Hydrogeological properties of degrading permafrost come to fruition with a new 3-D modeling study that highlights the increasing role of groundwater in the water cycle of high-latitude areas.
Water Resources Research
Trees Wearing Accelerometers Help Track Snowstorms
This device allows scientists to measure how much snow is trapped in canopies and predict changes to snowpack—a critical factor in annual water availability.
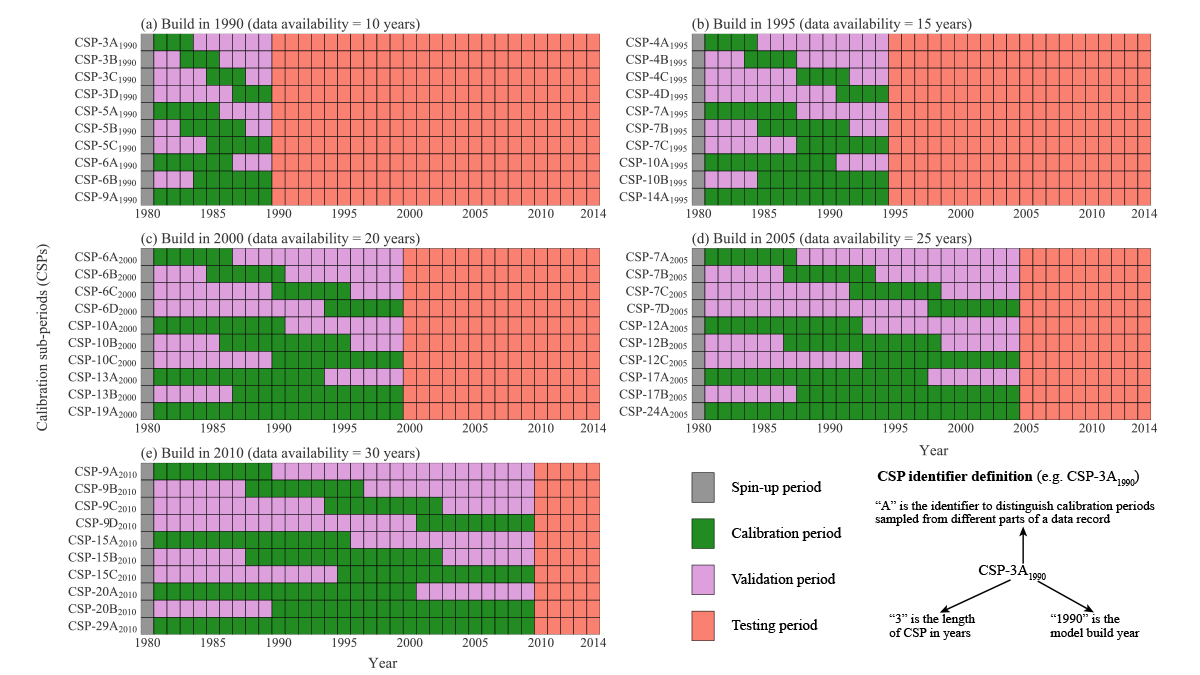
Hydrologists Should Reconsider How They Calibrate Their Models
A new study suggests that the commonly used split sample approach in hydrology, where time series are divided into a part for model calibration and a part for model validation, should be abandoned.
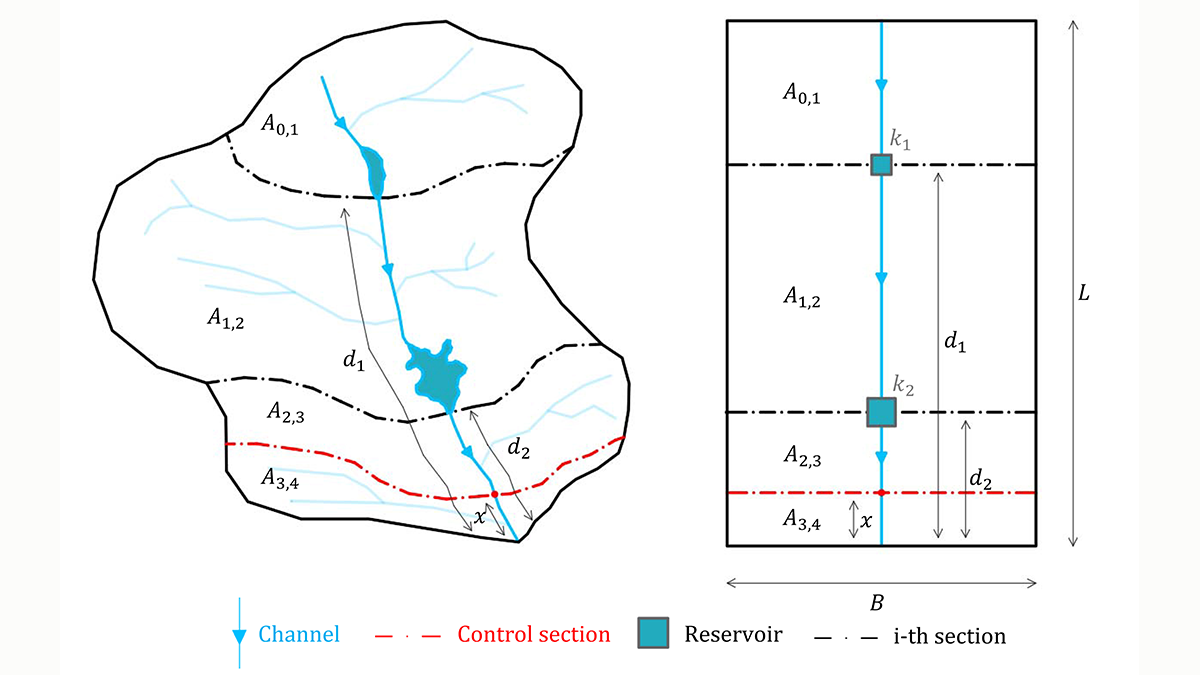
A New Index to Assess Multiple-Reservoir Effects on Peak Floods
A simple, yet quantitative, index is demonstrated to quantify reductions in the peak flood resulting from multiple reservoirs, arranged in series along the same river reach.
Tree Rings Reveal a Puzzling Trend in Monsoon Intensity
Tree rings confirm that in northern Australia, the past 40 years have experienced more rain than any similar length of time in the past 600 years.
Predicting Discharge Chemistry in Mine-Waste Rocks
Quantifying integrated hydrological processes, biogeochemical reactions, and mineralogical characteristics can help predict water quality and quantity for mine-waste rock piles.
Managing Strategic Water Resources in a Changing Climate
Another significant step has been taken in methods for managing water resources in the face of climatic changes and other future uncertainties. Dynamic adaptation is becoming a reality.
Modeling Mulch to Understand Agricultural Soil
A new model helps shed light on residue mulch, an important regulator of surface soil conditions.
Plant Root Exudates Mediate Soil Nutrient Transport
Plant roots mediate solute transport through the soil immediately surrounding them by introducing polymers and other binding compounds that disrupt water transport pathways between soil pore spaces.
Pro-Poor Flood Risk Management Can Reduce Urban Inequality
Rich people’s aversion to flood risk results in poor people living in the most vulnerable locations poverty. Pro-poor flood risk management policies could have a significant impact on inequality.

![A 3-D image of the study area of Liu et al. [2022] in Kuuguluk River at Salluit, Nunavik (Quebec), Canada. The image shows the locations of A-A’ and B-B’ and lines C1-5.](https://eos.org/wp-content/uploads/2022/04/2021WR031630-Figure-4.png)