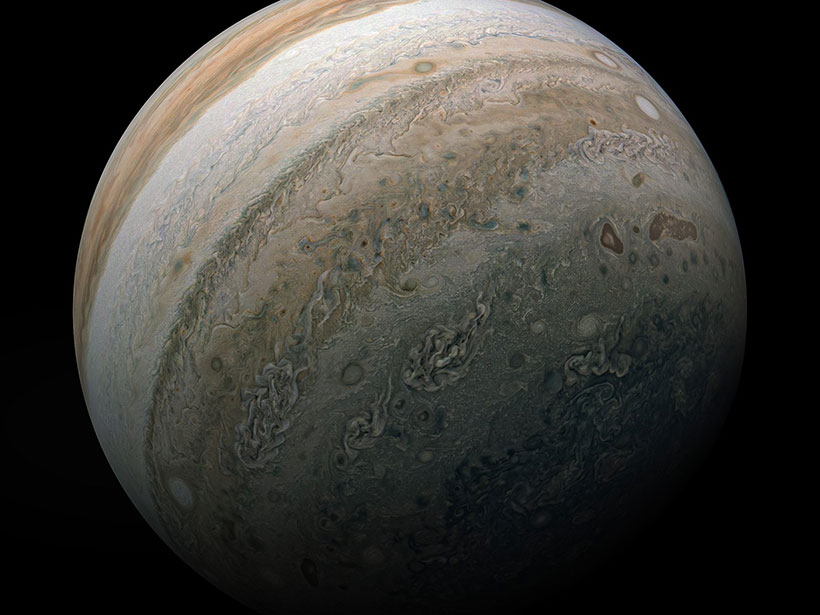
Updating a model developed during the Voyager flybys will enable better mission planning and a deeper understanding of Juno data.
Modeling
New Insights into Uncertainties About Earth’s Rising Temperature
A comparison of climate models finds that much of the variation in their predictions of global warming arises from differences in how they simulate the response of convective processes to warming.
Torrential Rains and Poor Forecasts Sink Panama’s Infrastructure
Scientists are working to improve the forecasting of heavy rains in Panama following several events over the past decade that caused substantial flooding and damage.
Modeling the Cascading Infrastructure Impacts of Climate Change
New research highlights how interdependences among infrastructure systems like roads can complicate climate adaptation.
A New Way to Fingerprint Drivers of Water Cycle Change
Simulations of tropical ocean convection help distinguish climate effects resulting from large-scale changes in atmospheric circulation from those resulting from higher temperatures.
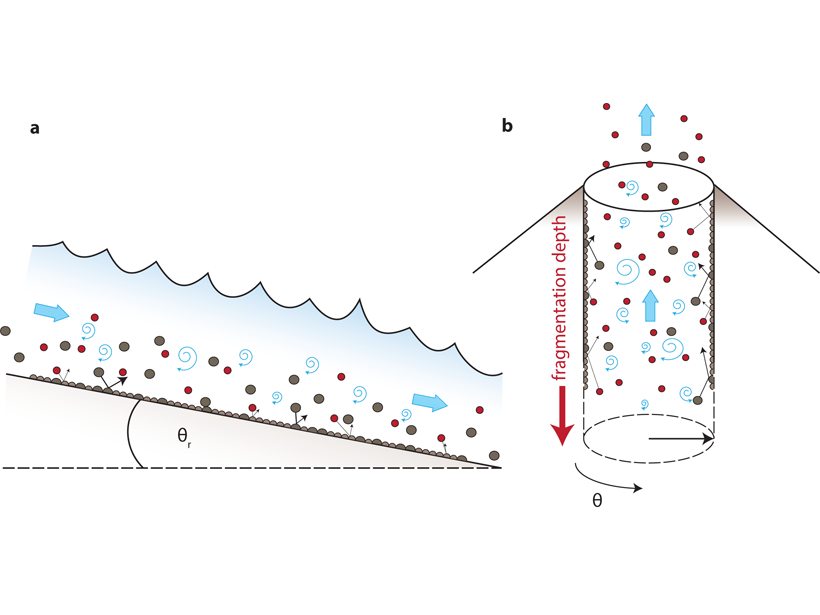
Eruption Seismic Tremor Modeled as a Fluvial Process
Impact and turbulence models for river tremor are adapted and combined into a model that predicts the amplitude and frequency content of volcanic eruption tremor.
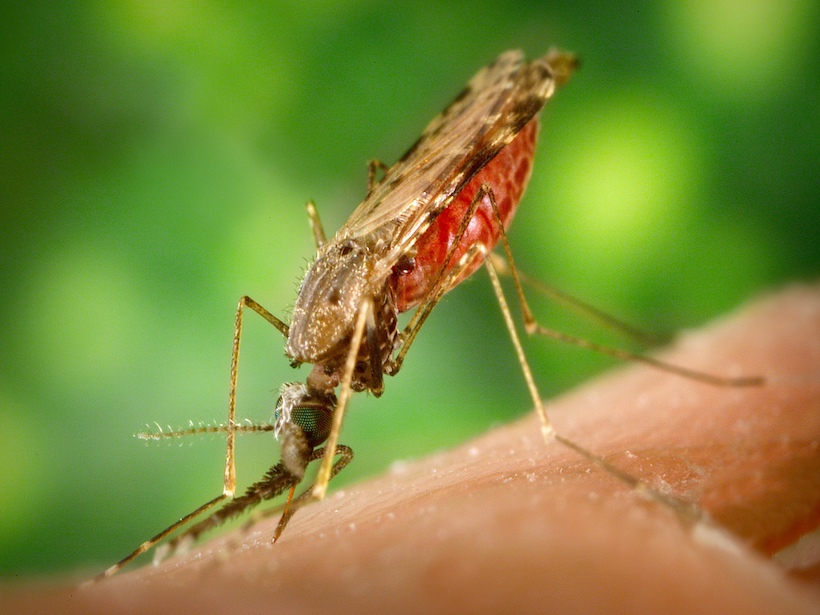
Hydrology Helps Identify Future Malaria Hot Spots
Complex hydrological processes—not just the amount of rainfall—help determine where malaria-transmitting mosquitoes can thrive.
Experimenting with Underwater Sediment Slides
Sediment-laden currents caused by breaching flow slides are hazardous to flood defenses and seabed infrastructure. New research shows that these phenomena must be accounted for in erosion simulations.
Scientists Claim a More Accurate Method of Predicting Solar Flares
Supercomputer 3D modeling of magnetic fields could help mitigate damage from geomagnetic storms.
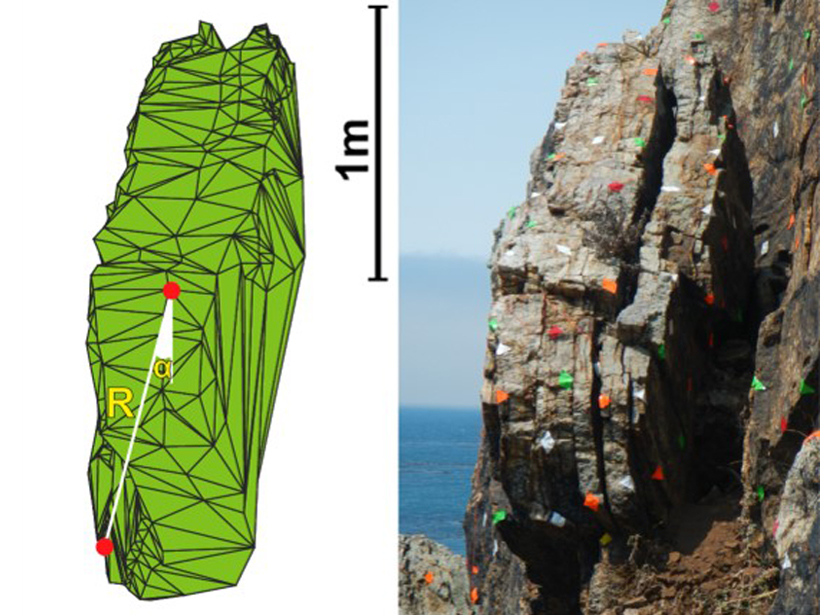
Earthquake Hazard Hanging in the Balance
Earthquake hazard calculations for California’s coast are refined with a view of precariously balanced rocks that would have fallen if the largest predicted shaking happened in the past 20,000 years.