Living in Geologic Time: Rafting through the past, present, and future of the Colorado River and the Grand Canyon.
plate tectonics
How Chemical Processes Influence Fracture Pattern Development
Many tools of chemical analysis, experimentation, modeling, and theory have the potential to increase our understanding of how fracture patterns develop at different geological time scales.
A New Dimension to Plate Tectonics
New tools to model and visualize subduction zones in 3-D are providing researchers with insights into the gaps inherent in the theory of plate tectonics.
Podcast: Plate Tectonics, the Theory That Changed Earth Science
Third Pod from the Sun talks with pioneering geophysicist Xavier Le Pichon about what it was like to be a young scientist challenging deeply held theories.
Can We Tell If Faults Grew During or Between Earthquakes?
Numerical simulations of earthquake cycle deformation reveal that co-seismic and interseismic fault propagation can produce distinct propagation angles that may be recorded in the crust.
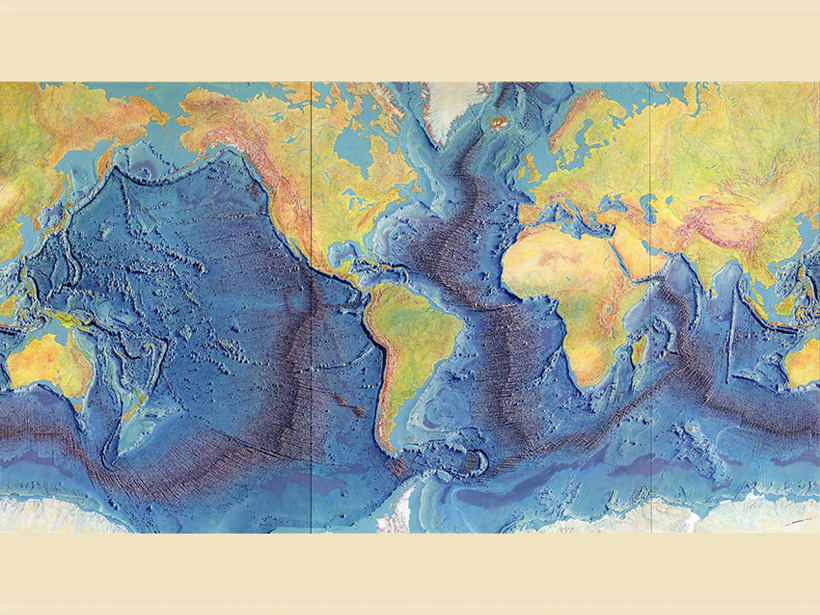
This Is How the World Moves
In October, we celebrate AGU’s Centennial by looking under our feet, where the relatively new study of plate tectonics is evolving rapidly.
How Volcanic Mountains Cool the Climate
Though coastal plutons spew greenhouse gases into the atmosphere as they form, they also pull some of those gases back out of the atmosphere as they break down over time.
New Volcanic Complex Found Below the Southern Tyrrhenian Sea
Researchers have identified a previously unknown volcanic-intrusive complex that originated through the melting of mantle material at the northern edge of the Ionian slab.
Déjà Vu: Understanding Subduction Zones’ Cycle of Seismicity
A unique geodetic data set from Japan’s Nankai subduction zone offers an unparalleled opportunity to study surface deformation spanning almost an entire seismic cycle.
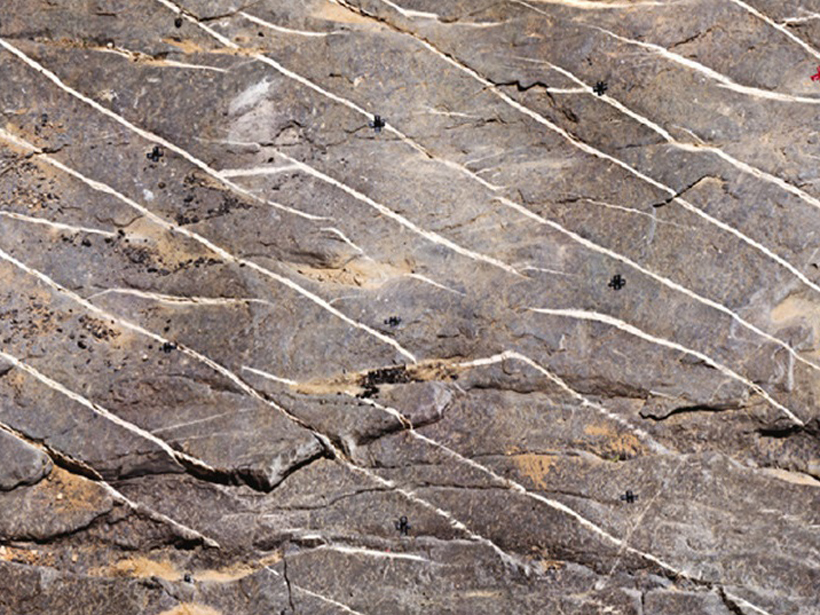





![Figure 4 from paper by Preuss et al. [2019]](https://eos.org/wp-content/uploads/2019/09/2019JB017324-Figure-4-sized.png)