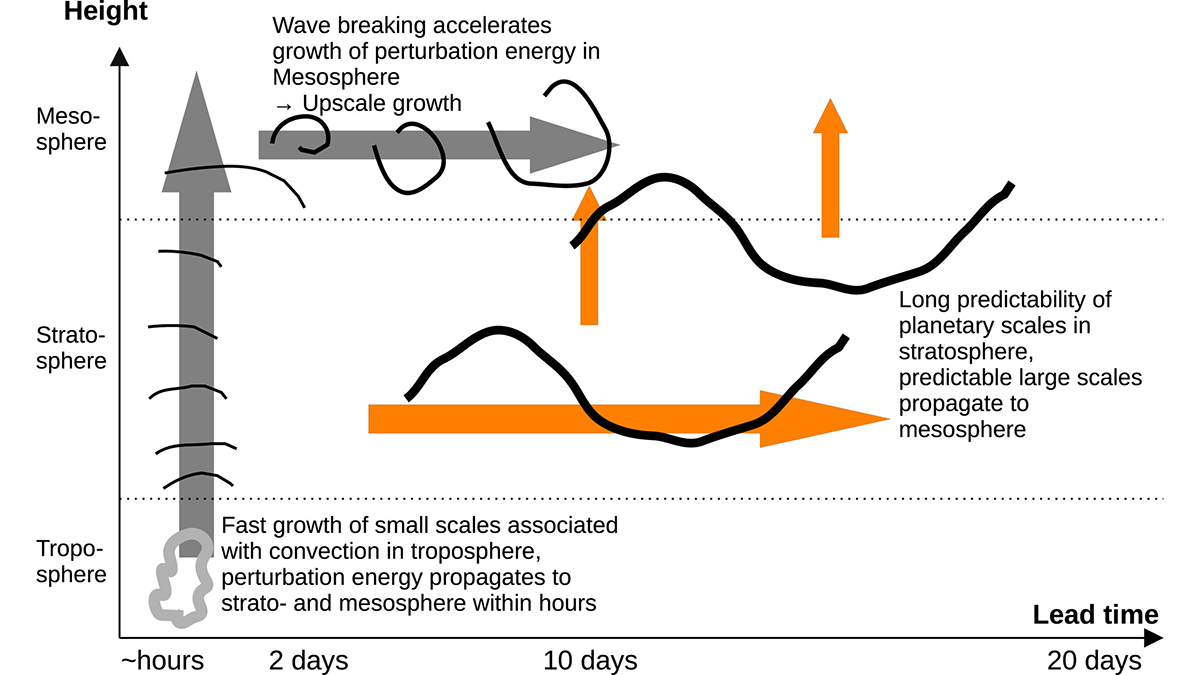
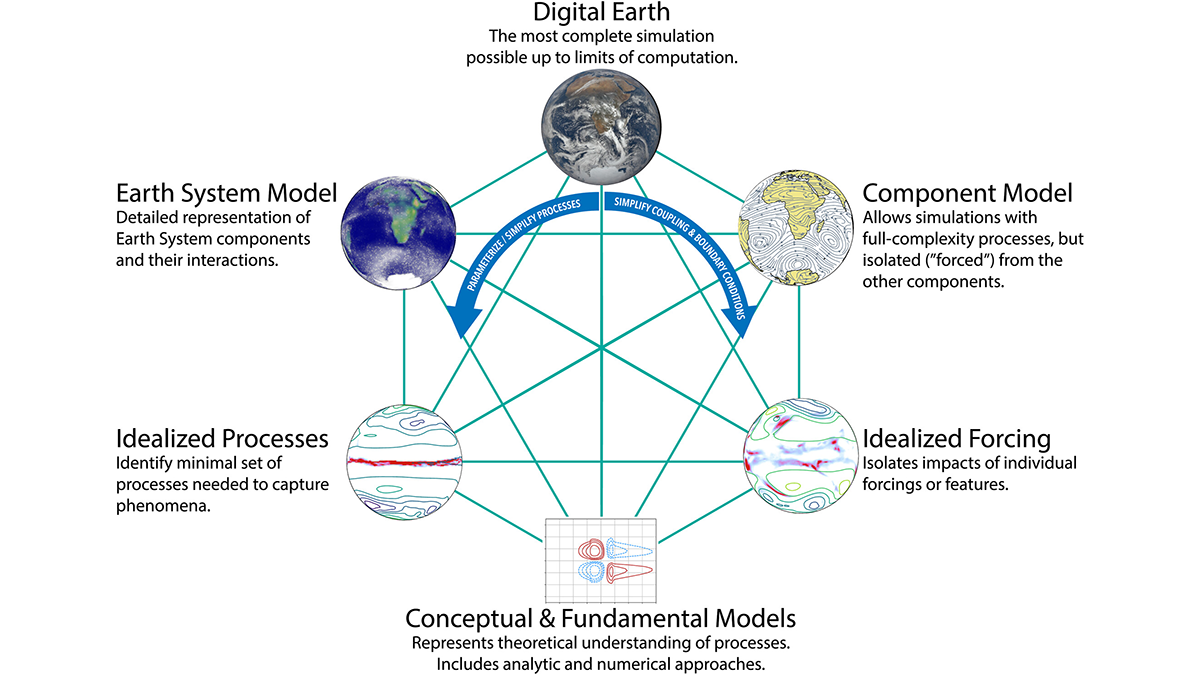
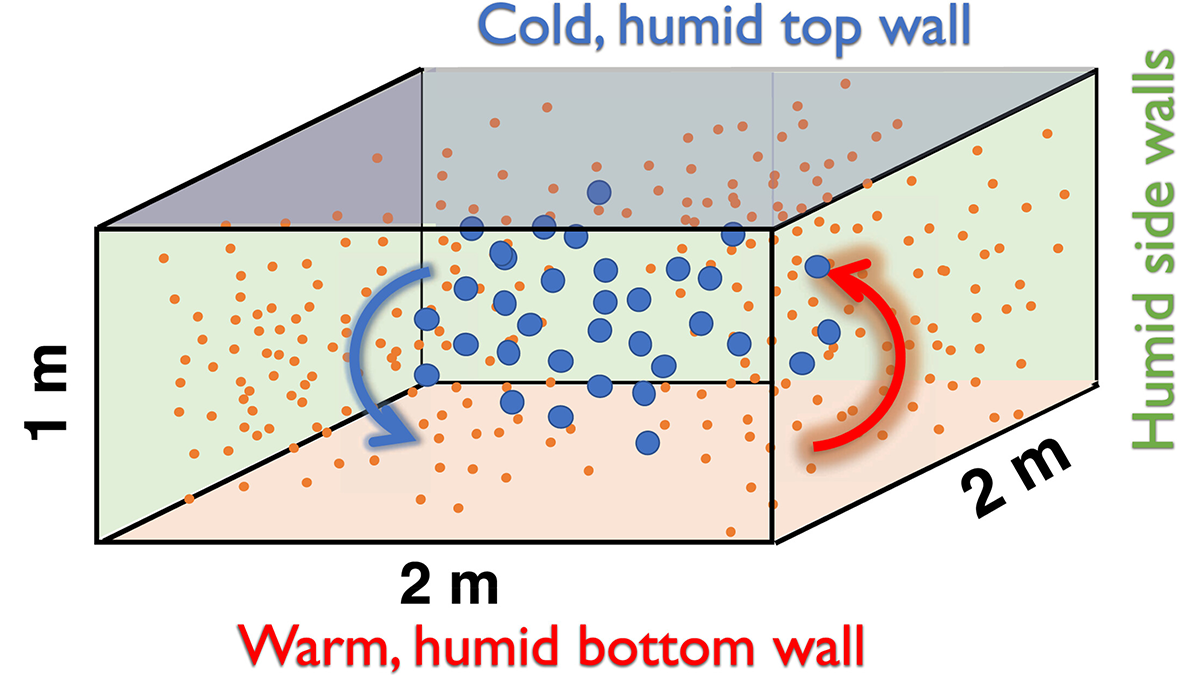
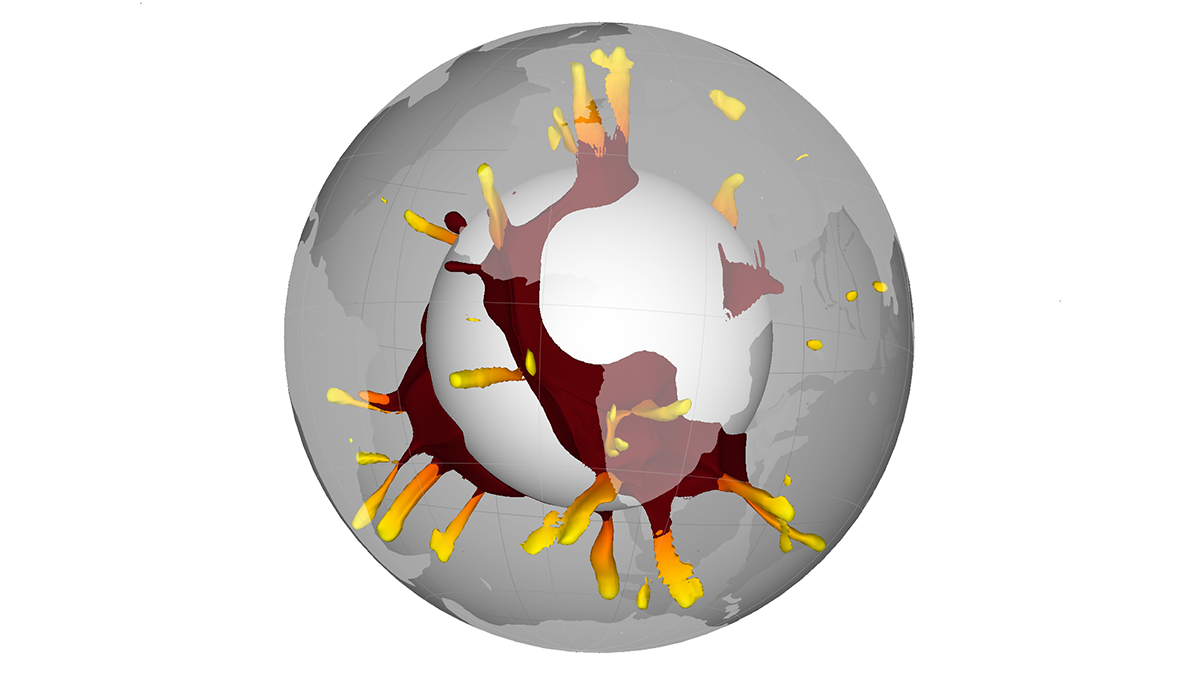
A new high-resolution global model is used to study predictability of atmospheric circulation from the surface to 120 kilometers.
Modeling
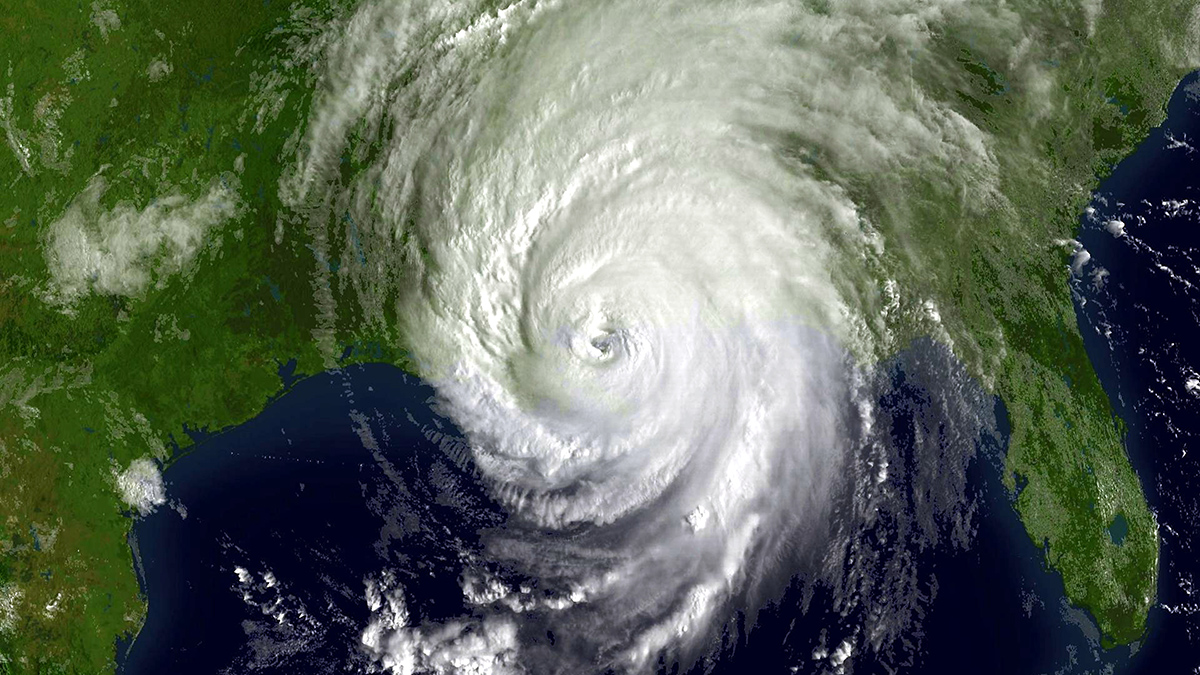
How Researchers Have Studied the Where, When, and Eye of Hurricanes Since Katrina
Twenty years after one of the country’s deadliest storms, scientists reflect on improvements in the ability to understand and predict disasters.
As Simple as Possible: The Importance of Idealized Climate Models
As models that simulate Earth’s climate system become increasingly complex, the use of simpler and more flexible idealized models remains important for science and education.
Machine Learning Simulates 1,000 Years of Climate
The Deep Learning Earth System Model is competitive with CMIP6 models and uses less computational power.
From Aerosols to Clouds: Testing Models with a Convection Cloud Chamber
Researchers benchmark seven cloud models against cloud chamber measurements to reveal how well models capture aerosol-cloud-turbulence interactions and where models still diverge.
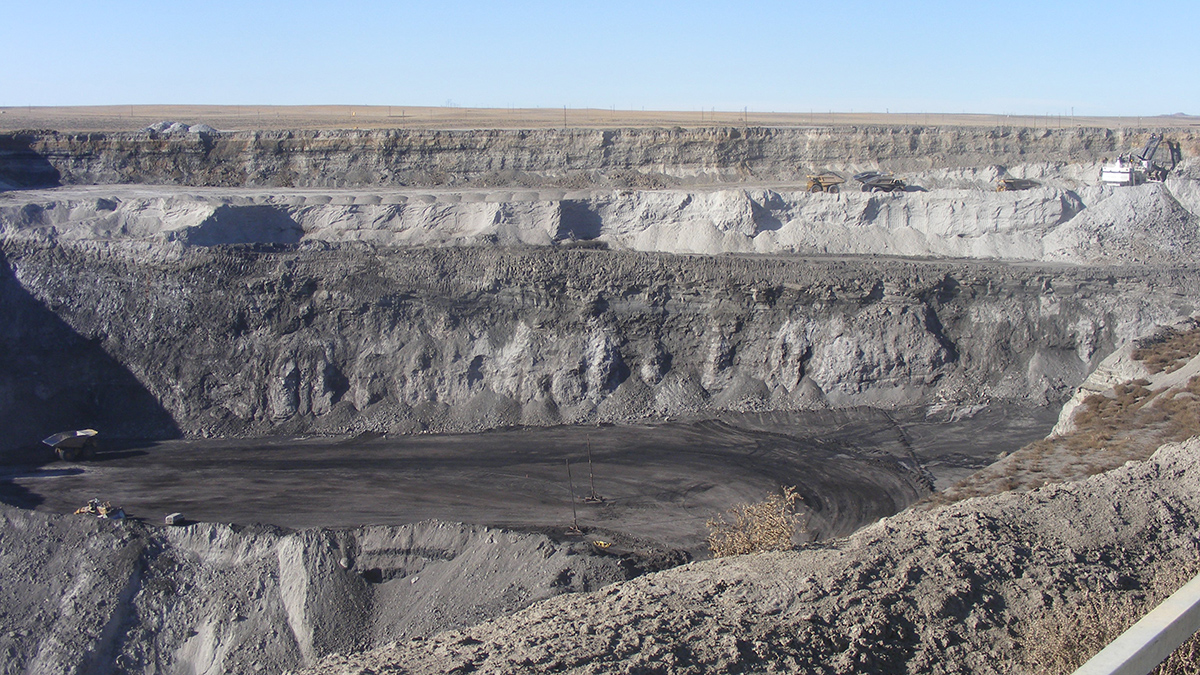
By 2051, Emissions from Coal Mining on Federal Lands Could Drop by 86%
Researchers predict that if early 2024 policies hold, emissions related to coal’s extraction, transportation, and combustion will drop over the next 25 years.
Blame It on the BLOBs
For decades, scientists have suspected that large volcanic eruptions have their origins in two mysterious massive regions at the base of our planet’s mantle. Now, it’s been statistically proven.
Arctic Ice Shelf Theory Challenged by Ancient Algae
Chemical signatures of marine organisms reveal that seasonal sea ice, not a massive ice shelf, persisted in the southern Arctic Ocean for 750,000 years.
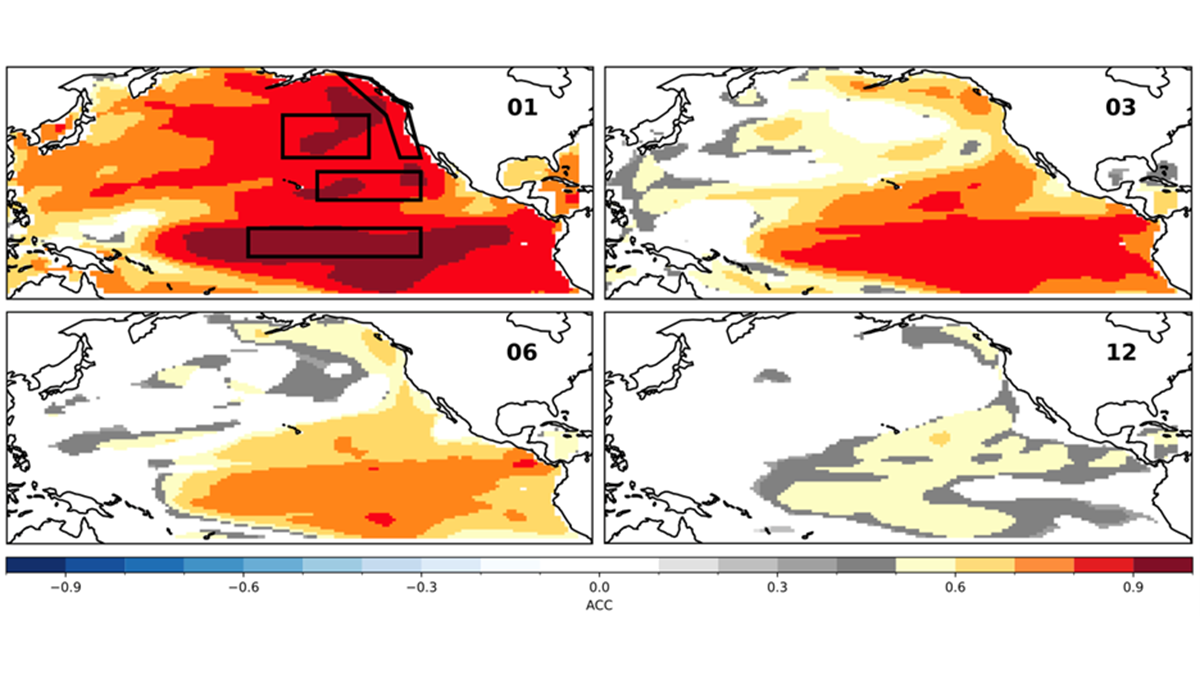
Decadal Forecasts with a SMYLE
Scientists use a large suite of simulations with an established climate model to predict the Pacific Decadal Oscillation up to one year in advance, but El Niño can still get in the way.
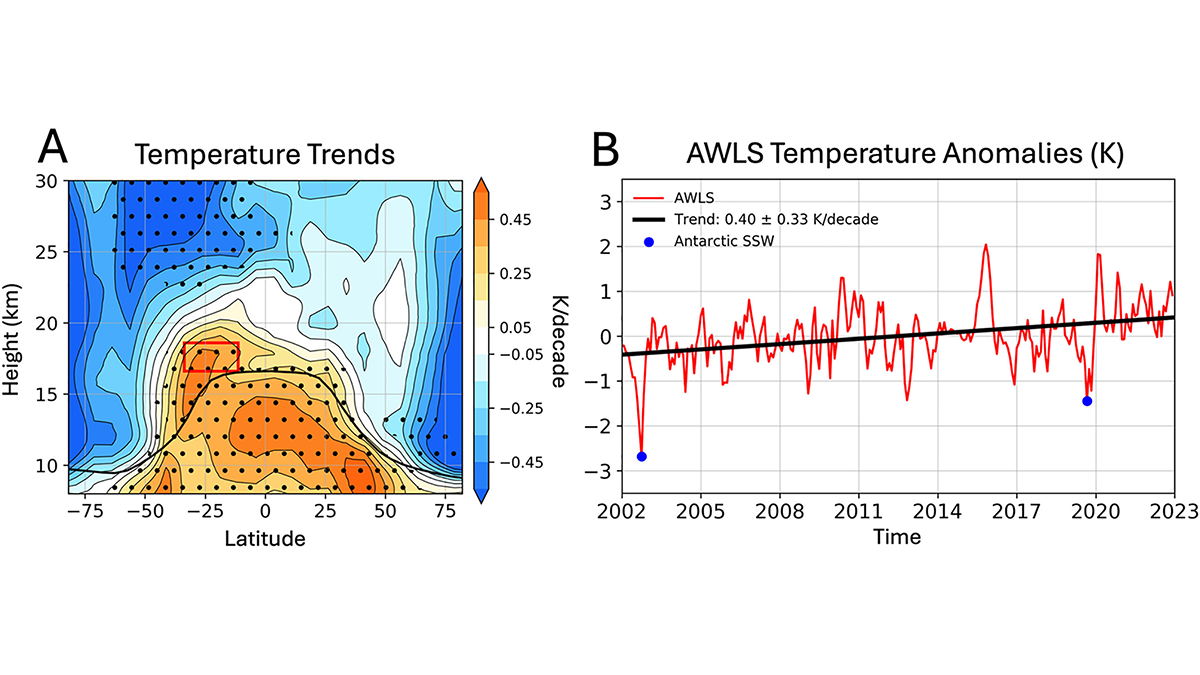
Southern Hemisphere Subtropical Lower Stratosphere is Warming
Warming of the Southern Hemisphere (SH) subtropical lower stratosphere is due to slowing of Brewer-Dobson Circulation, thus cooling the Antarctic lower stratosphere and masking anticipated ozone recovery.