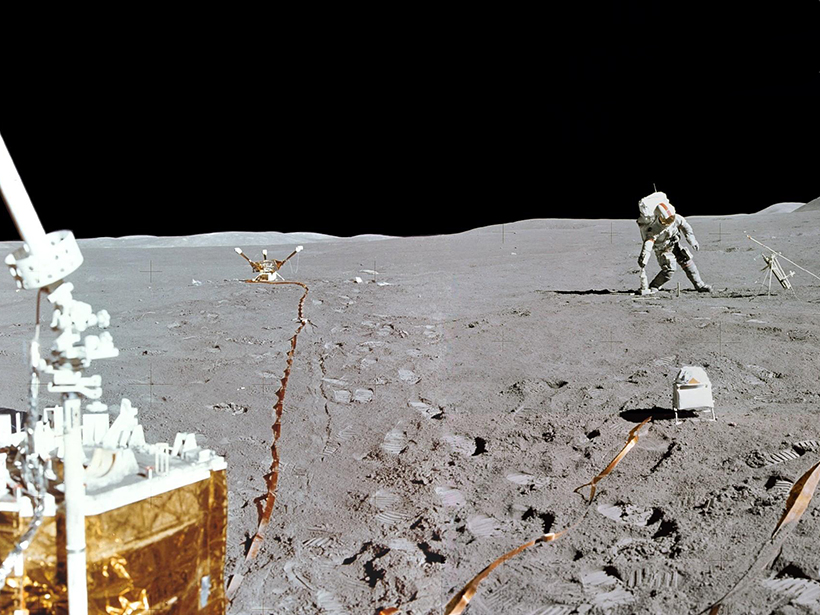
Decades-old data analyzed for the first time suggest that astronauts’ disturbance of the Moon surface increased solar heat intake, warming the ground below.
cool tools
A Near-Real-Time Tool to Characterize Global Landslide Hazards
By fusing susceptibility information with precipitation data, a new model generates “nowcasts” to predict the potential for rainfall-triggered landslides in steep terrain between 50°N and 50°S.
Harnessing Remote Infrasound to Study Volcanic Eruptions
Data from the 2015 eruption of Chile’s Calbuco volcano suggest the international network built to monitor nuclear explosions may also be used to detect and characterize volcanic activity.
Getting Littoral with Lake Carbon Efflux
Next generation forced diffusion chambers reveal dynamic environment for lake carbon exchange with distance from shoreline.
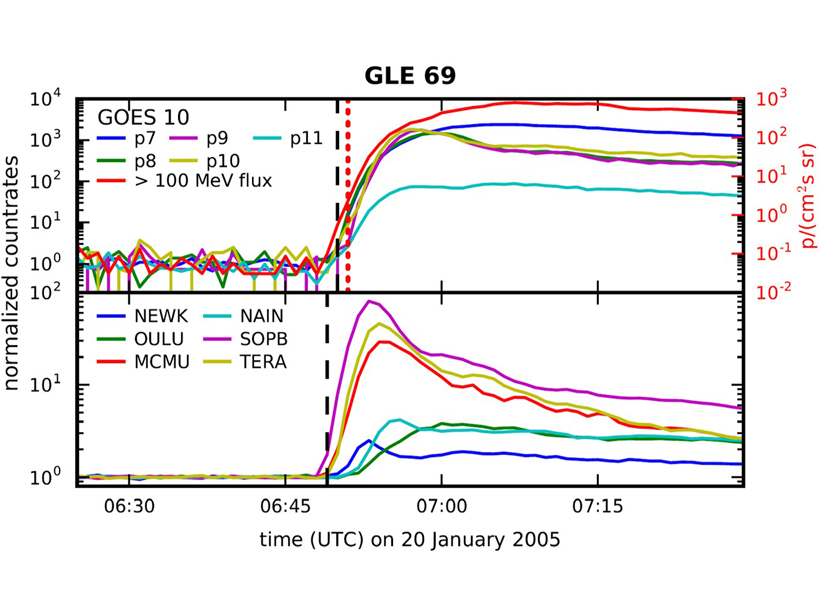
Catching the Oncoming Radiation Storm
Improved processing enables satellite-based radiation sensors to match ground-based sensors in providing prompt warnings of the onset of atmospheric radiation storms that can endanger civil aviation.
Five Weird Archives That Scientists Use to Study Past Climates
When tree rings, ice cores, and cave formations can’t cut it, try your luck with whale earwax or bat poop.
Virtual Mentoring Rewards Scientists at All Career Stages
Five geoscience organizations recently established an online global mentoring service for their disciplines.
Ten Everyday Objects That Can Be Used for Science
Need a way to store sediment cores or grind up soil? These scientists have your answer.
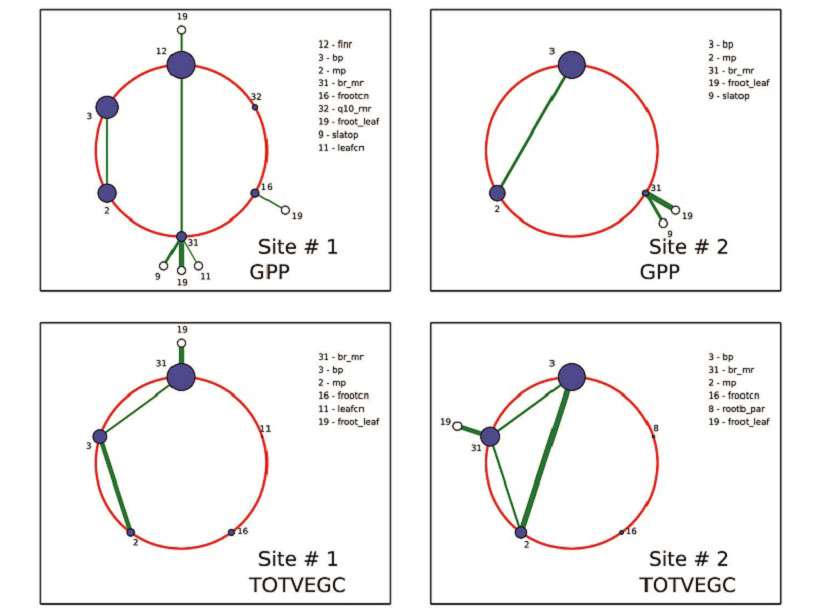
A Powerful New Tool to Analyze and Calibrate Earth System Models
Polynomial chaos and Bayesian compressive sensing are applied to a land surface model to understand how large numbers of tunable parameters interact and may be optimized.
Virtual Poster Showcase Experienced Steady Growth in 2017
A pilot project for high schools and a geographic information system map, as well as other embellishments, have enhanced a program that enables students to present research electronically.