A new index insurance contract – a financial product innovation seeking to cope with climatic variability – could help hydropower operators to manage climate risks.
Water Resources Research
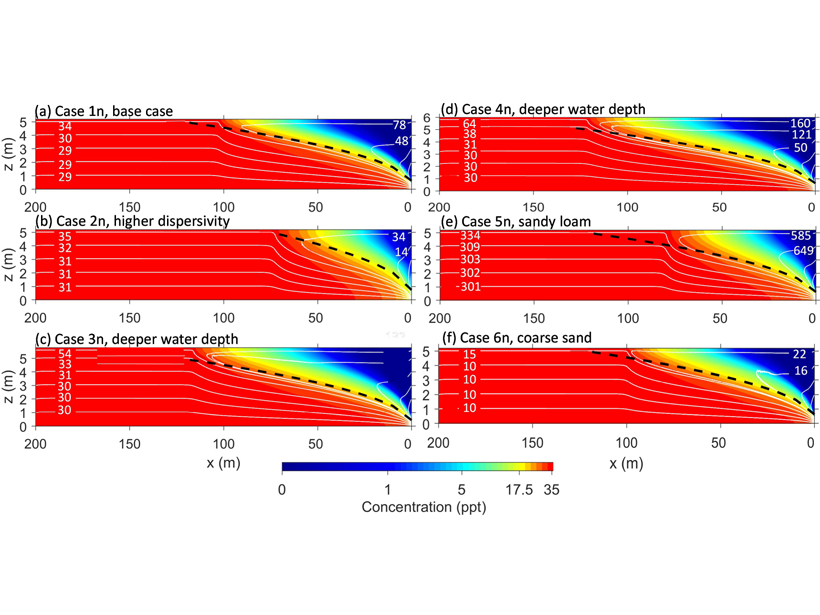
Evaporation Reverses Groundwater Flow and Forms Hyper-Salinity
A numerical model of groundwater-surface water systems shows how floodplain evaporation can reverse stream-groundwater flow and produce strong buoyancy changes associated with salinity.
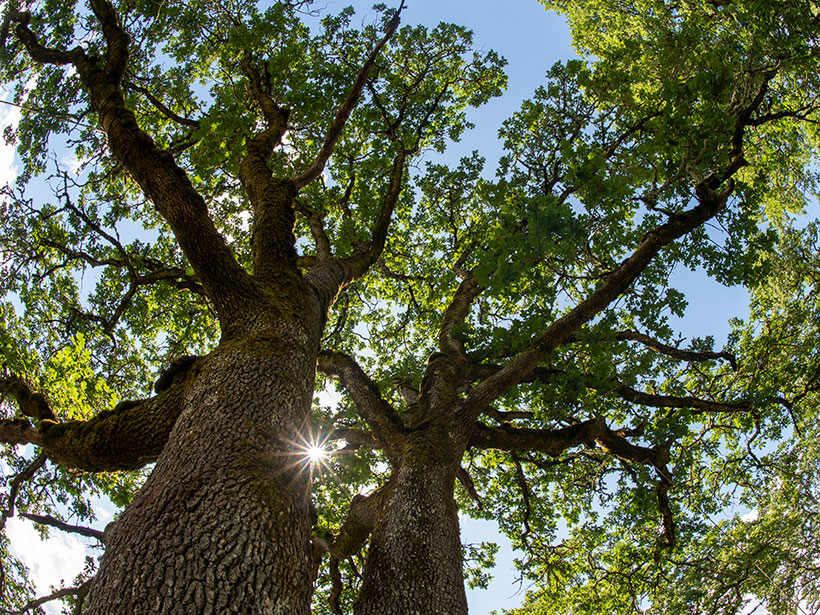
How Some Trees Survive the Summer Dry Season
Oak trees in California seasonally tap moisture in unsaturated soil and weathered bedrock, even when the groundwater table is within reach of their roots.
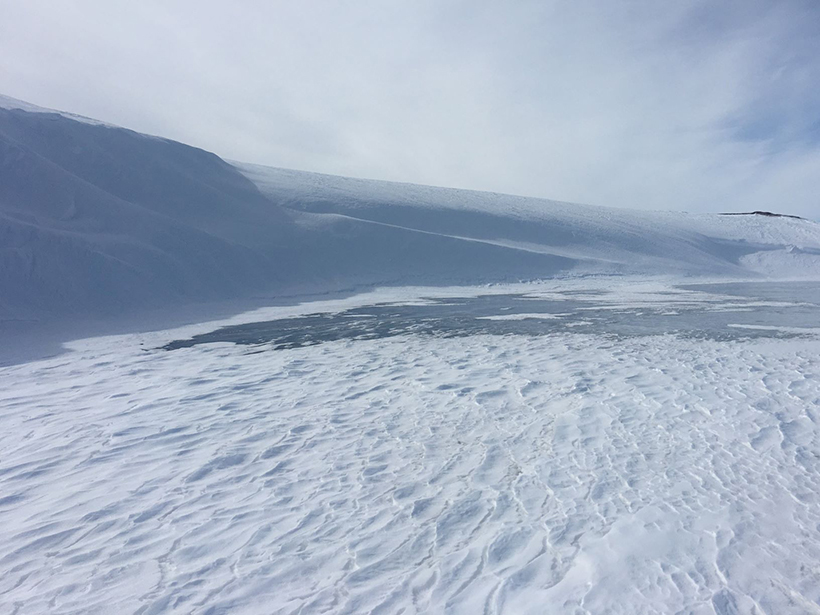
A Census of Snowdrifts in Northern Alaska
Snowdrifts prove less ephemeral than they might seem, occurring in the same places year after year.
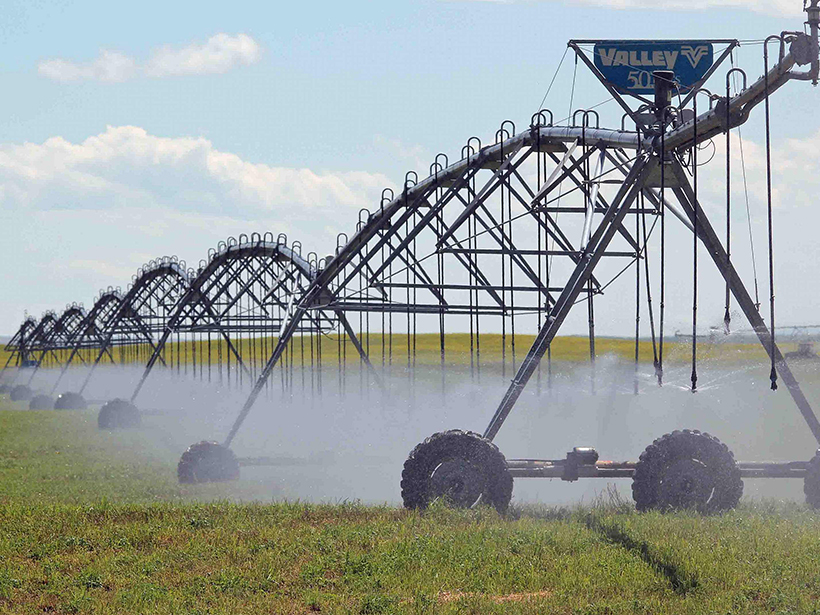
Can Satellites Fill Gaps in Agricultural Water Monitoring?
Past studies that have estimated irrigation water usage based on satellite remote sensing have had large uncertainties that could hamper effective water management.
The Ocean-Land Connection of Droughts
Around 16 percent of large-scale droughts over land originate above the ocean and these types of droughts are more extensive and severe than droughts that originate over land.
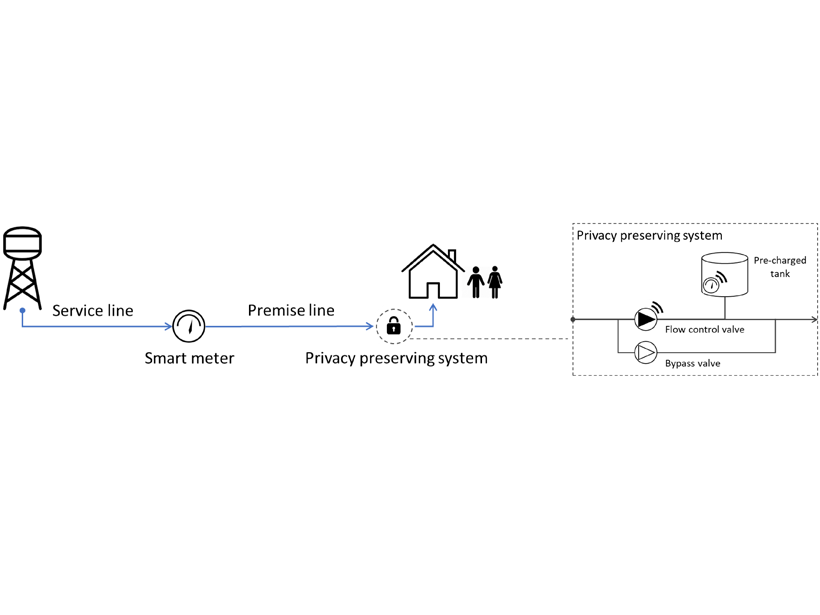
Smart Water Metering Need Not Compromise People’s Privacy
Scientists have devised a way of preserving privacy for smart water metering users while also providing water suppliers with information they can use to improve the efficiency of water services.
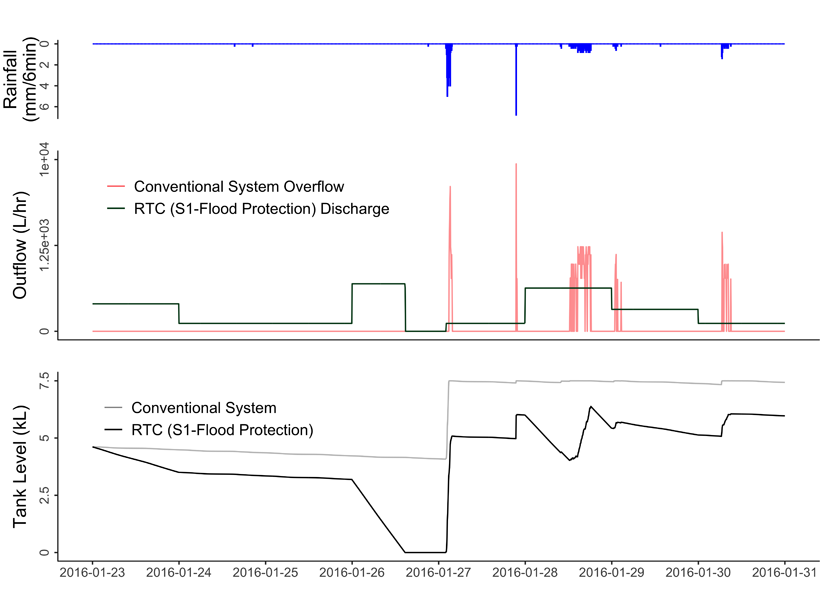
Rainwater Harvesting Can Reduce Flooding as Well as Saving Water
Weather forecasting can greatly improve benefits of rainwater harvesting.
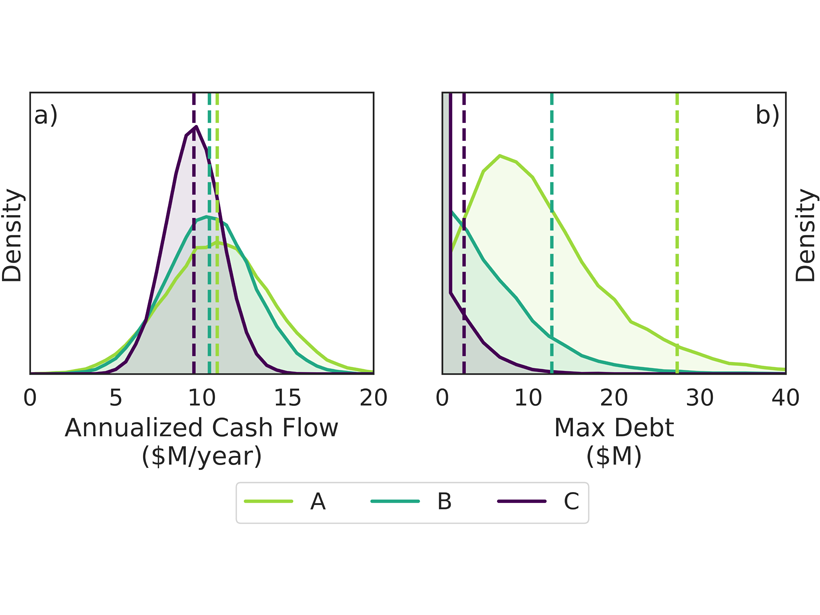
Environmental Impact Bonds Incentivize Watershed Restoration
Environmental Impact Bonds for financing new water and environmental infrastructure can be properly priced with the help of watershed modelling.
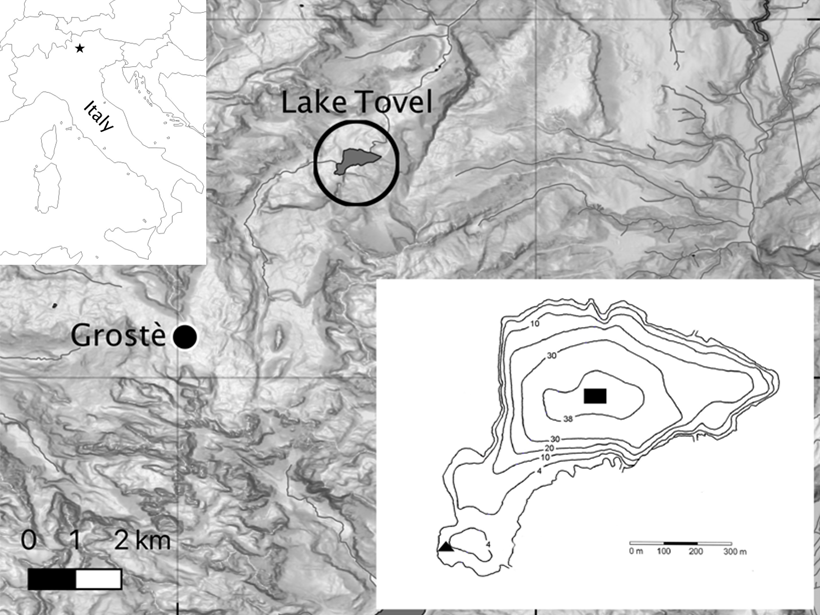
Climate Warming Improves Oxygen Mixing in a High-Altitude Lake
Long term weather and lake data from a high elevation lake in the Alps demonstrate that climate warming may actually improve the ability of high-altitude deep lakes to mix their waters.