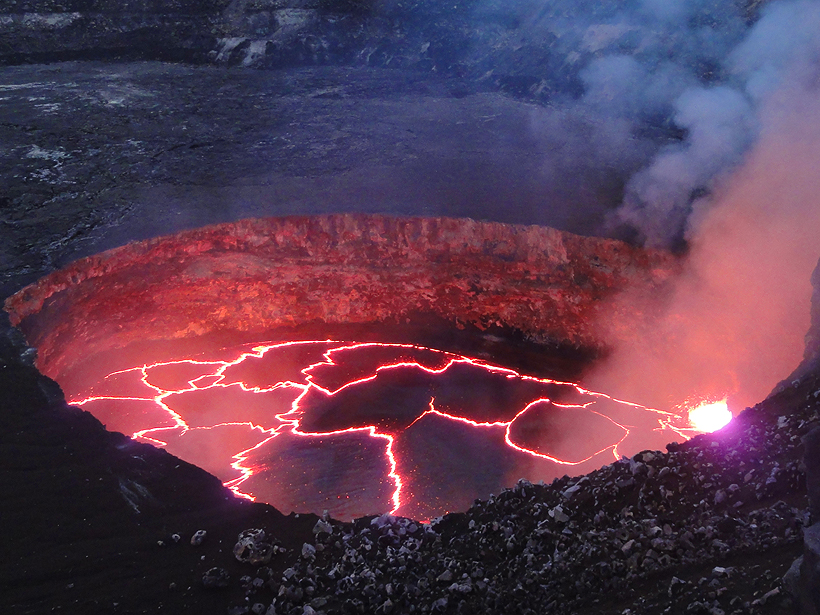
Geophysicists used unique seismic signatures to track the cyclic rise and fall of lava inside Hawai'i Volcanoes National Park's Overlook crater.
Modeling
Electric "Tornadoes" in Space Drive Disturbances Down to Earth
New simulations show how shocks in space can trigger vortexes in Earth's magnetic field, causing magnetic disturbances that are detectable from the ground.
Model of Solar Cycle's Impact on Climate Gets Upgrade
A new model of how the Sun's 11-year cycle affects climate leads to slight changes in model results on atmospheric chemistry, but temperature and wind results are consistent with the previous model.
Mercury's Magnetosphere Model Gets Retro Makeover
New observations from Mercury revive a once-abandoned model for its magnetic field, resulting in a new profile that better fits the data.
Cloud Overlap Observations Put Simulations to the Test
Fine-scale simulations of cumulus cloud layers could help improve weather and climate models.
Forecast Versus Reality: High-Resolution Weather Prediction
Researchers test the High-Resolution Rapid Refresh model with real-life observational data to evaluate forecast accuracy.
Low-Altitude Clouds Play an Important Role in a Changing Climate
Scientists uncover the mechanics behind tropical marine low cloud cover and its influence on models of anthropogenic climate change.
Improving Representation of Snow on Sea Ice in Climate Models
Snow on Sea Ice Workshop; Barrow, Alaska, 29 April to 1 May 2015
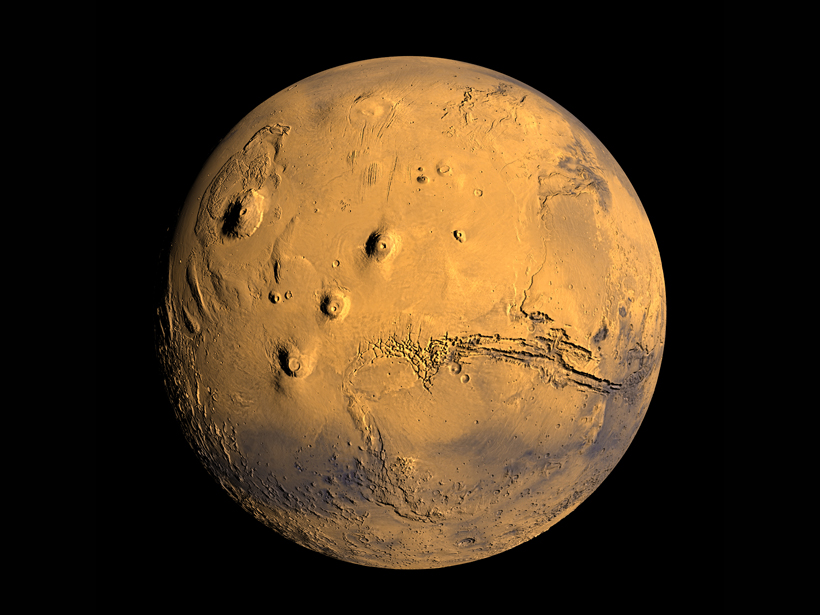
3-D Models Put Scientists, Students in Touch with Planets
Three-dimensional printing gives planetary scientists new ways to explore distant worlds and engage students.
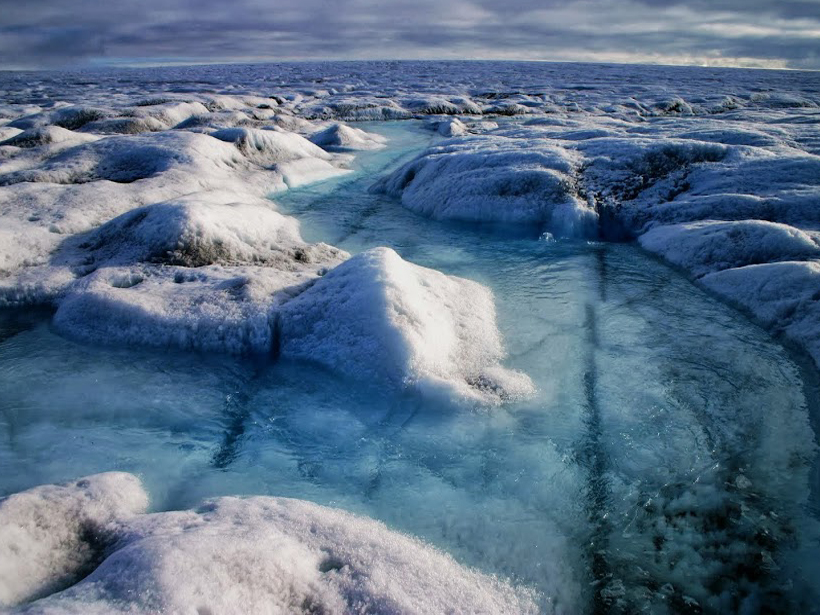
Sea Level Rise Due to Warming, Weakening of Greenland Glaciers
Increasing ice temperatures and decreasing ice viscosities could lead to "thermal-viscous collapse" of the Greenland ice sheet, raising sea levels as much as 51 centimeters over the next 500 years.