A decade of continuous GPS measurements in South America indicates that enhanced strain accumulation following a great earthquake can initiate failure along adjacent fault segments.
faults
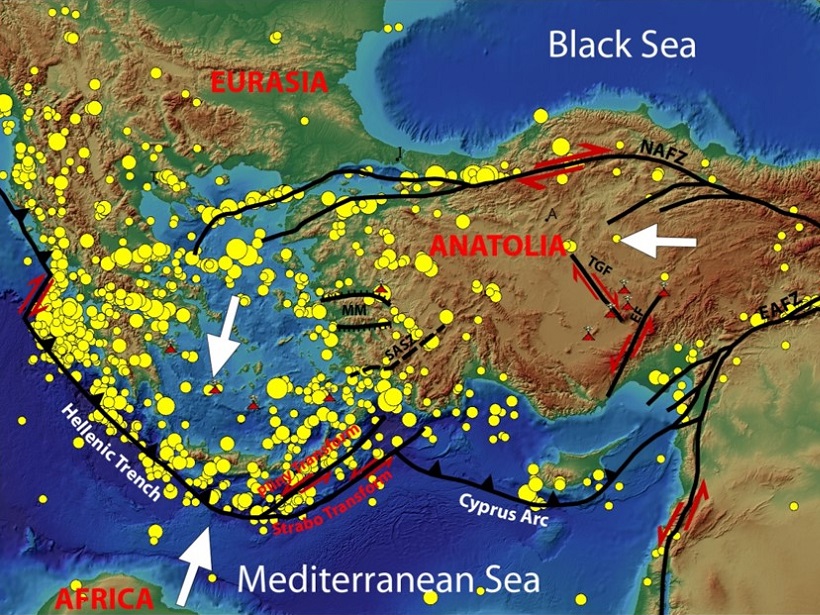
Neotectonics and Earthquake Forecasting
The editors of a new book describe the evolution of major earthquake producing fault zones in the eastern Mediterranean region and explore how earthquake forecasting could improve.
On the Origin of Low-Angle Detachment Faults
Data from California's Whipple Mountains suggest this complex was formed by a succession of steep normal faults, challenging the paradigm that detachments are different types of faults.
Alteration Along the Alpine Fault Helps Build Seismic Strain
Detailed analysis of cores drilled through New Zealand's most dangerous on-land fault indicates that its permeability and strength are altered by mineral precipitation between seismic events.
Studying Martian Rocks Without Leaving Planet Earth
Matching Martian rock formations to those found on Earth can help researchers learn more about the Red Planet.
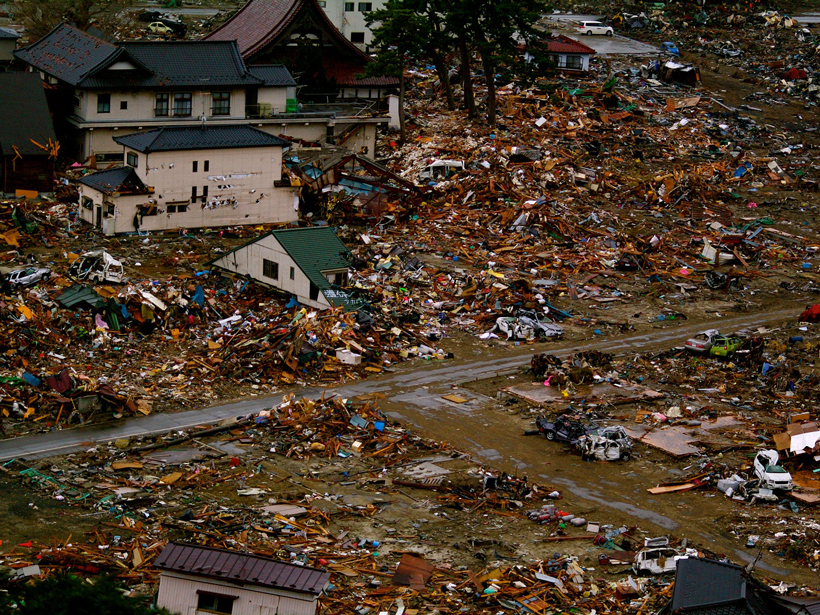
An Up Close Look at the Megaquakes That Cause Tsunamis
Researchers recreate changes in the seafloor during Japan's devastating 2011 tsunami.
Characterizing the Faults Beneath Germany
A team of researchers has described how the faults within the German Alpine Molasse Basin initially developed.
Cold Temperatures Set Off Slow-Moving Landslides
Falling ground temperatures in the cold season are found to trigger shallow, slow-moving landslides on slopes with clayey soil.
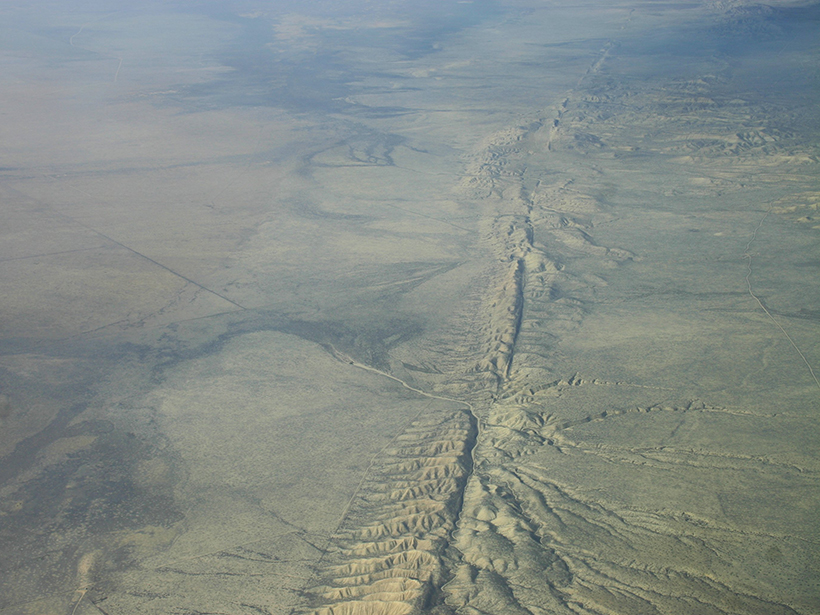
Tiny, Deep Quakes Increase on San Andreas as Tides Tug on Fault
When the gravity of the Sun and Moon causes Earth's crust to bulge every 2 weeks, slow-moving earthquakes proliferate in the lower reaches of the San Andreas, a new study finds.
Revising the Displacement History of New Zealand's Alpine Fault
A reinterpretation of structural and paleomagnetic data suggests that New Zealand's Alpine Fault accommodates a far greater percentage of geologically recent plate motion than previously thought.