Evidence from collision zones suggests that the high temperatures that create regional zones of metamorphic minerals occur in wide, hot back arcs prior to continental collision deformation.
plate tectonics
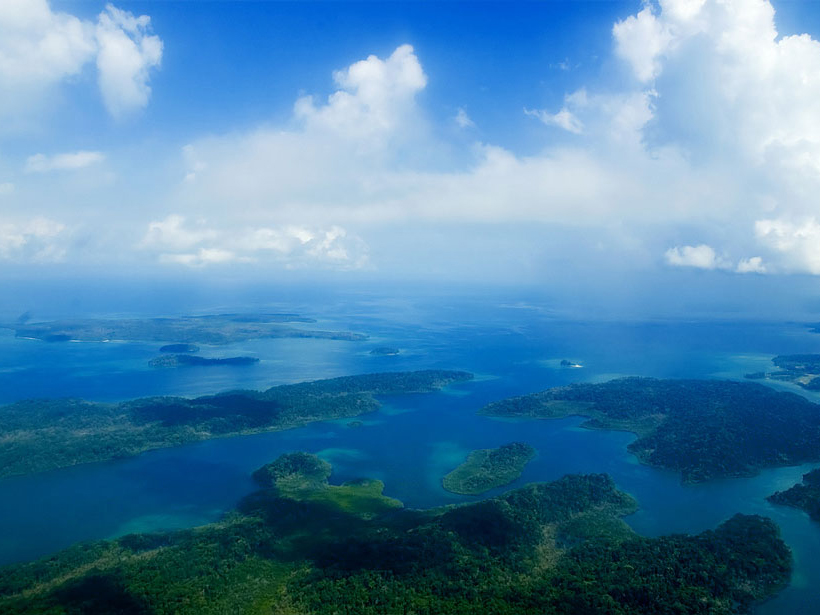
Investigating the Northern Indian Ocean’s Puzzling Geodynamics
International Ocean Discovery Program (IODP) Proposal Nurturing Workshop on Indian Ocean; Goa, India, 17–18 September 2018
In a Submarine Trough, Permeable Rocks May Lead to Quakes
In Japan’s submarine Nankai Trough, rock permeability is much higher when measured at larger scales, likely because of big fractures and faults that are not captured at small scales.
Van Dinther Receives 2018 Jason Morgan Early Career Award
Ylona van Dinther will receive the 2018 Jason Morgan Early Career Award at AGU’s Fall Meeting 2018, to be held 10–14 December in Washington, D. C. The award is for “significant early career contributions to tectonophysics through a combination of research, education, and outreach activities.”
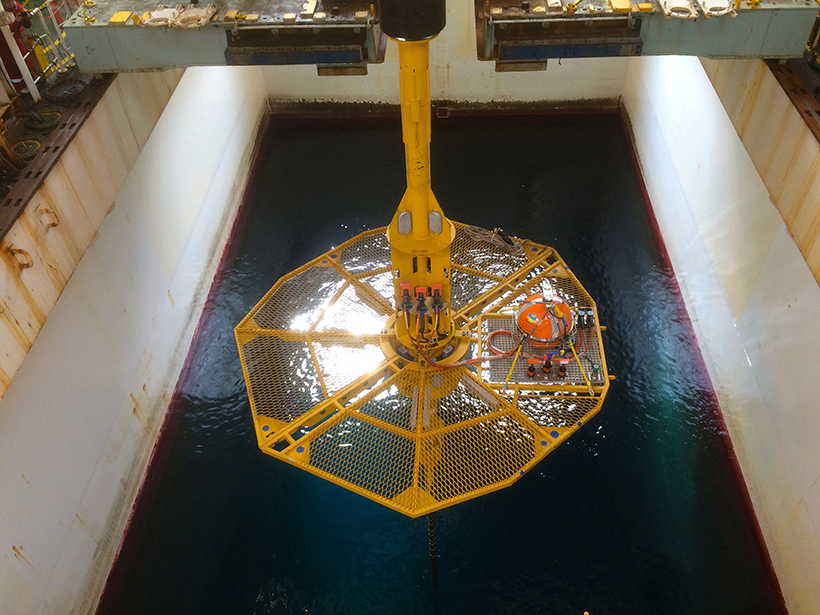
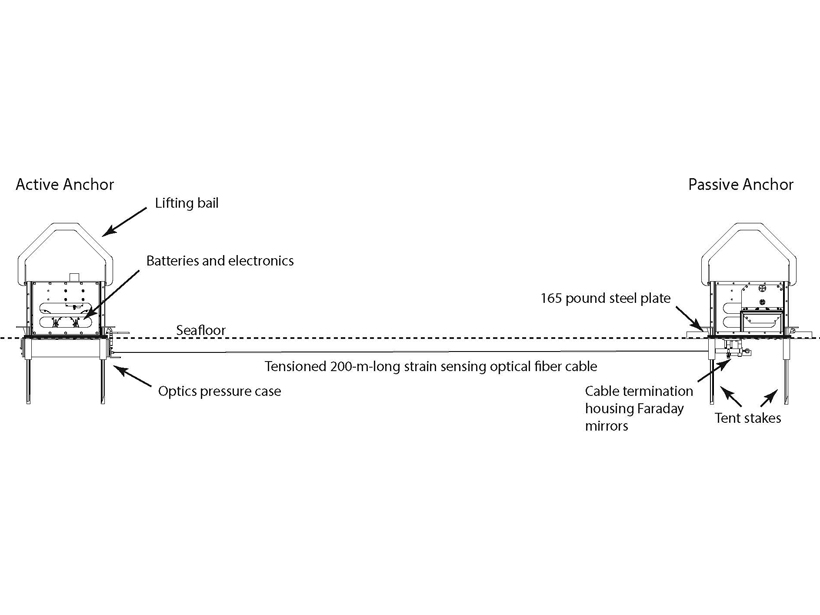
Successful Testing of Technique to Measure Seafloor Strain
A new optical fiber interferometry strain sensor tested off the Oregon coast holds promising prospects for seafloor geodesy.
Is Mars Not So Earthlike After All?
Light-colored Gale crater rocks could have formed from intraplate volcanoes, not continental crust, new study finds.
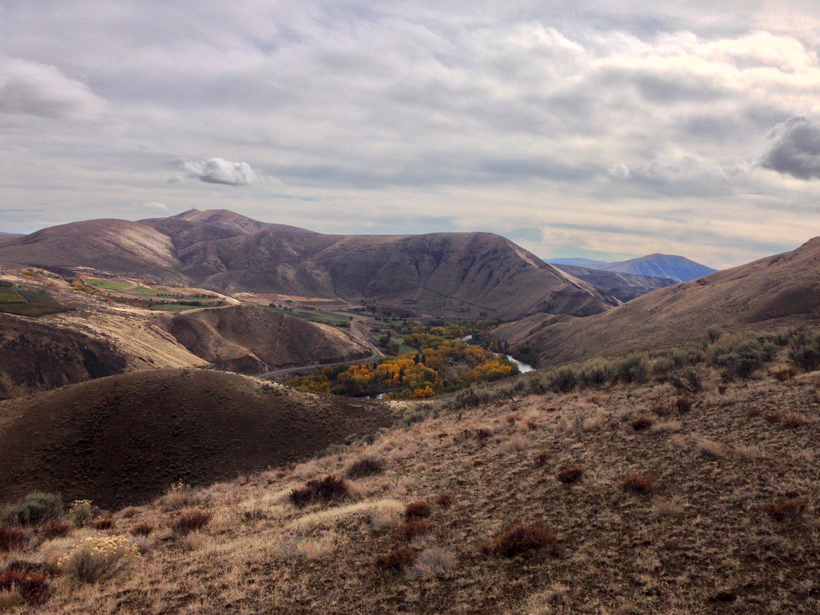
Constraining Central Washington’s Potential Seismic Hazard
Fault geometry and slip rate analyses show deformation in the Yakima Fold Province accelerated in the Pleistocene and has remained elevated, offering new insights into earthquake recurrence intervals.
Linking Mantle Plumes to Volcanoes and Hot Spot Tracks
Study bolsters hypothesis that volcanoes on China’s Hainan Island were formed by a hot spot.
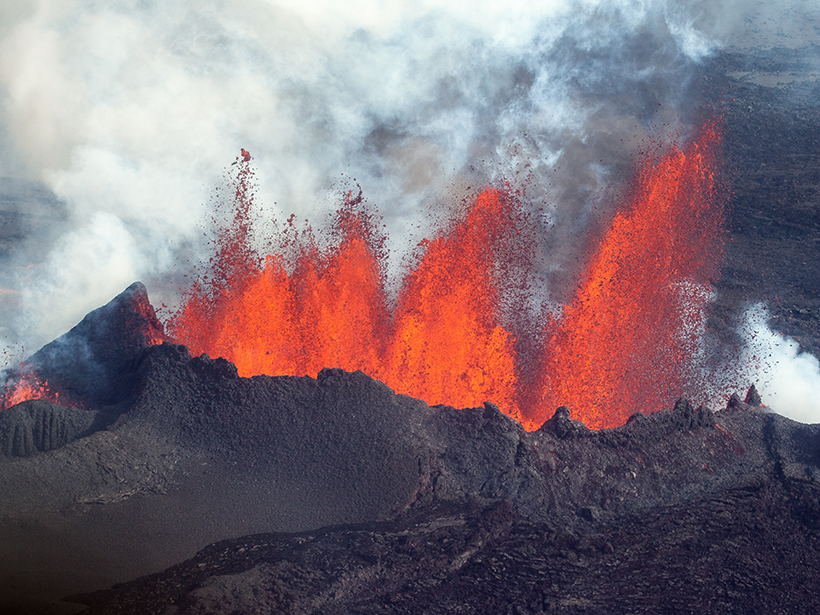
Magma Flow in a Major Icelandic Eruption
Mechanical modeling suggests that previous, undetected eruptions released tectonic stress near the ice-covered Bárðarbunga volcano.
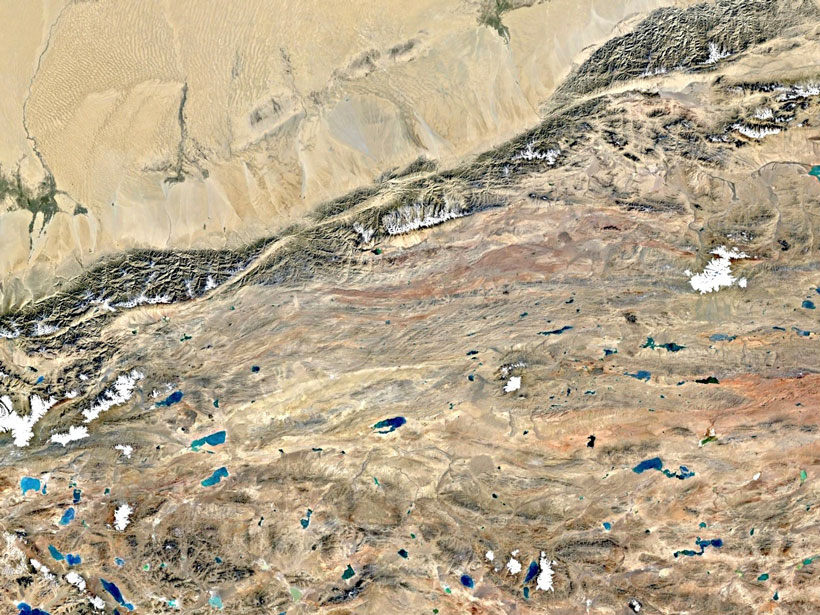
New Insights into Continental Deformation in Northwestern Tibet
A new surface velocity map shows strain localized along major strike-slip features, suggesting the central Tibetan Plateau is not deforming as a fluid in response to gravitational collapse.