El estratovolcán en el centro de México presenta un interesante caso de estudio sobre la percepción del riesgo, la comunicación de la ciencia y la preparación en torno a los peligros naturales.
Mexico
Forecasting Earthquake Ruptures from Slow Slip Evolution
A new generation of physics-based models that integrate temporal slip evolution over decades to seconds opens new possibilities for understanding how large subduction zone earthquakes occur.
El despertar del Popocatépetl: Transformando la vulcanología en México
La erupción del “Don Goyo” de 1994 en México central aceleró el interés académico en la vulcanología.
Five Key Needs for Addressing Flood Injustice
Better data and assessment metrics—and improved researcher involvement in communities—are needed to understand and redress inequitable vulnerabilities to and recoveries from flooding.
How Dangerous Is Mexico’s Popocatépetl? It Depends on Who You Ask
The stratovolcano in central Mexico presents a rich case study of risk perception, science communication, and preparedness surrounding natural hazards.
Popocatépetl’s Wake-Up Call: Transforming Volcanology in Mexico
The 1994 eruption of “Don Goyo” in central Mexico accelerated an academic interest in volcanology.
Researchers Develop Mexico’s First Comprehensive Greenhouse Gas Budget
A new study delves into 2 decades of data to create a comprehensive quantification of carbon, methane, and nitrous oxide sources and sinks that could help guide climate policy.
La extracción de agua subterránea está causando el hundimiento de la CDMX
Investigadores aseguran que saber cuánta agua está siendo extraída es crucial para resolver la crisis de infraestructura y de abastecimiento de agua en la capital.
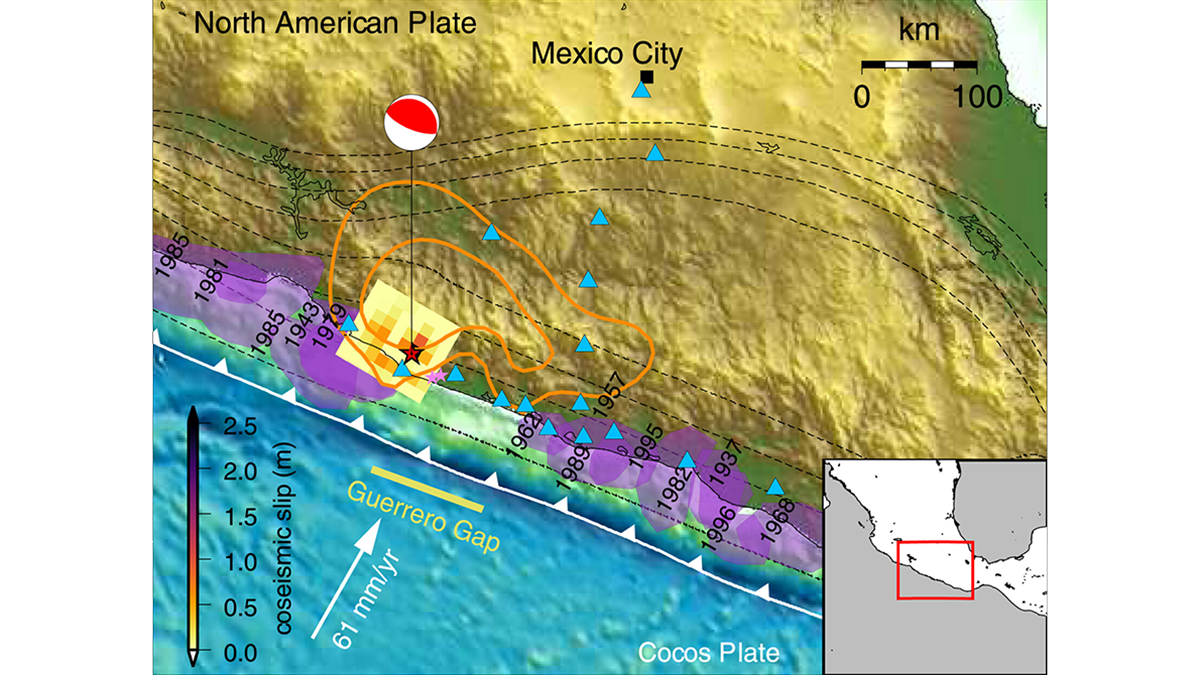
Talc May Make Mexico’s Subduction Zone More Slippery
Production of the weak, water-bearing mineral at the interface between the Cocos and North American Plates could contribute to the occurrence of poorly understood episodic tremor and slow slip.
Understanding an Extreme Weather Event with Science and Local Knowledge
Researchers in Mexico integrate science and community knowledge to assess the ecological and social impact of an extreme frost.