Dramatic erosion of a sand dune in Viña del Mar, Chile appears to be related to maintenance of a drainage pipe.
erosion & weathering
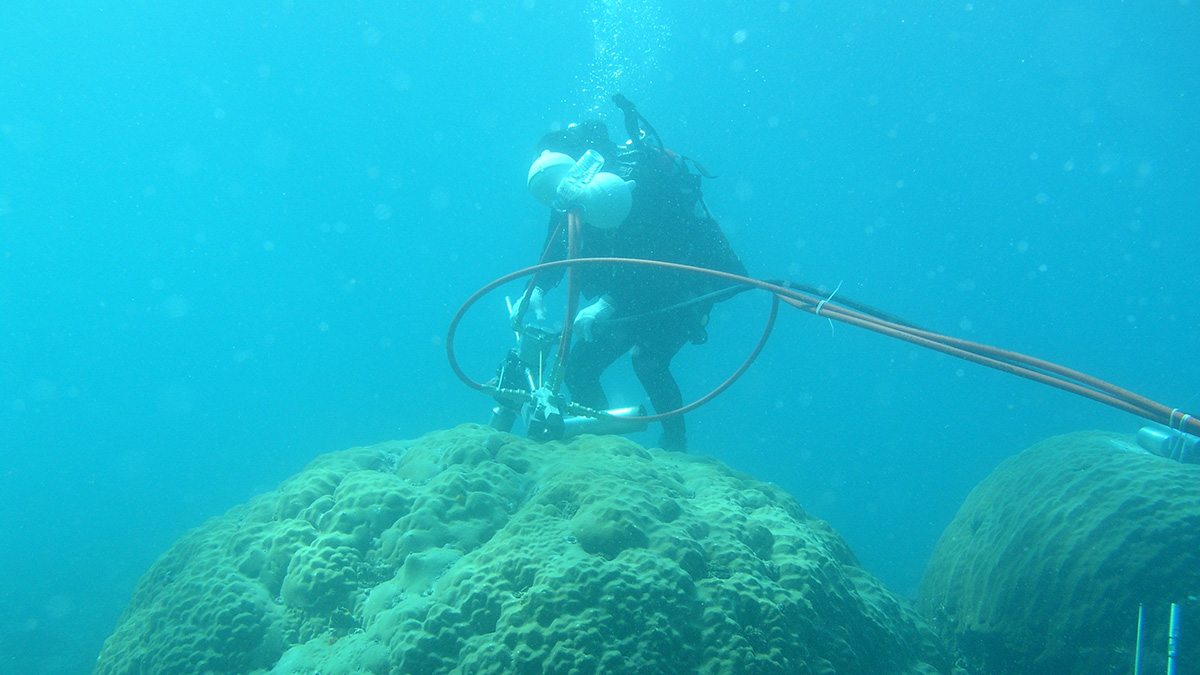
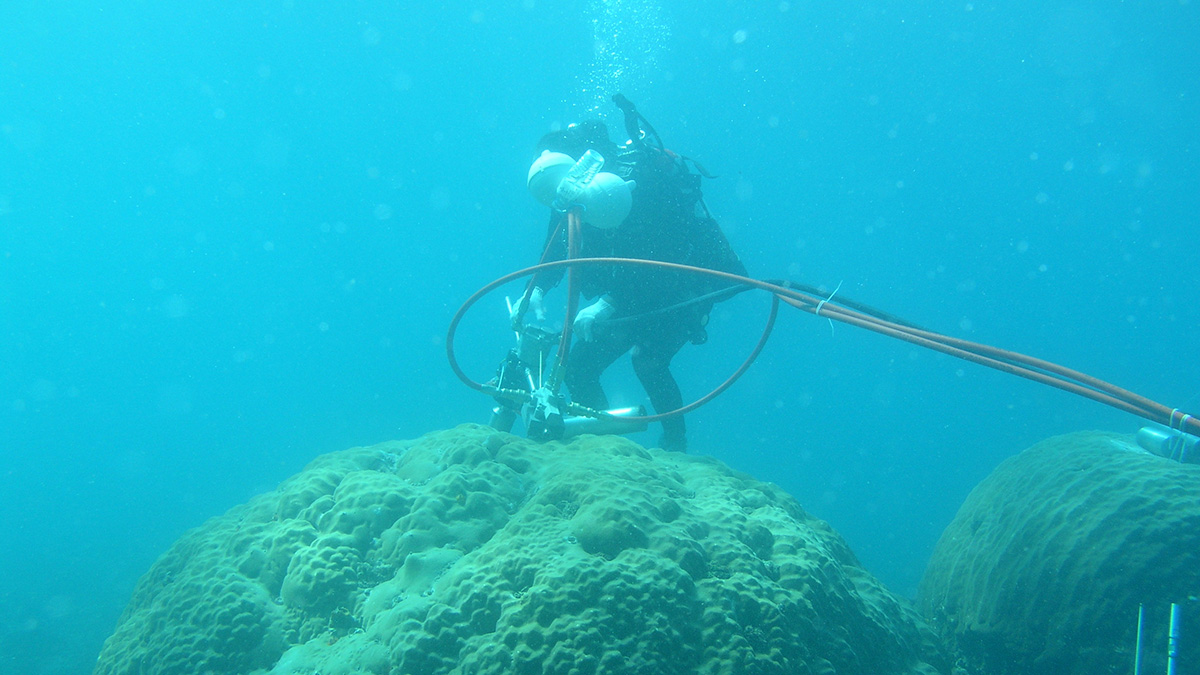
La chimie du corail reflète l’expansion économique d’Asie du Sud-Est
Les sols en érosion en raison du développement économique ont transporté des sédiments en mer de Chine méridionale… et jusque dans le squelette corallien.
Frozen Riverbanks May Erode Faster in a Warming Arctic
Frozen flume experiments reveal the sensitivity of permafrost riverbank erosion to water temperature, bank roughness, and pore-ice content.
Plants Build Dunes but Can Speed Erosion During Severe Storms
When waves hit vegetated dunes, waterlogged areas form in front of plants, making for sand that’s easier to wash away. But you still need plants to form dunes in the first place.
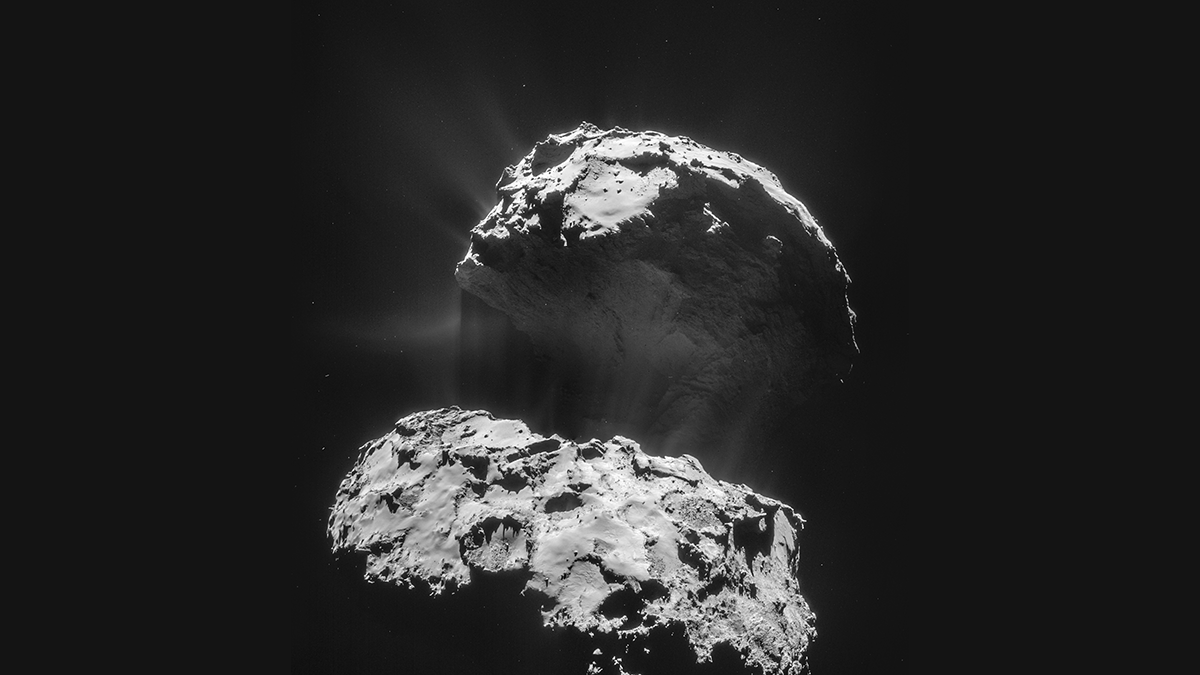
Dancing Dust on Comet 67P/Churyumov-Gerasimenko
Cometary activity moves sediments over the surface of 67P/Churyumov-Gerasimenko, with long-term sinks near the poles of the comet.
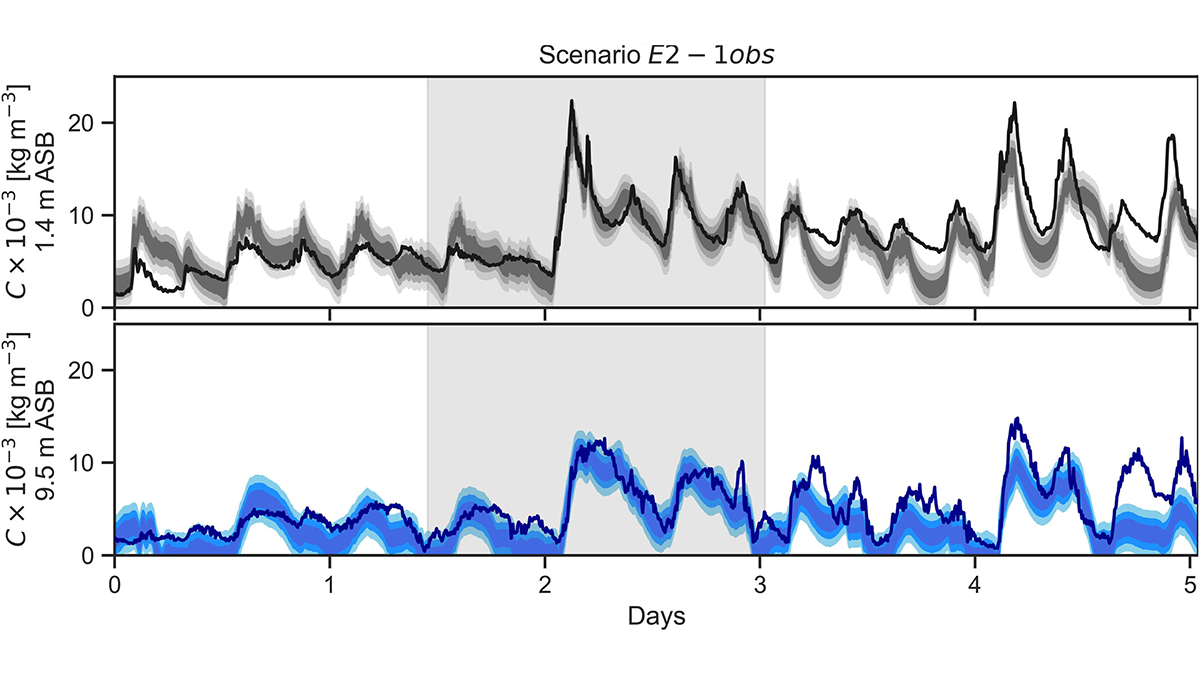
Using Bayesian Inference to Improve Sediment-Transport Models
A new Bayesian approach is used for the estimation and uncertainty quantification of unobservable parameters required to model tracer evolution in ocean sediment transport and tracer concentrations.
La química de los corales refleja la expansión económica del sudeste asiático
La erosión del suelo derivada del desarrollo económico mueve sedimentos hacia el mar del sur de China y también hacia los esqueletos de los corales.
Supersized Potholes Discovered off South African Coast
Curious circular pits off South Africa’s Eastern Cape coast are larger than any similar feature previously recorded. Their origin remains a morphological mystery.
Coral Chemistry Reflects Southeast Asia’s Economic Expansion
Soil erosion from economic development sent sediments into the South China Sea—and into coral skeletons.