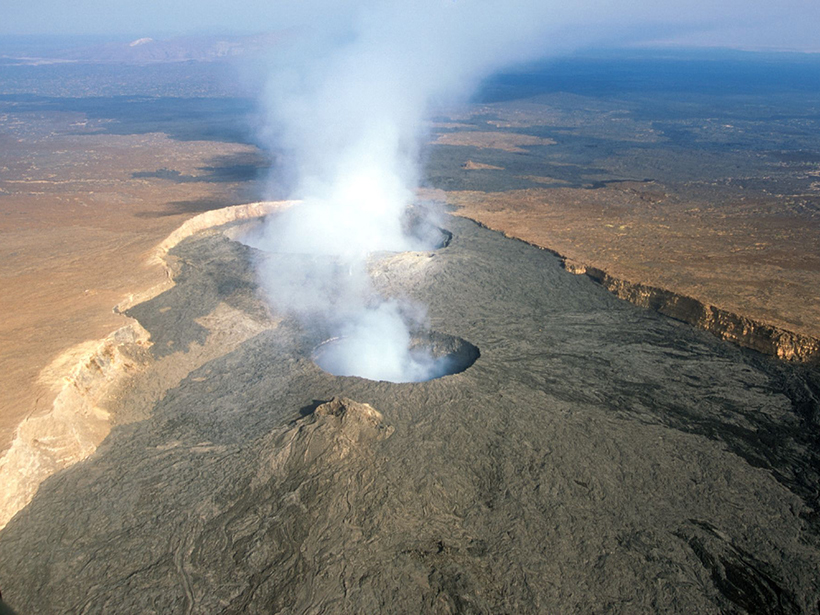
Are We Seeing a New Ocean Starting to Form in Africa?
Although shallow magma storage at Erta Ale volcano hints at a rift-to-ridge transition, the tectonic future of the Afar region is far from certain.
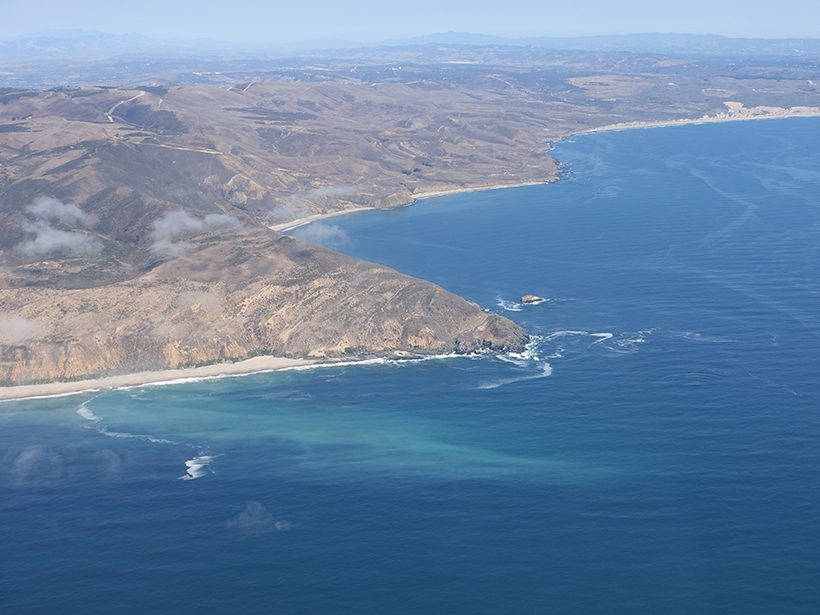
Untangling a Web of Interactions Where Surf Meets Coastal Ocean
In 2017, an ocean research team launched an unprecedented effort to understand what drives ocean currents in the overlap regions between surf zones and continental shelves.
Very Warm Water Observed Along West Antarctic Ice Shelf
Two years of mooring observations at the edge of the continental shelf show that wind stress and upwelling control the inflow of some of the warmest water observed at an ice shelf front in Antarctica.