The chemical composition of orogenic igneous rocks and their zircons is sensitive to crustal thickness and can be used to quantify the evolution of Moho depths beneath continents back in time.
plate tectonics
Probing the Sedimentology of a Continental Megathrust
Detailed analysis of sediments covering the Main Frontal Thrust in Nepal show how climate-driven baselevel changes affect sedimentation and should be considered when inferring thrust activity.
Months of Gravity Changes Preceded the Tōhoku Earthquake
Using GRACE satellite data, researchers discovered anomalous gravimetric signals that occurred before a seismic event that started deep within Earth.
Uncovering the Formation of the Western Nepal Embayment
Using thermokinematics, researchers have found that crustal accretion along the megathrust at mid-lower crustal depths shapes plateau growth and regional drainage development.
Earth’s Lower Mantle Is Drier Than Previously Thought
Scientists have long known that the two layers of Earth’s mantle have different chemical compositions. Now, modeling shows that different water concentrations may keep them from mixing.
Stretching Crust Explains Earth’s 170,000-Year-Long Heat Wave
During a brief period in Earth’s past, a massive emission of carbon abruptly raised global temperatures, acidified oceans, and stamped out species. New data may help explain how it happened.
Vashan Wright: A Champion for DEI in the Geosciences
While studying tectonic plates and sand, Wright works on a program to make the geosciences more equitable.
Zircons and Plate Tectonics
New data on ancient zircons points to a transition from stagnant lid to subduction style tectonics at 3.6 Ga ago.
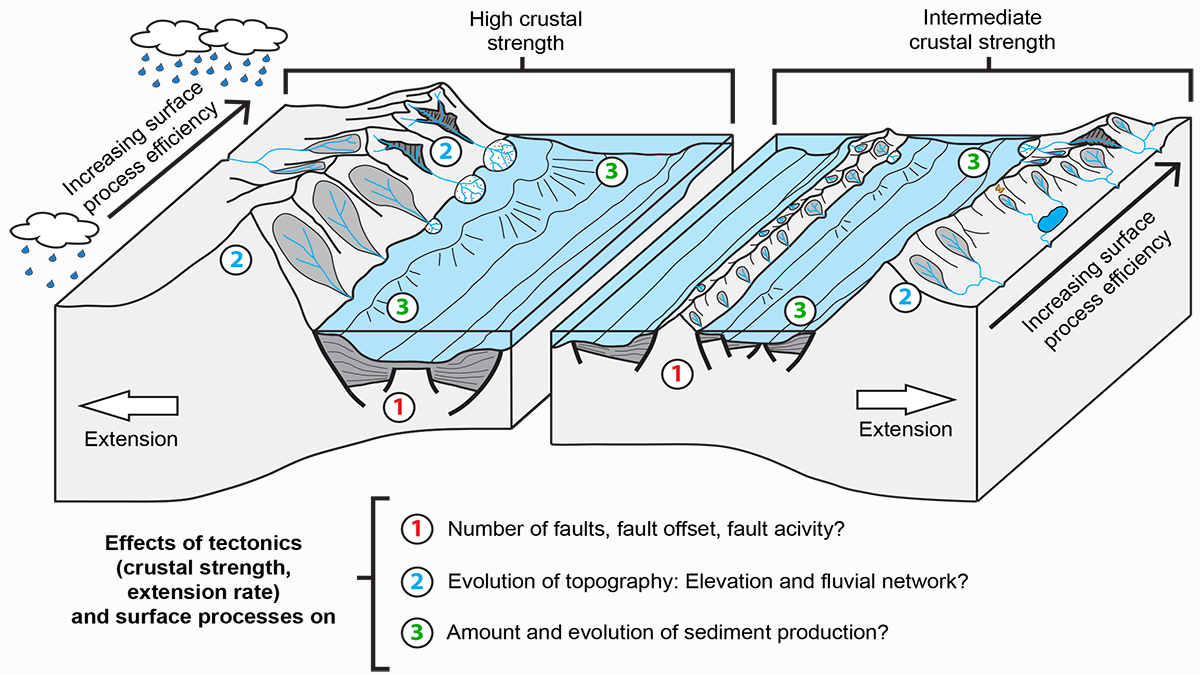
The Lost Topography Around Continental Rifts
Numerical models provide quantitative constraints on topography lost to erosion, showing how the sediment influx in a sedimentary basin reflects its tectonic and topographic evolution.
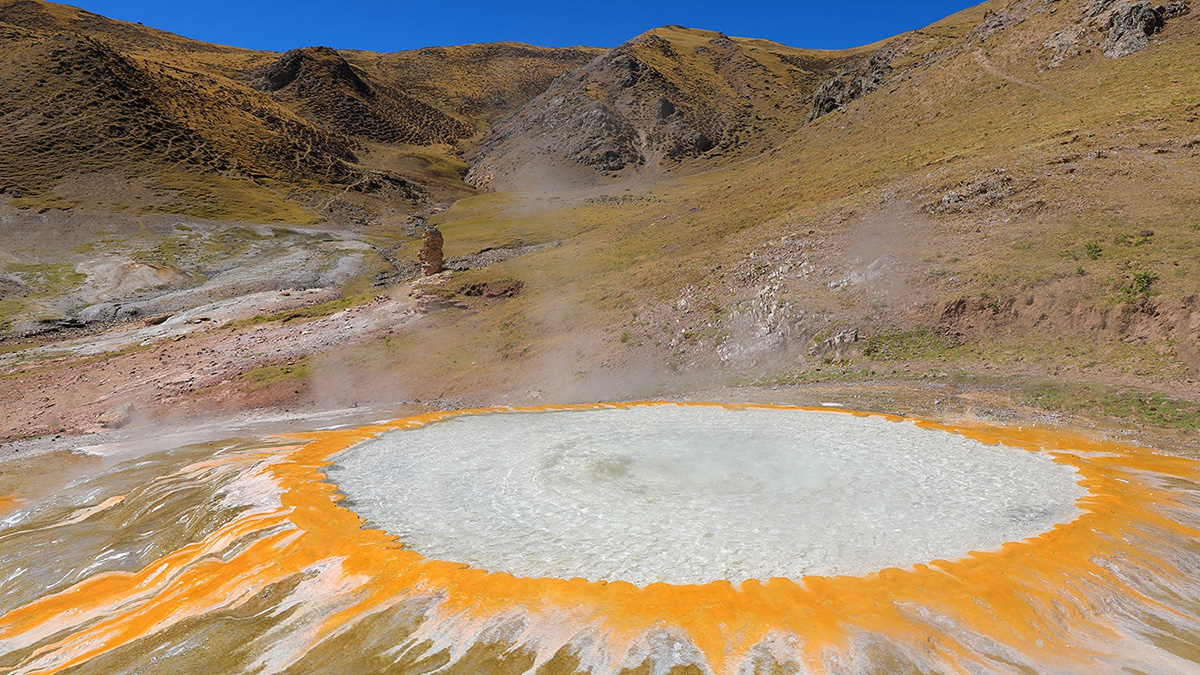
Hot Springs Suggest How the Tibetan Plateau Became the Roof of the World
Helium isotopes found in water samples provide a snapshot of what lies beneath the plateau and stimulate debate within the geosciences community.