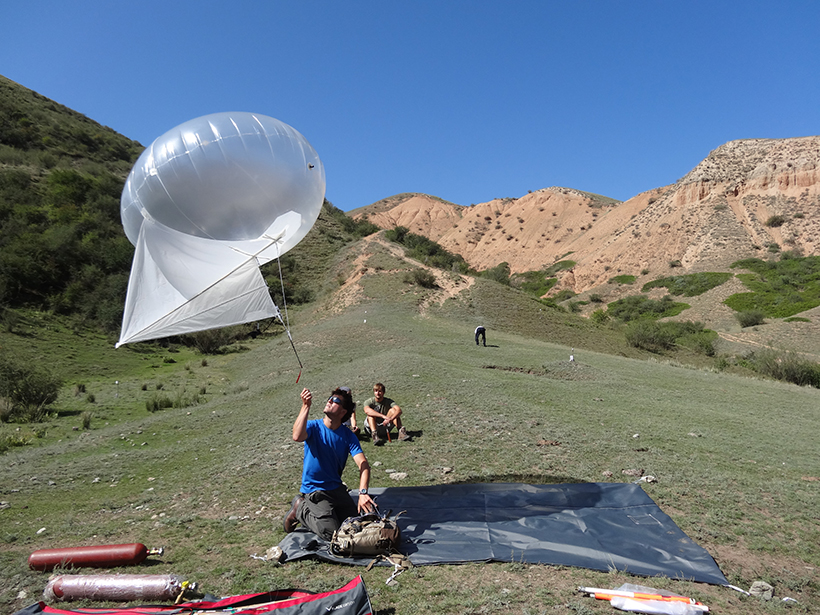
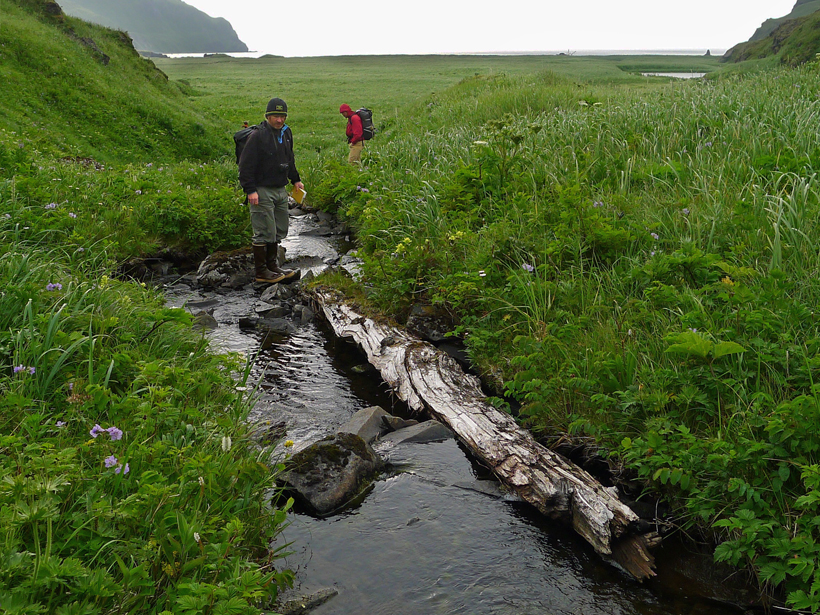
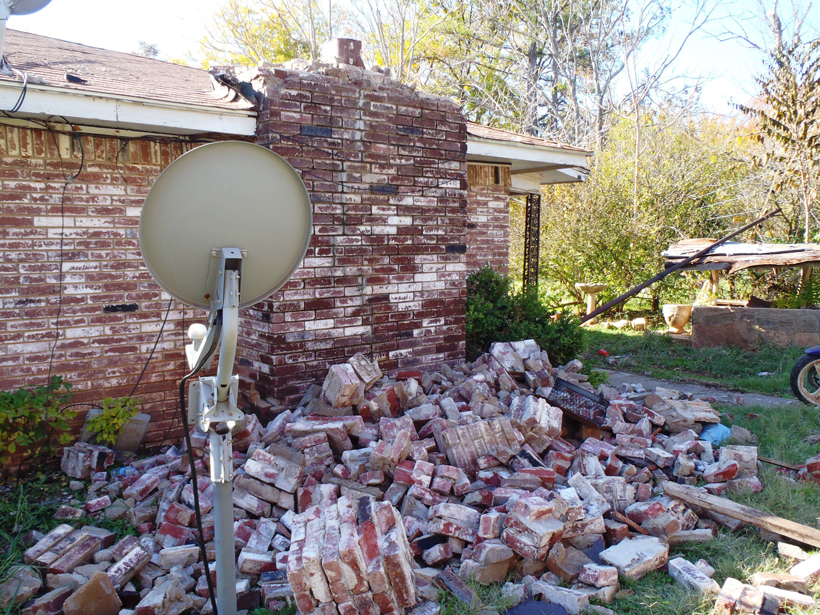
New fieldwork and satellite data suggest that three faults may have caused a large earthquake near Almaty, Kazakhstan, more than a century ago.
faults
Flash Heating May Lubricate Rubbing Rock Faces in Earthquakes
A new laboratory study examines the small-scale physics at play as two pieces of granite are smashed together in a scaled-down version of a real earthquake.
A Hole in Earth’s Surface
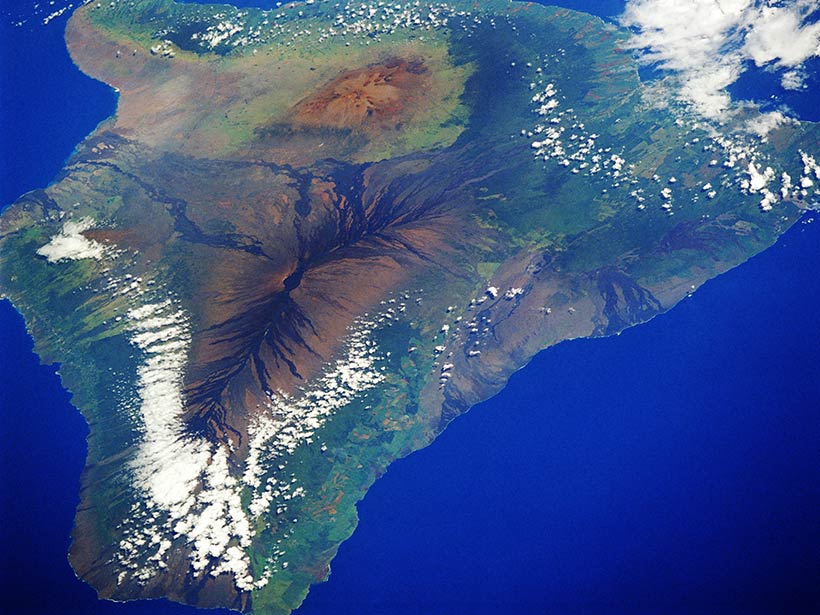
Research shows that a broken lithosphere underneath the island of Hawai'i could explain the island's patterns of seismic activity.
The Role of Water in Earth's Tectonic Plumbing Systems
Tidal forces act on well water around the San Andreas Fault, giving researchers a new window into the hydrogeological structure of fault zones.
Unknown Tsunami Trigger Hides Along a Creeping Aleutian Fault
A seismically quiet part of the Aleutian Subduction Zone may have caused tsunamis in the past—and may cause future tsunamis that could travel across the Pacific Ocean.
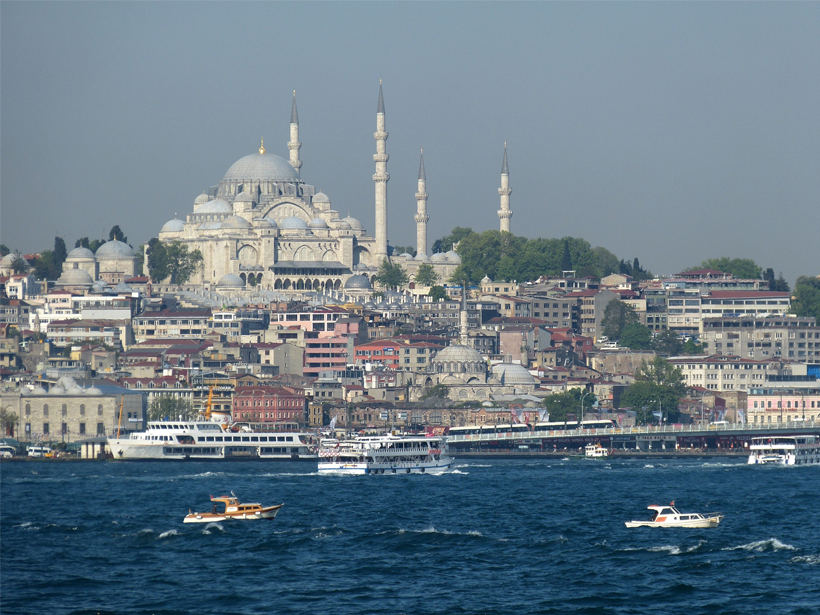
Characterizing the Fault Beneath the Marmara Sea
Researchers mine seismic wave data to elucidate the stress relief system of the Main Marmara Fault beneath Turkey's inland sea.
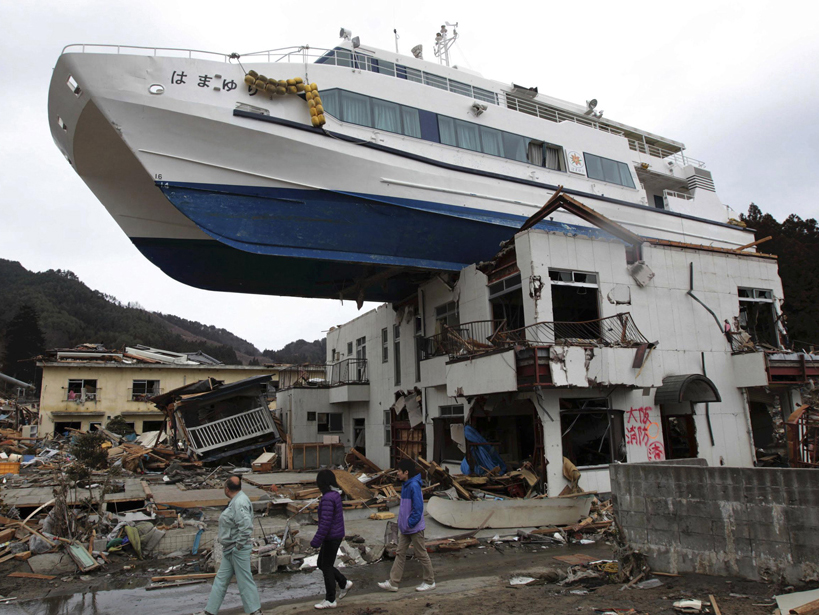
Alaska's Semidi Segment Could Unleash a Devastating Tsunami
Study reveals structures along the Alaskan convergent margin capable of generating a powerful tsunami directed toward the United States's West Coast.
Subtle Seismic Movements May Help Forecast Large Earthquakes
Where a plate of Earth's crust slides under another and when frequent episodes of plate slippage occur without noticeable earthquakes, large temblors will more likely strike, a new study finds.
Oklahoma's Dormant Faults Hide Huge Seismic Risk Potential
Researchers look at induced seismicity data in Oklahoma to spot an increase of stress in faults that could cause even more damage than recent quakes.
Active Mud Volcano Field Discovered off Southeast Alaska
A cruise to study landslide potential along an earthquake-prone fault found a surprising methane plume.