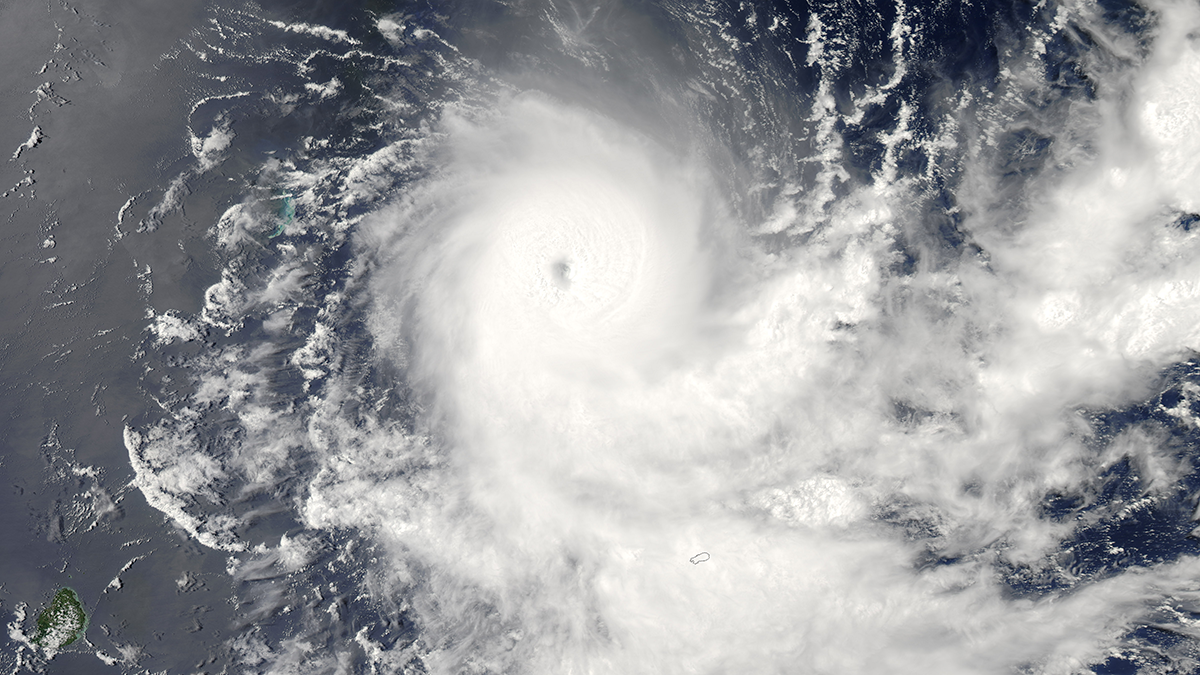
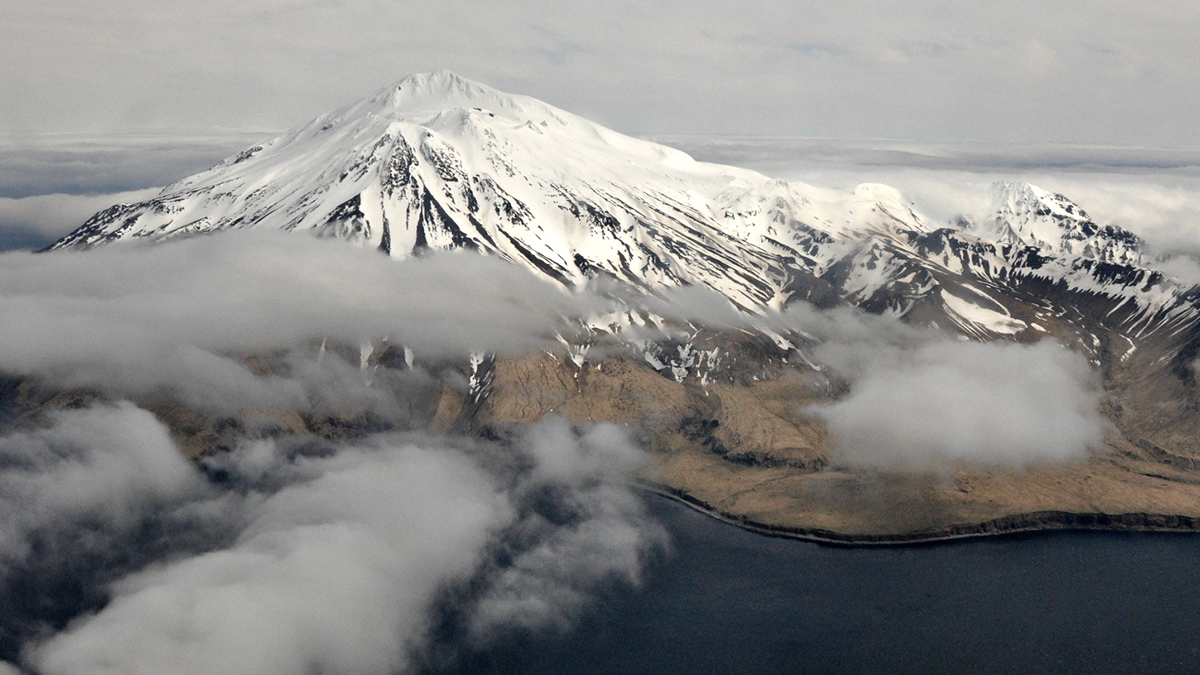
Tropopause temperature biases create major tropical cyclone differences in models; cooler air boosts storm potential intensity, raising global cyclone frequency and hurricanes in experiments.
Geophysical Research Letters
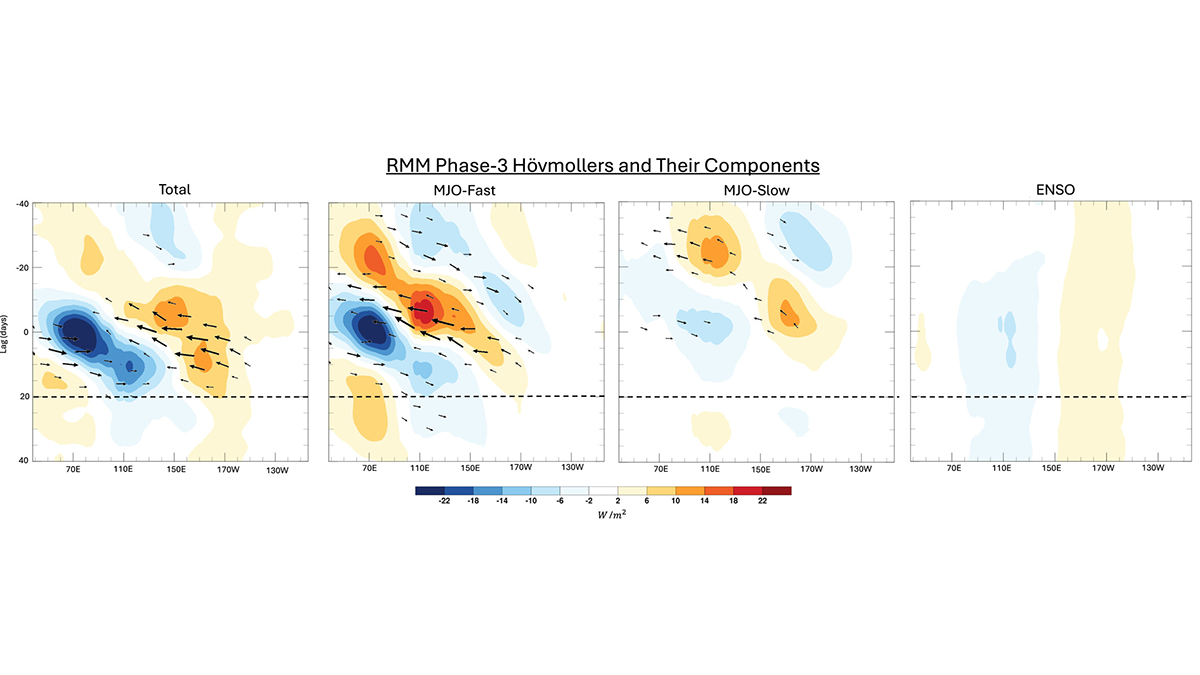
Slow and Fast Madden-Julian Oscillation Modes
The skill of Madden-Julian Oscillation (MJO) forecasts can be improved by identifying slow- and fast-MJO modes and their superposition.
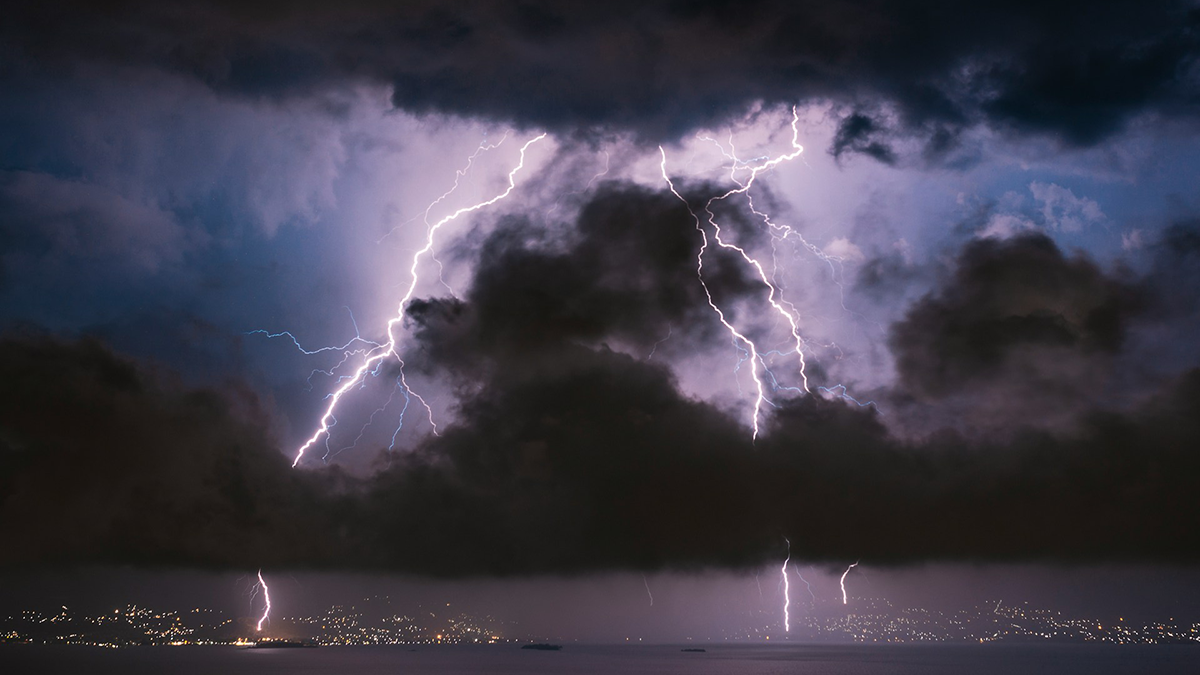
Why Are Thunderstorms More Intense Over Land Than Ocean?
A new perspective on convective instability sheds light on the factors controlling intensity in the rising motions that produce precipitation, and occasionally thunder and lightning, over land.
Where the Tianshan Will Break Next: Strain, Slip, and Seismic Hazard
Geodetic strain and slip deficits reveal where the Tianshan is storing stress and which faults may generate the next major earthquakes in the region.
Wintertime Spike in Oceanic Iron Levels Detected near Hawaii
Seasonal rainfall and runoff of sediments from the Hawaiian Islands could be responsible for the previously undetected peak.
Maybe That’s Not Liquid Water on Mars After All
A “very large roll” of a radar instrument offers new insight into a highly reflective area near the Martian south pole.
From Mantle Flow to River Flow: Shaping Earth’s Surface from Within
The convection of the Earth’s mantle shapes its surface, carving fault networks into the lithosphere that can guide the course of rivers.
Understanding Cloud Droplets Could Improve Climate Modeling
The microphysical structure of cloud droplets affects behavior like precipitation. Current models may be underestimating how much these structures can vary within a single cloud.
New Earthquake Model Goes Against the Grain
Subducting plates are stronger in certain directions than others, which may be a factor in how earthquakes occur and how seismic waves propagate.
Finding the Gap: Seismology Offers Slab Window Insights
Studying slow tremors has helped researchers home in on the youngest part of the Chile Triple Junction’s gap between subducting plates, which offers a window to the mantle.