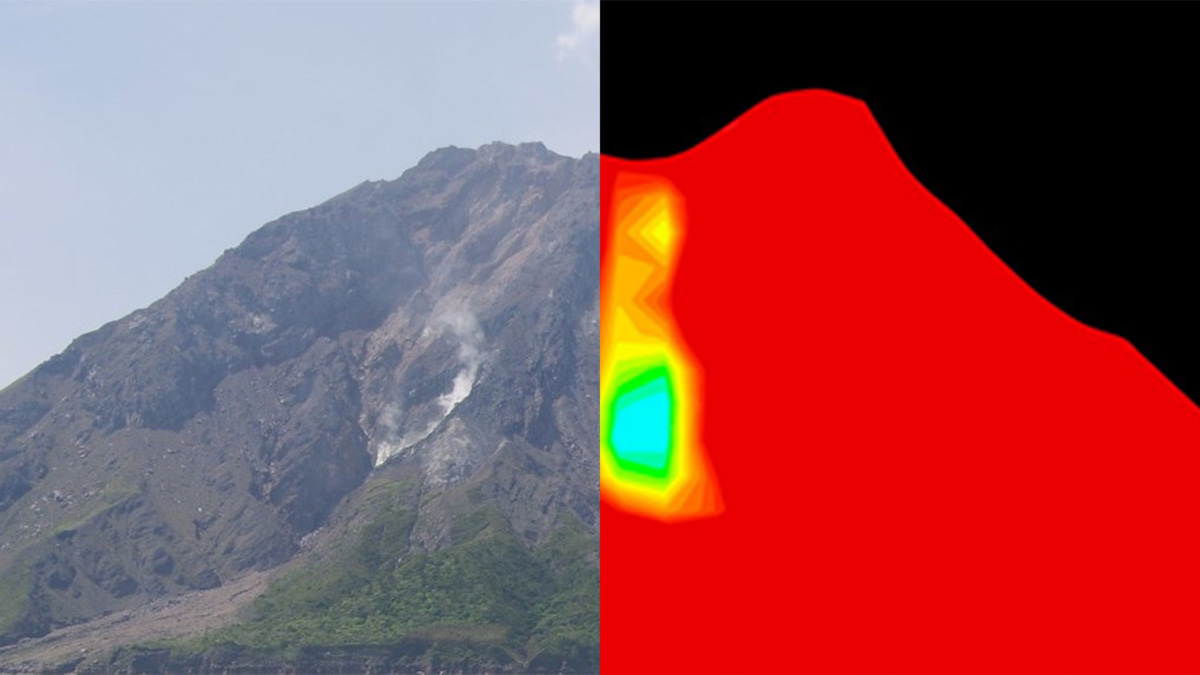
A new book describes muography, an imaging technique that can be used to visualize the internal density composition of geological structures.
imagery
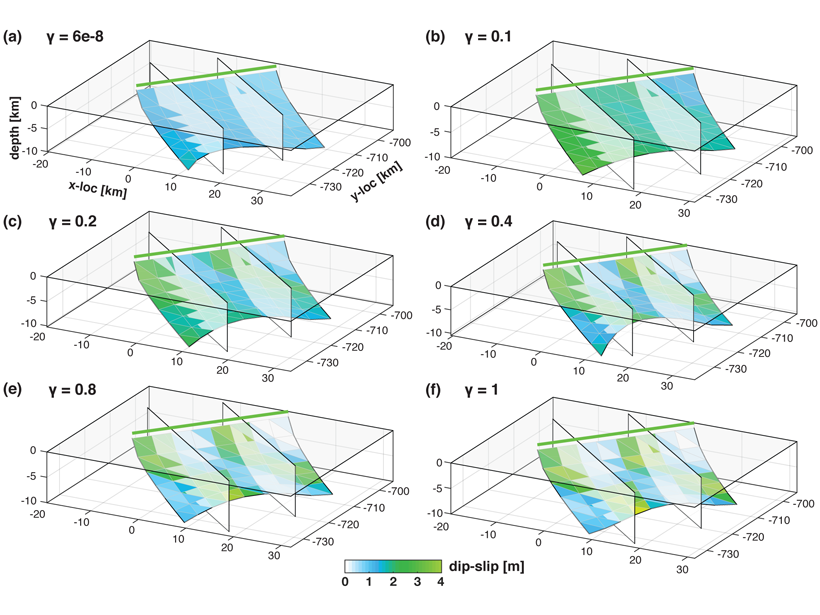
New Inversion Method Improves Earthquake Source Imaging
A new method uses Bayesian inference to jointly invert for non-planar fault geometry and spatially variable slip (with associated uncertainties) in earthquake source modeling, based on geodetic data.
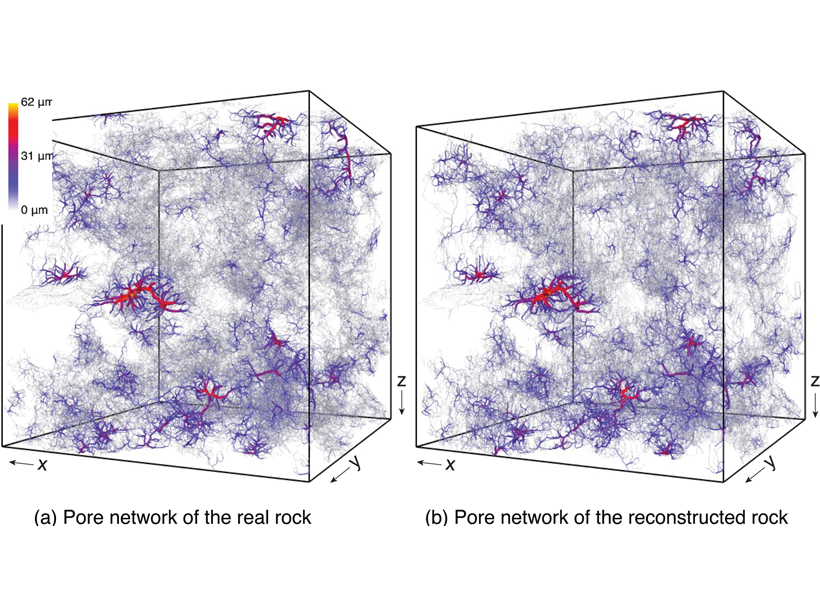
Reconstructing Rocks with Machine Learning
Machine learning can be used to accurately reconstruct high-resolution, 3D images of rocks from 2D cross-sections, which opens the door to more detailed simulations.
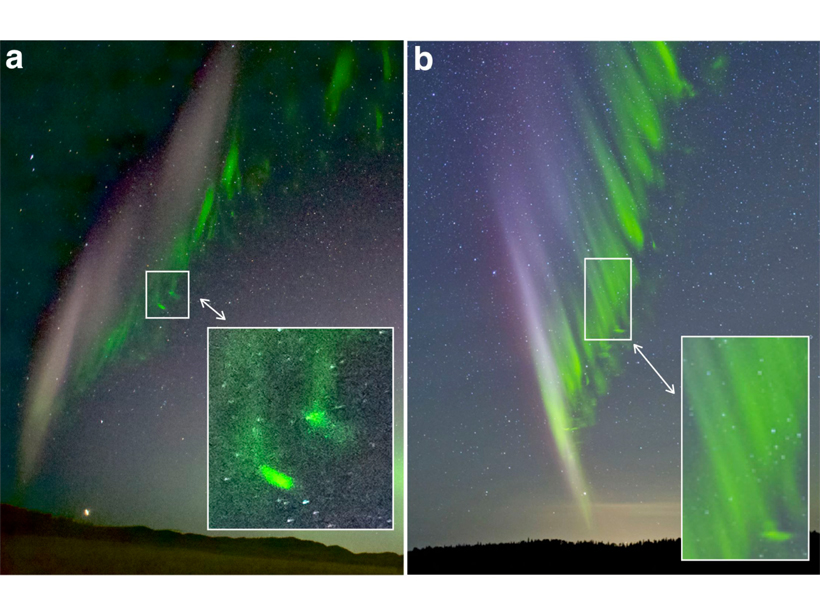
Citizen Scientists Observe Mysterious Green Streaks Below STEVE
Citizen scientists provided images of sub-auroral STEVE (Strong Thermal Emission Velocity Enhancements) showing fine-scale green features with narrow streaks propagating poleward toward STEVE.
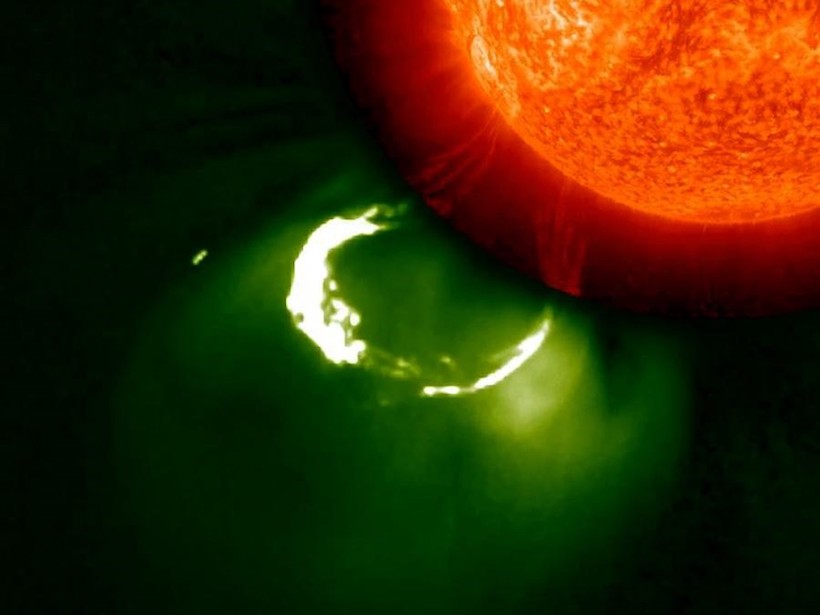
The “Complicated” Complexity of Solar Storms
Researchers turned to crowdsourced science to identify patterns in coronal mass ejections.
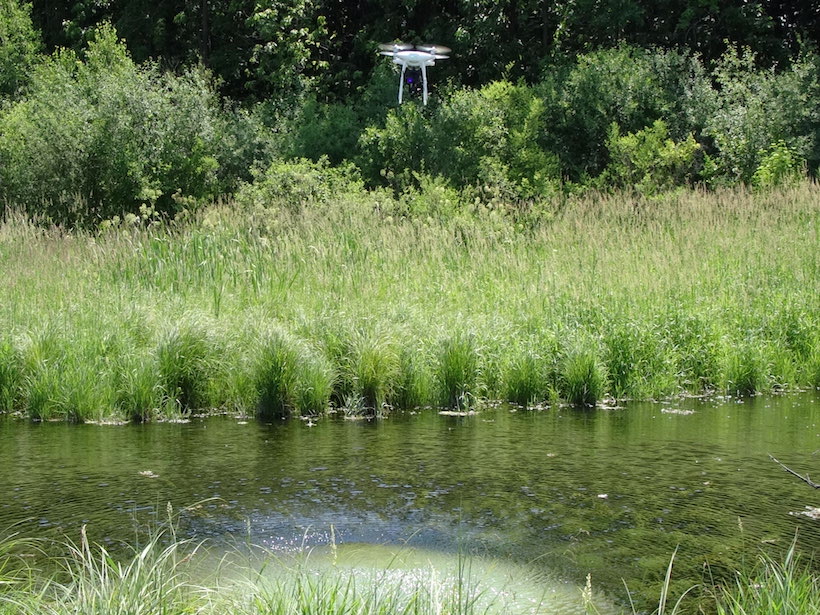
Taking an Aerial View Underground
Wisconsin geologists are testing using drones equipped with thermal cameras to measure shallow soil depths in areas prone to groundwater contamination.
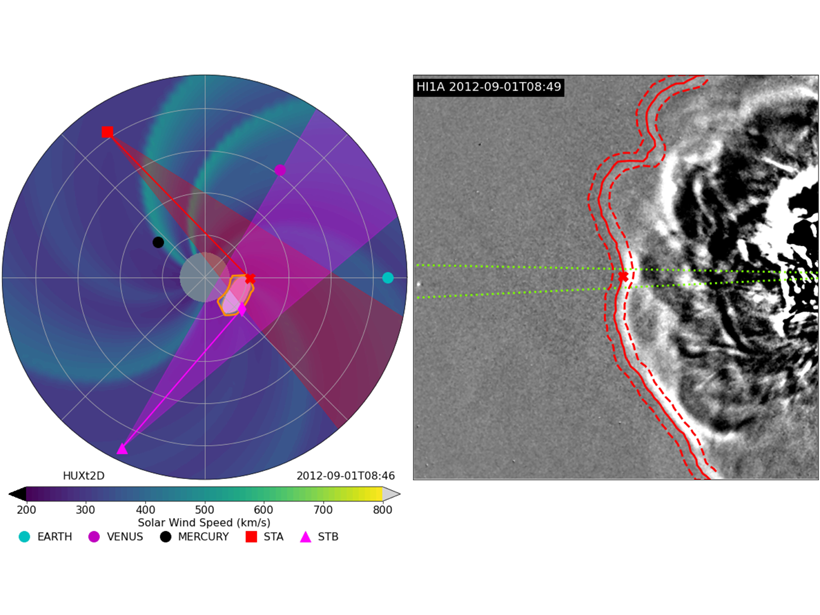
Ensemble Modeling of Coronal Mass Ejection Arrival at 1 AU
Heliospheric imaging data can be used in ensemble modeling of CME arrival time at Earth to improve space weather forecasts, treating the solar wind as a 1-D incompressible hydrodynamic flow.
World’s Deepest Freshwater Cave May Be a Kilometer Deep
The Czech Republic’s Hranice Abyss is more than twice as deep as researchers thought.
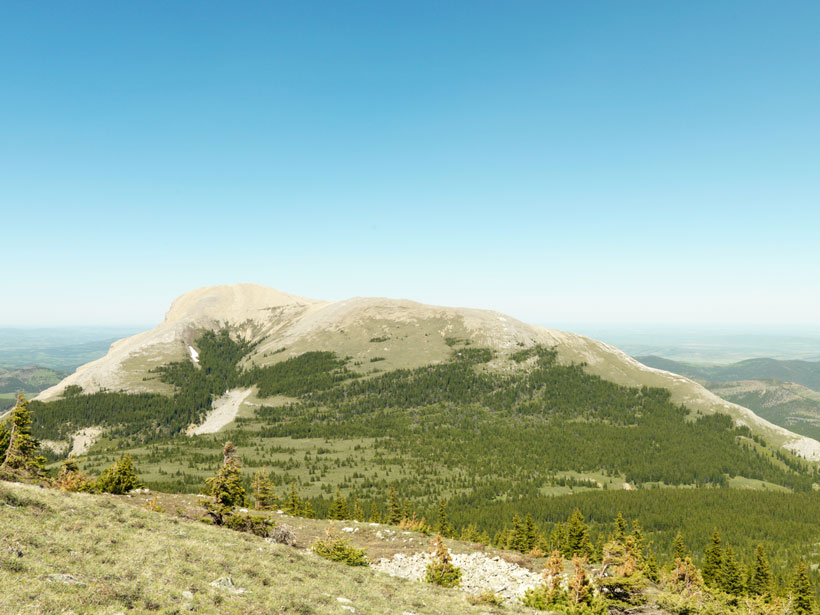
Canada’s Rocky Mountain Forests Are on the Move
Using century-old surveying photos, scientists have mapped 100 years of change in the Canadian Rockies to document the climate-altered landscape.
Imaging Seismic Sources
Waveform‐based location methods are being used to better characterize and understand seismic sources from the laboratory to the global scale.