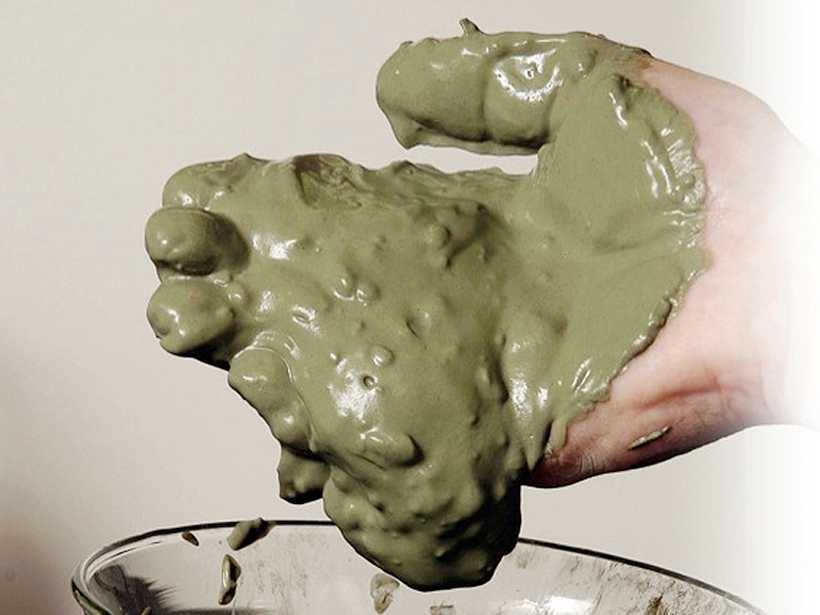
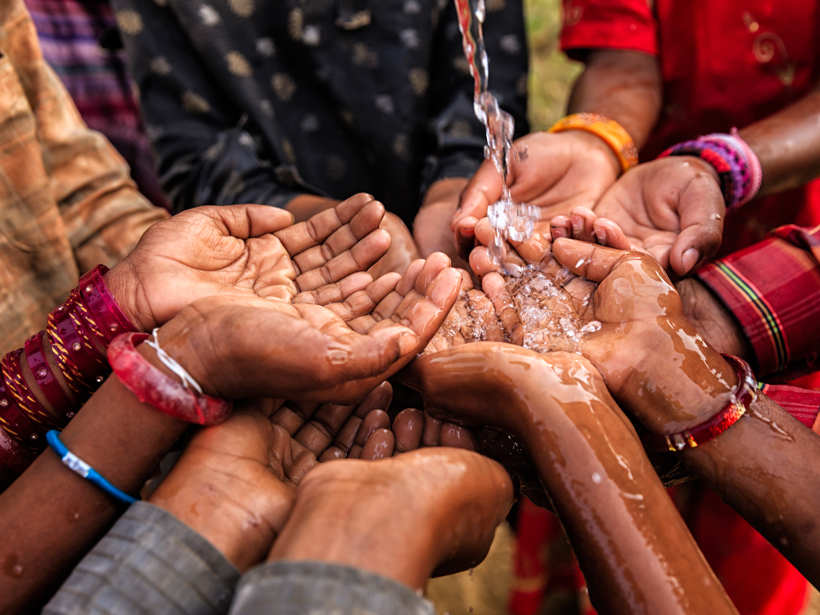
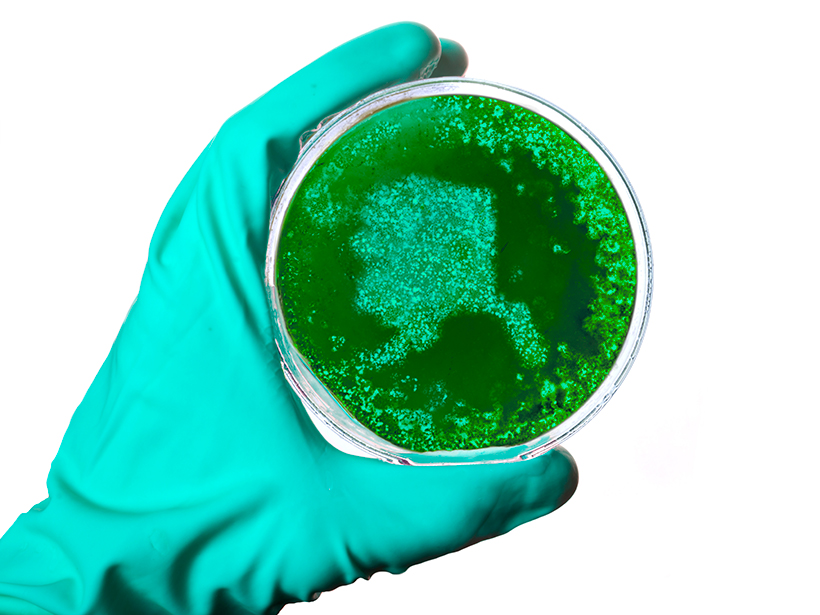
An ancient folk remedy, blue-green iron-rich clay, kills antibiotic-resistant bacteria using a one-two punch, a new study shows.
geohealth
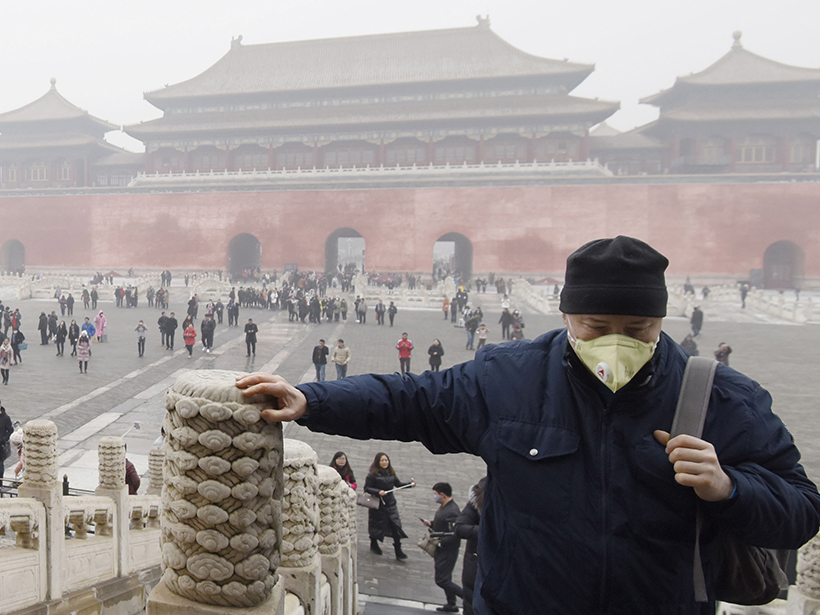
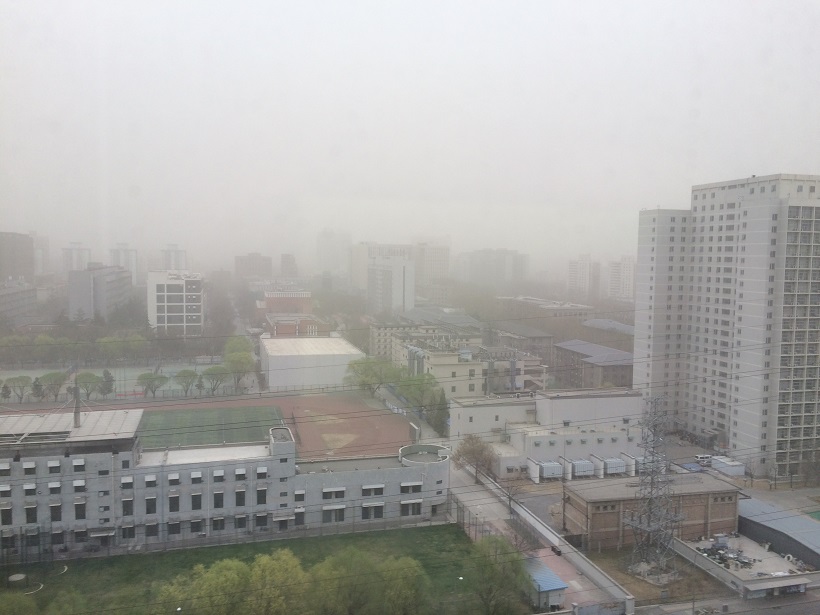
Heavy Air Pollution May Lower Cognitive Test Scores
A new study found that verbal and math test scores in China dropped with reduced air quality. The effects were especially pronounced for men and elderly populations.
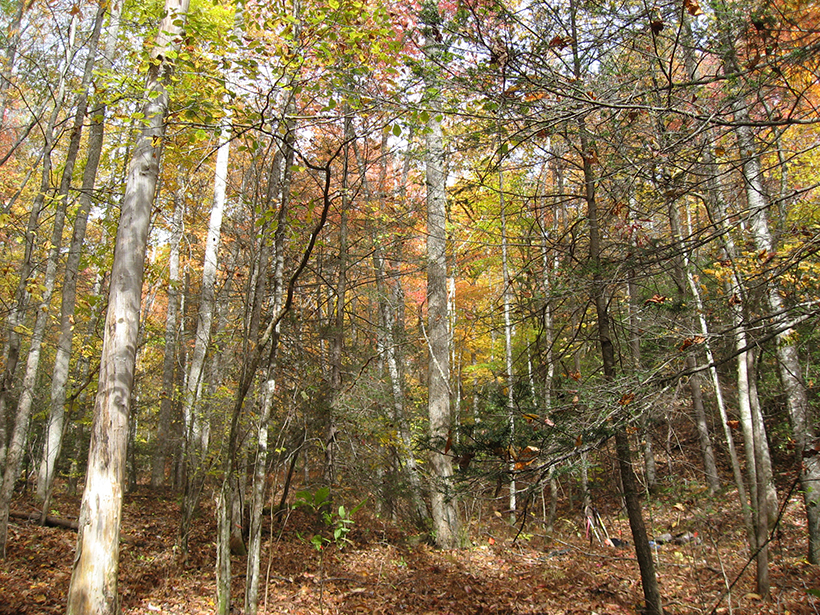
Insect Infestations Alter Forest Carbon Cycle
A hemlock woolly adelgid outbreak in southern Appalachia prompted a transformation in where the forest stores carbon.
Microbes Meet Geoscientists
A new collaboration brings together the two worlds of microbiology and geoscience with the common goal of improving public health outcomes.
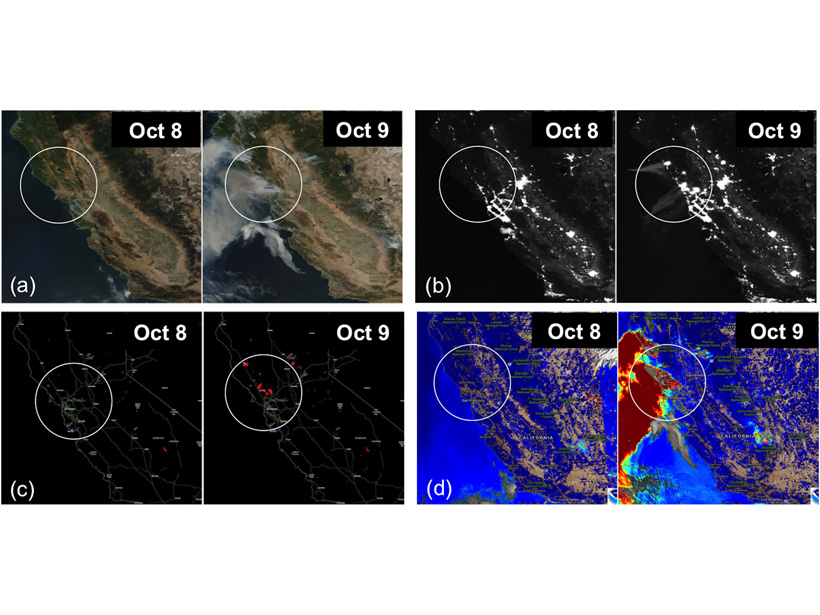
New Strategies to Protect People from Smoke During Wildfires
Satellite measurements coupled with inexpensive air quality monitors could help protect humans from smoke particulates during wildfire events.
Aspiring Toward Healthy Cities in China
One of the authors of a new report on efforts to create healthy cities in China describes challenges and opportunities for urban health and healthcare.
Sea Level Rise Threatens Hundreds of Wastewater Treatment Plants
Untreated sewage could affect 5 times more people than direct flooding, a new study shows.
Satellites and Cell Phones Form a Cholera Early-Warning System
A new initiative combines satellite data with ground observations to assess and predict the risk of cholera outbreaks in Bangladesh’s vulnerable populations.
Alaska Spotlights Its Health Risks from Climate Change
In the only Arctic state in the United States, Alaskans have already been affected by health repercussions of warming. More and worse lie ahead, a new state health report says.
Exciting Section and Focus Group News
The American Geophysical Union announces new engagement pilots, simplified naming structure, and new GeoHealth section.