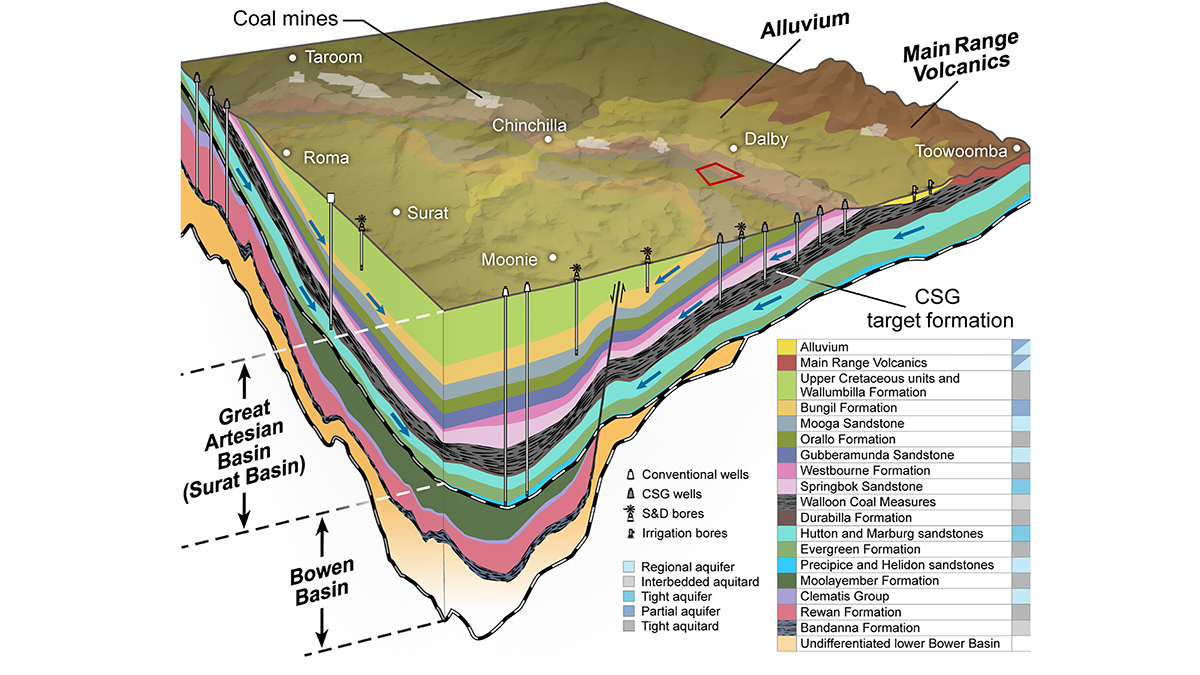
A new model shows how coal seam gas extraction causes land to sink by linking groundwater loss and coal shrinkage, helping predict impacts on farming in gas-producing areas.
Modeling
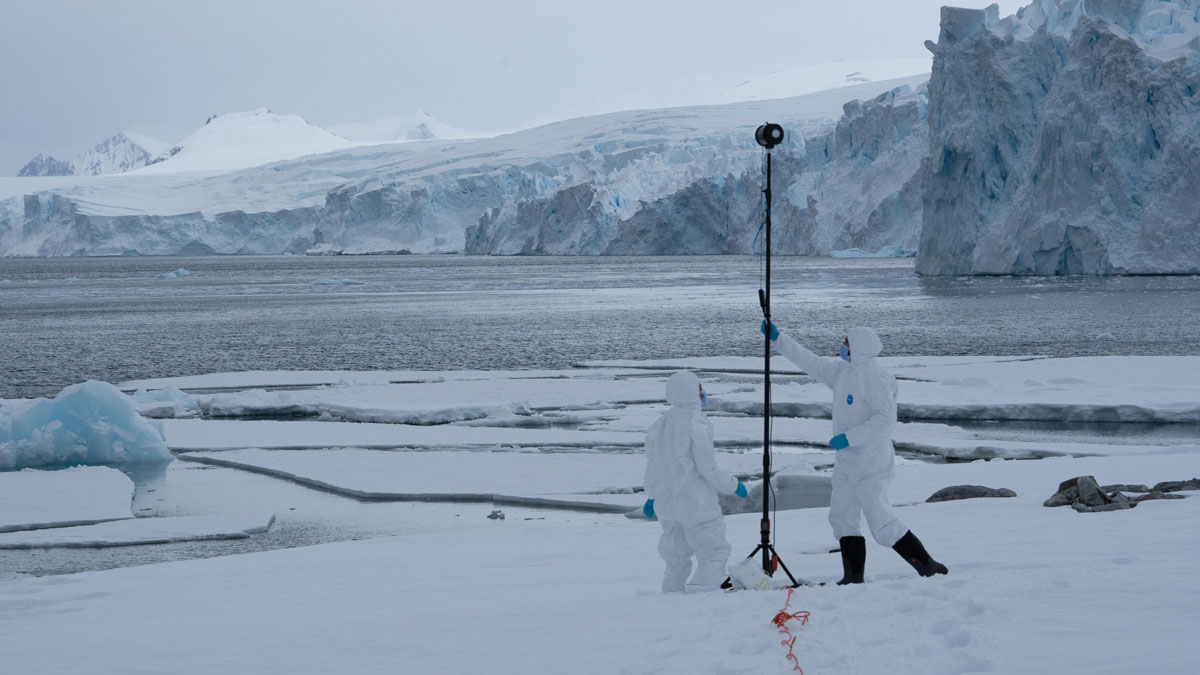
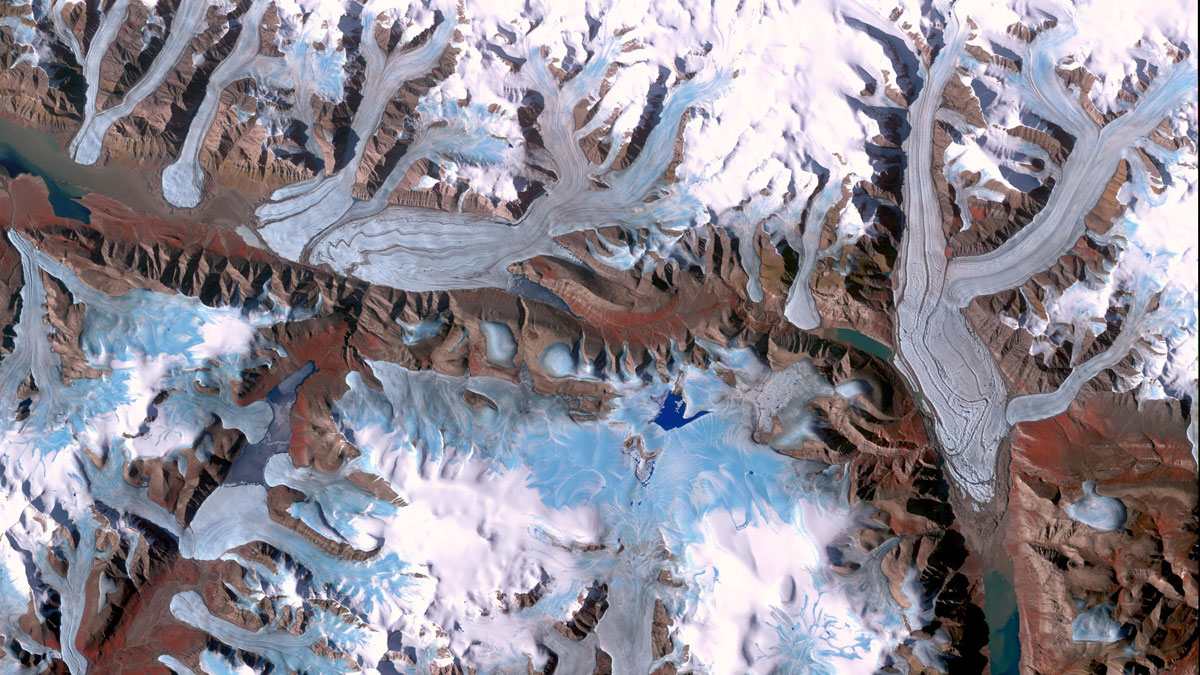
Glacier Monitoring from Space Is Crucial, and at Risk
A new community effort shows that Earth has lost 5% of its global glacier mass since 2000. The work highlights the necessity of spaceborne glacier observations and upcoming gaps in long-term monitoring.
Can Microorganisms Thrive in Earth’s Atmosphere, or Do They Simply Survive There?
A bottom-up modeling approach could bring scientists closer to understanding communities of microbes in the atmosphere.
Warming Winters Sabotage Trees’ Carbon Uptake
In temperate forests, the biomass-building benefits of warmer growing seasons are offset by damaging variability in winter weather—a disparity that climate models may miss.
Lucia Perez Diaz: Expressing Earth with Art
A geoscientist and illustrator finds artistic inspiration in plate tectonics and geodynamics.
Jeff Massey: Atmospheric Science Meets the Private Sector
Expertise in weather modeling has applications in business, this atmospheric scientist found.
Getting Schooled in Complex Earth System Modeling
Training schools focused on modeling solid Earth responses to ice mass changes offer lessons on how early-career scientists can build professional networks and learn skills to solve complex problems.
New Insights into How Rocks Behave Under Stress
New 3D imaging techniques show hidden patterns of stress that help explain how and why rocks break.
Groundwater Pollution in Karst Regions: Toward Better Models
New advances in modeling contaminant transport offer a clearer picture of how to protect karst aquifers.
Abrupt Climate Shifts Likely as Global Temperatures Keep Rising
A computer vision technique modified to scan climate model data is helping scientists predict where and when rapid climatic shifts will happen in the future.