A new model determines freshwater and dissolved organic carbon discharge to the Gulf of Alaska from one of the most geographically diverse but understudied regions on the planet.
Modeling
Deep Decarbonization? Yes We Can!
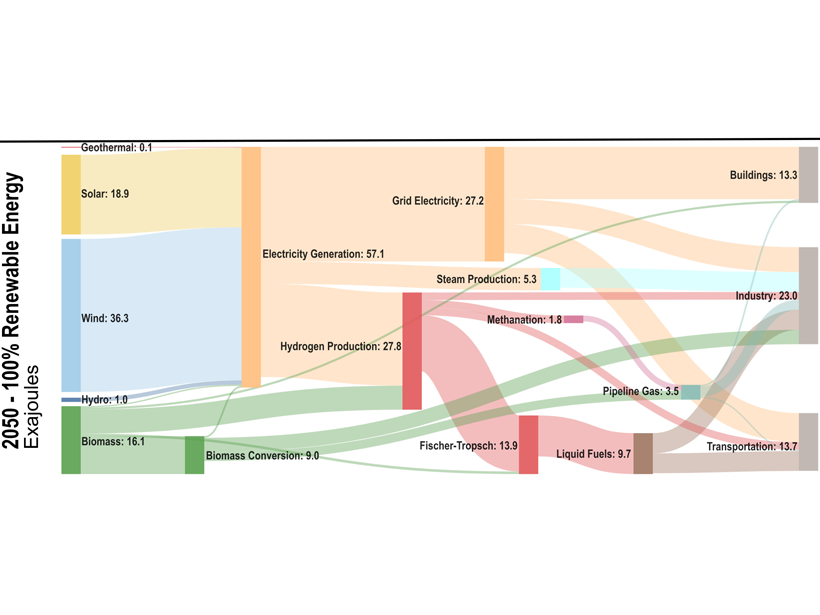
Modeling the U.S. energy system demonstrates several pathways to net-zero CO2 emissions by 2050. The pathway with the lowest cost, 0.2–1.2% of GDP, relies on >80% contribution of renewables.
Modeling Earth’s Ever-Shifting Magnetism
The World Magnetic Model, updated every 5 years through an international collaboration, supports numerous technologies that help us find our way.
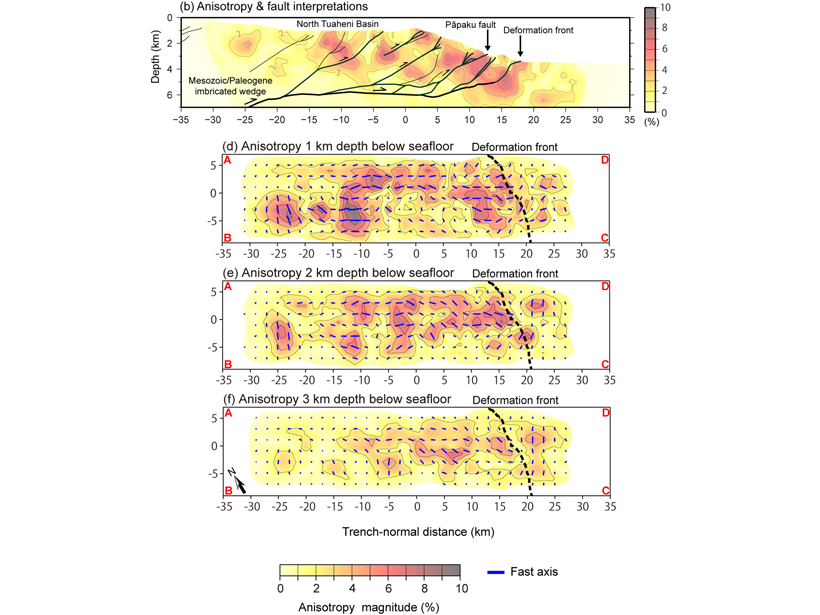
Fault Related Anisotropy in the Hikurangi Subduction Zone
A new study provides the first high-resolution three-dimensional anisotropic P-wave velocity model of the shallow part of the Northern Hikurangi subduction zone offshore New Zealand.
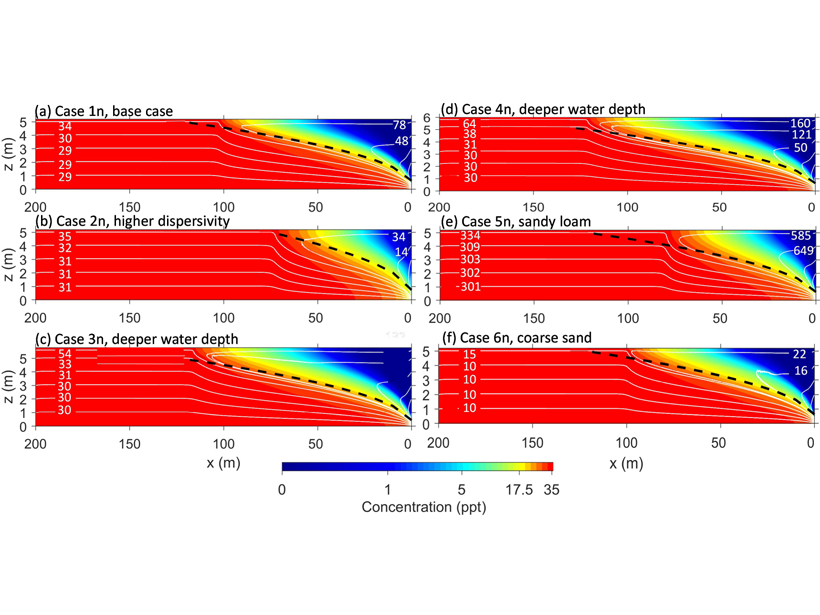
Freshened Groundwater in the Sub-seafloor
Scientists are using a variety of geochemical, geophysical, and numerical methods to study offshore freshened groundwater and better understand its role in the global water cycle.
To Make Better Hurricane Models, Consider Air Pollution
New research uses Hurricane Harvey as a case study to demonstrate the devastating power of aerosols to supercharge tropical storms.
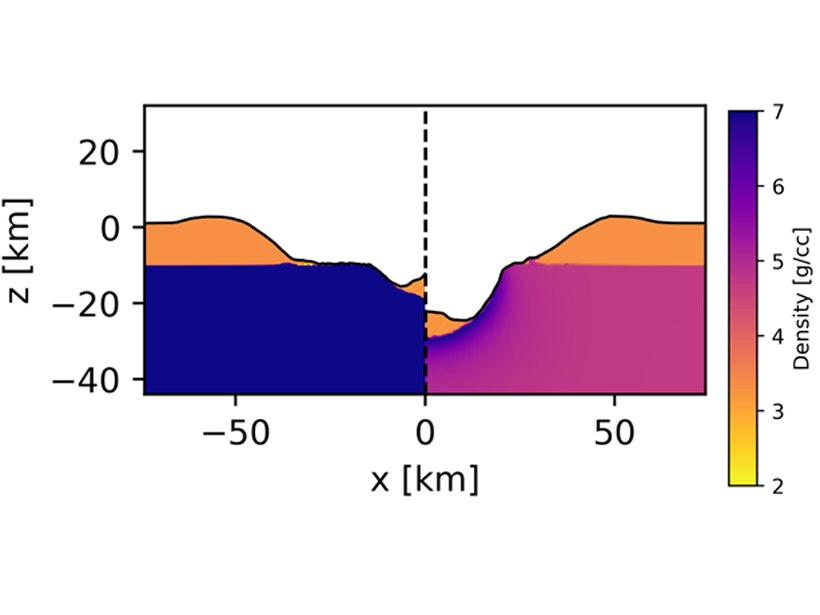
Predicting the Unique Shape of Craters on Asteroid (16) Psyche
Models link the variety of crater shapes expected on (16) Psyche with the interior structure of this unique asteroid, in preparation for the arrival of the Psyche probe in 2026.
The Debate over the United Nations’ Energy Emissions Projections
A new study finds the economic factor driving the divergence between emissions trajectories in climate assessments and reality.
Geologists to Shed Light on the Mantle with 3D Model
The model, which will incorporate 227 million surface wave measurements, could help with everything from earthquake characterization to neutrino geosciences.
Evaporation Reverses Groundwater Flow and Forms Hyper-Salinity
A numerical model of groundwater-surface water systems shows how floodplain evaporation can reverse stream-groundwater flow and produce strong buoyancy changes associated with salinity.