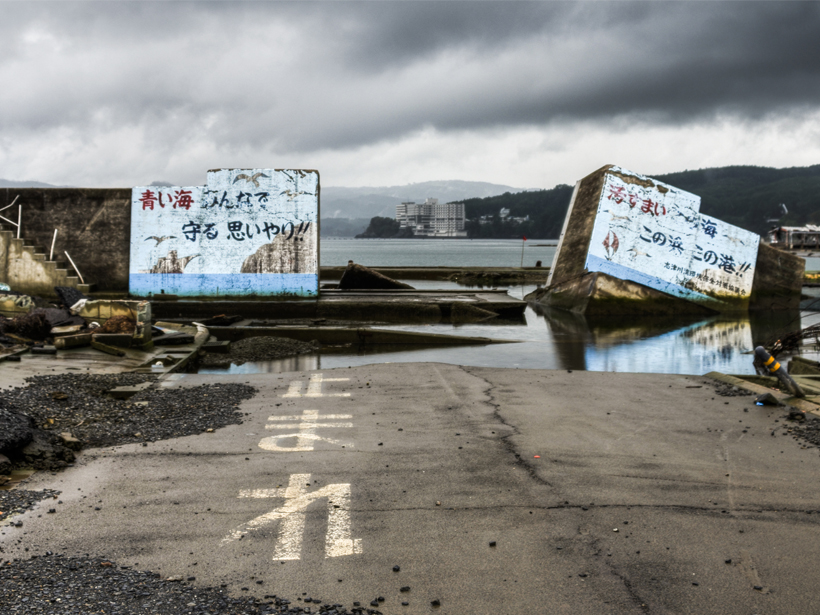
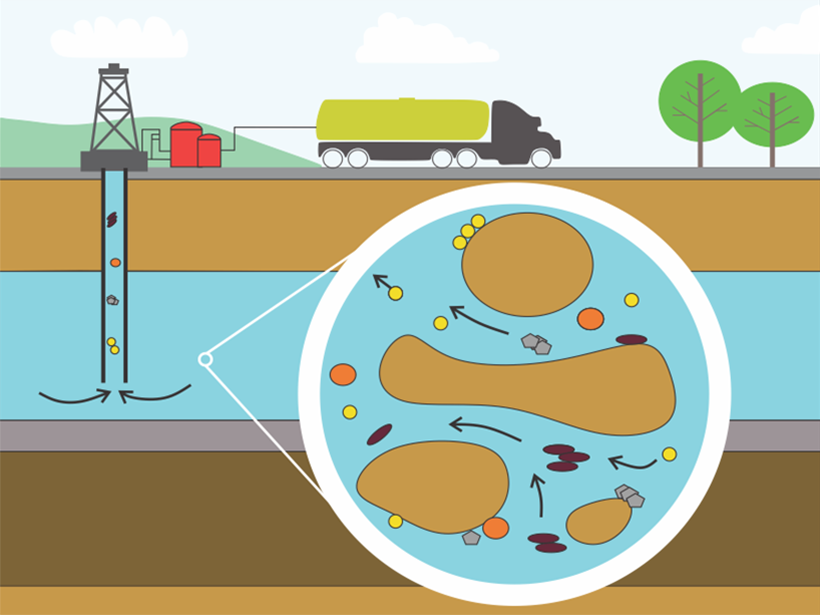
Increased permeability temporarily boosts water flow.
Water Resources Research
Capturing Snowmelt Patterns from Cloudy Satellite Images
A new modeling strategy could improve streamflow predictions in places where mountain snow is a critical source of water.
Treating Colloids as Clusters Better Predicts Their Behavior
New research suggests that an accurate prediction of colloidal particle mobilization in the environment should account for the effect of clustering.
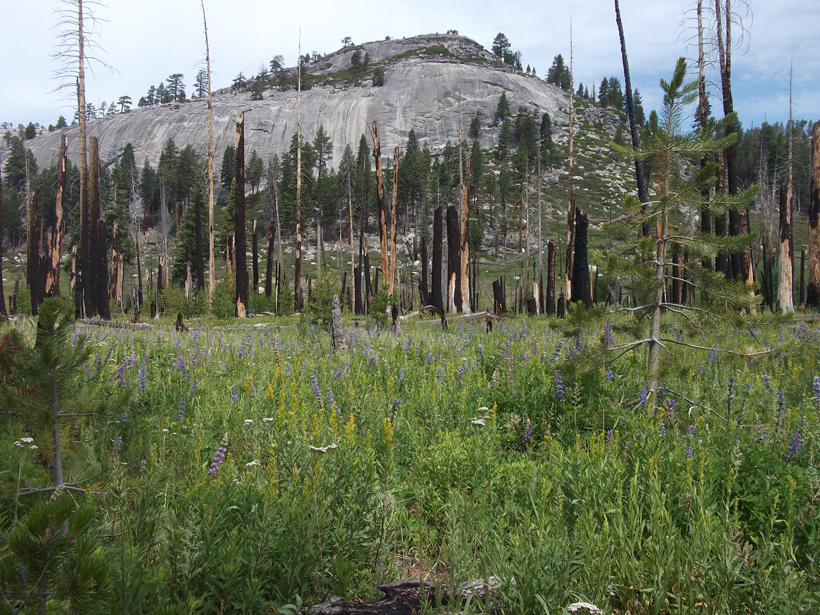
Restoring Natural Fire Regimes Can Yield More Water Downstream
Research in Yosemite National Park offers a new benchmark for understanding water balance changes in a mountainous basin 4 decades after its natural wildfire regime was reestablished.
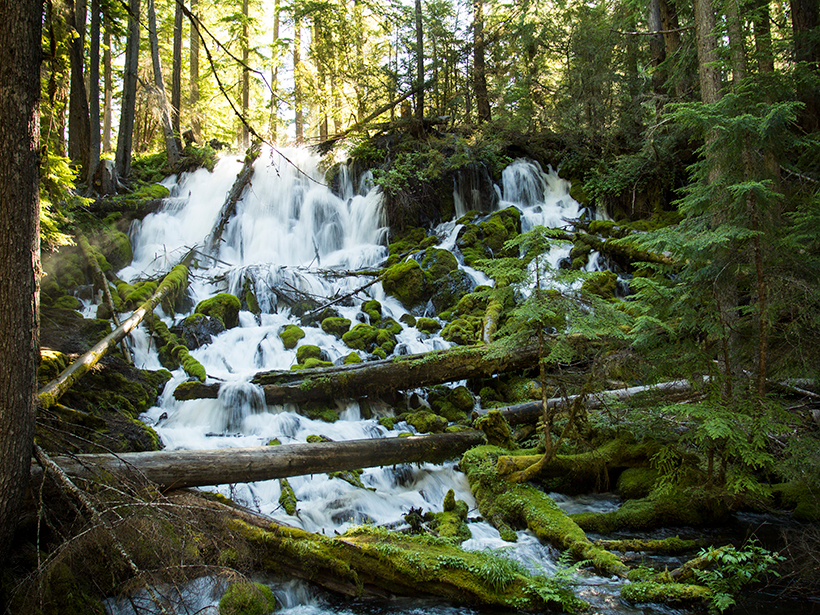
Forested Streams May Warm More Than Observations Predict
Understanding how temperatures of cold-water streams respond to global warming could help clarify the impacts of climate change on aquatic ecosystems.
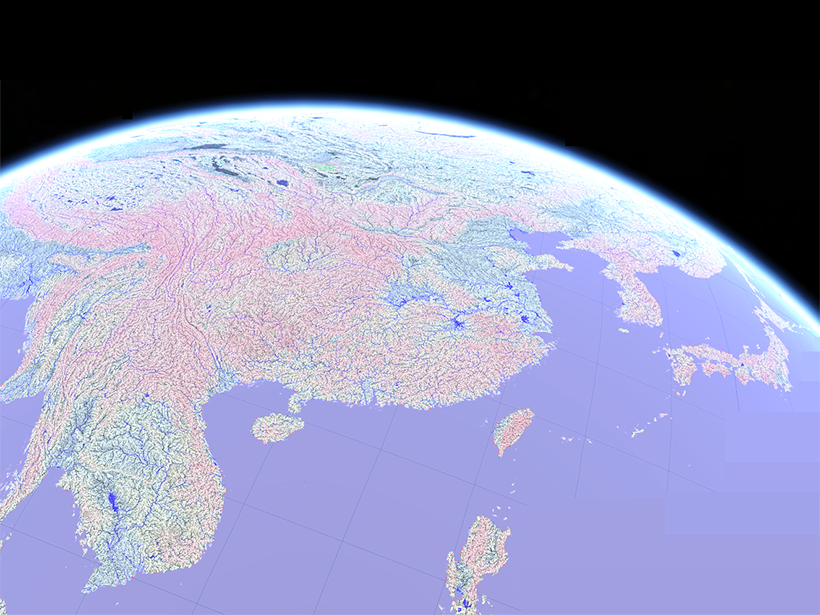
A More Accurate Global River Map
A new map of global river systems is based on crowdsourcing and the latest topography data sets.
Extreme Precipitation Expected to Increase with Warming Planet
A new analysis indicates that the frequency and magnitude of extreme precipitation events are expected to increase as Earth continues to warm.
Ordinary Security Cameras Could Keep an Eye on Rainfall
A new opportunistic sensing strategy could use existing closed-circuit television networks to accurately capture rainfall intensity, despite low-cost equipment and visually complex scenes.
Using GPS Sensors to Capture Key Snowpack Properties
A low-cost, two-antenna GPS setup could enable valuable snow measurements in remote locations, improving predictions of runoff and avalanche risk.
Answer to California Landscape Riddle Lies Underground
Scientists link vegetation mosaics in California to patterns of weathered bedrock.