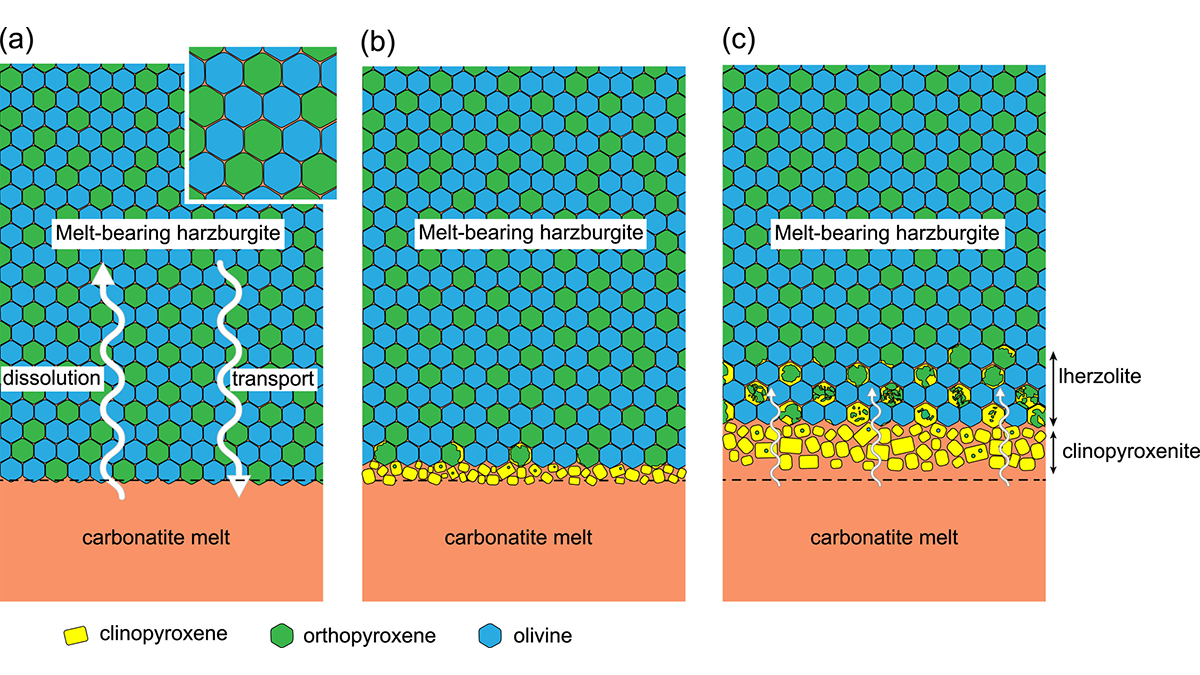
A new study suggests that carbonatite metasomatism, not silicate metasomatism as previously thought, was dominant prior to the removal of the North China Craton in the early Cretaceous.
Editors’ Highlights
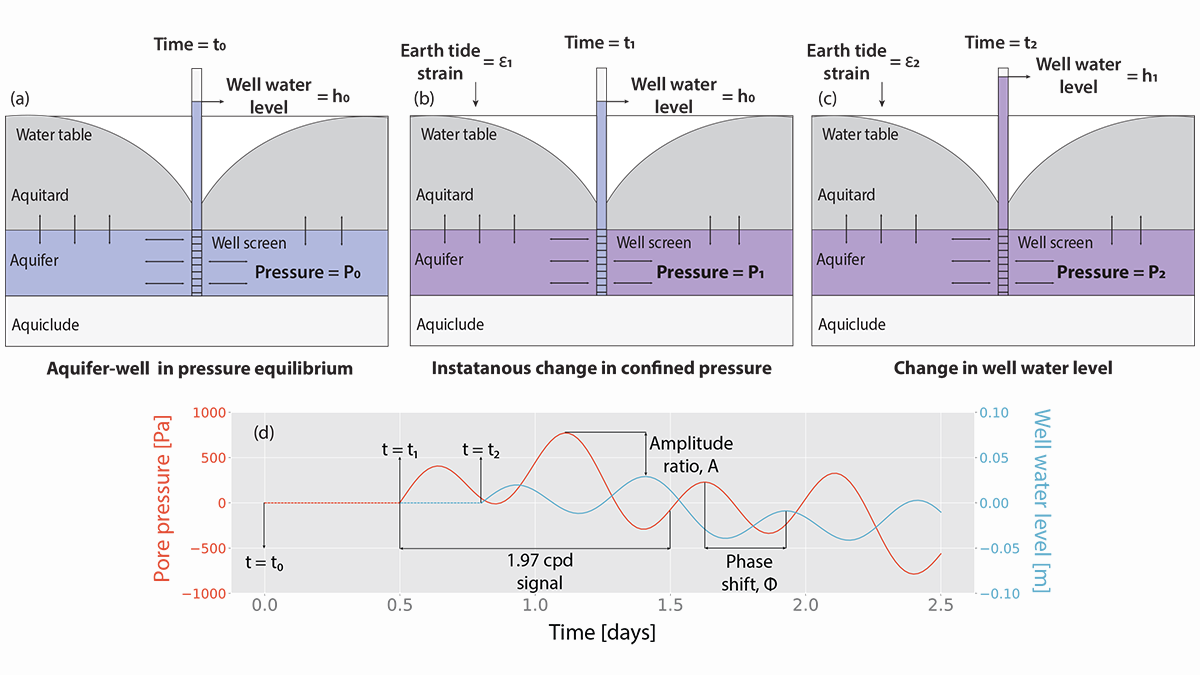
Modeling Groundwater Responses to Earth Tides
Tidal fluctuations in water well levels can reveal characteristics of the subsurface, and a new model based on coupled physics delineates the limitations of inherently simplistic analytical solutions.
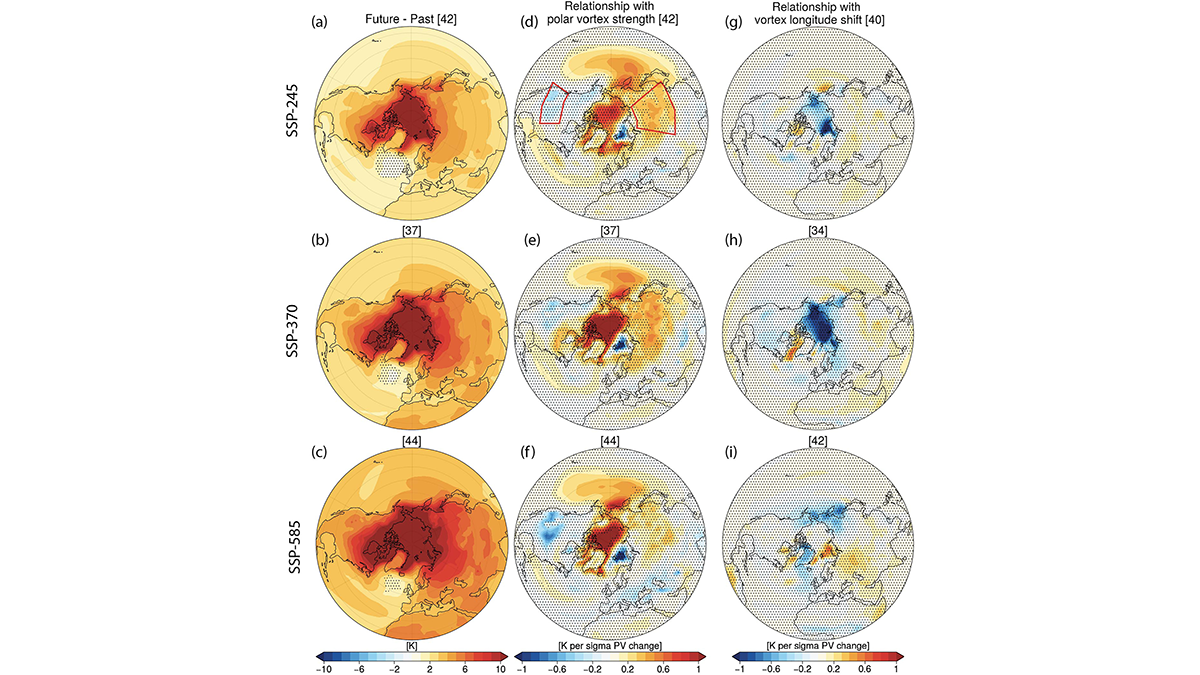
Modeling Stratosphere-Troposphere Coupling in a Changing Climate
Climate models have disagreed on the future evolution of the stratospheric polar vortex and links to the troposphere, but a new study revisits this problem with state-of-the-art climate models.
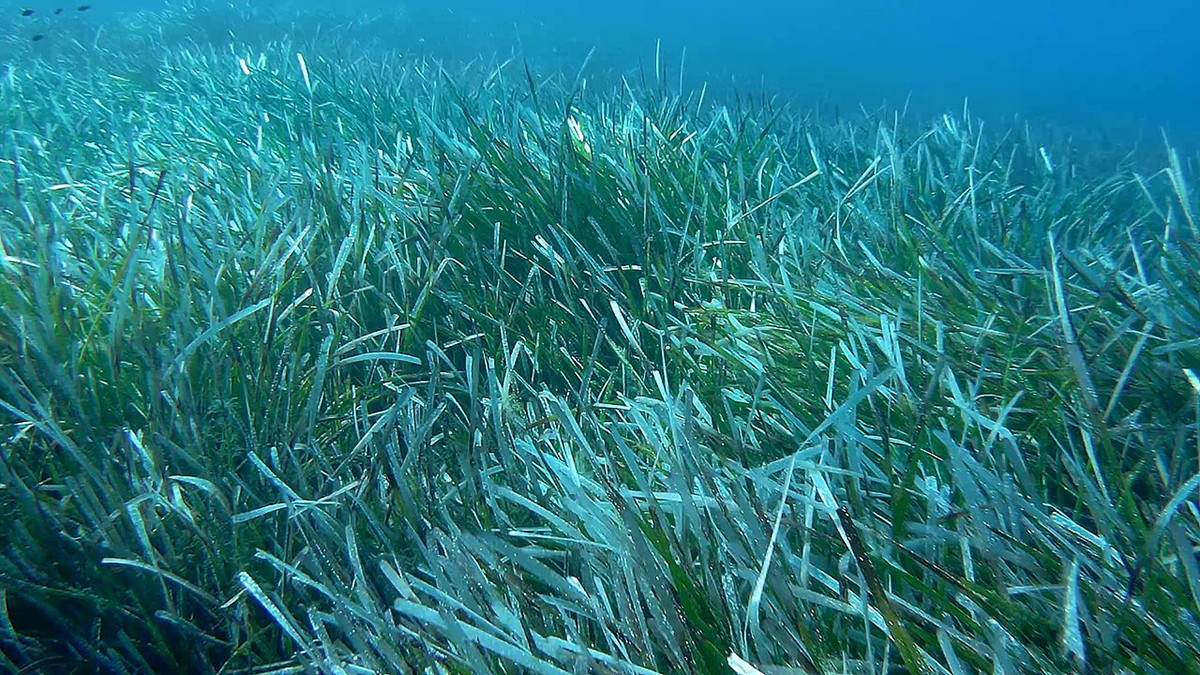
Warming and Agitation Intensify Seagrass Meadow Carbon Fluxes
Carbon dioxide emissions surge in sediments when temperature and agitation increase, both of which are likely to continue rising in degraded Mediterranean seagrass meadows.
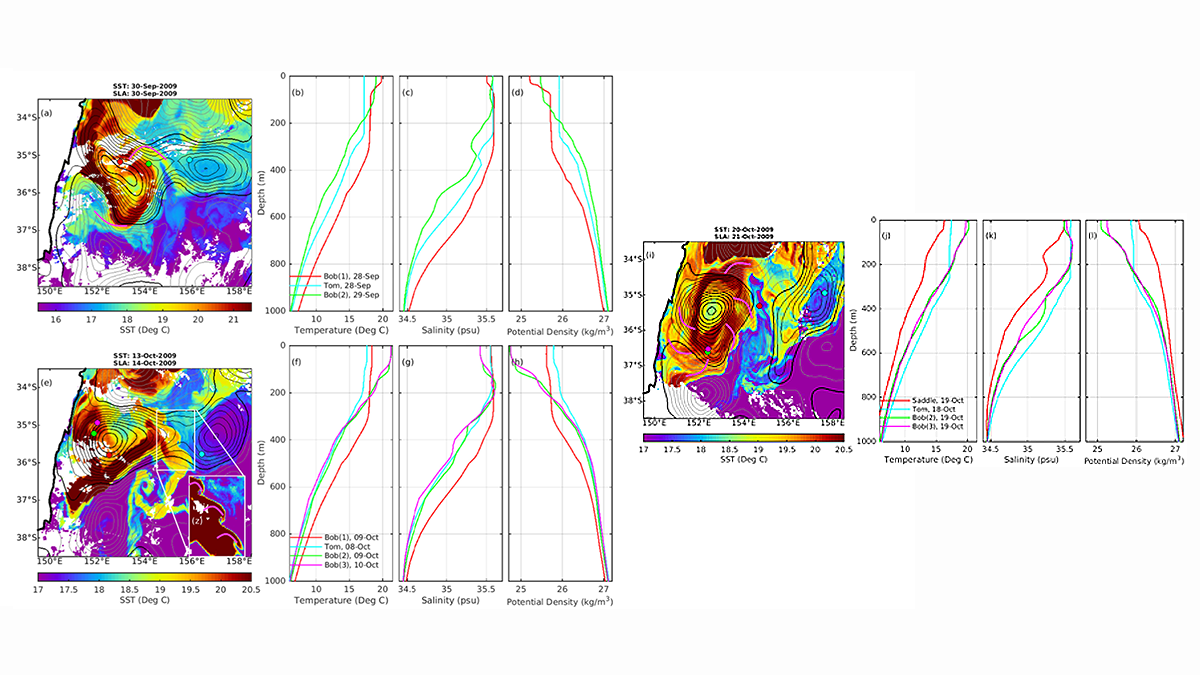
How do Bob and Tom Eddies Meet, Pair-Spin, and Twist?
Autonomous float data reveal that mergers of two eddies, known to have spiraling subducting water surrounding each other, happens more frequently than previously thought.
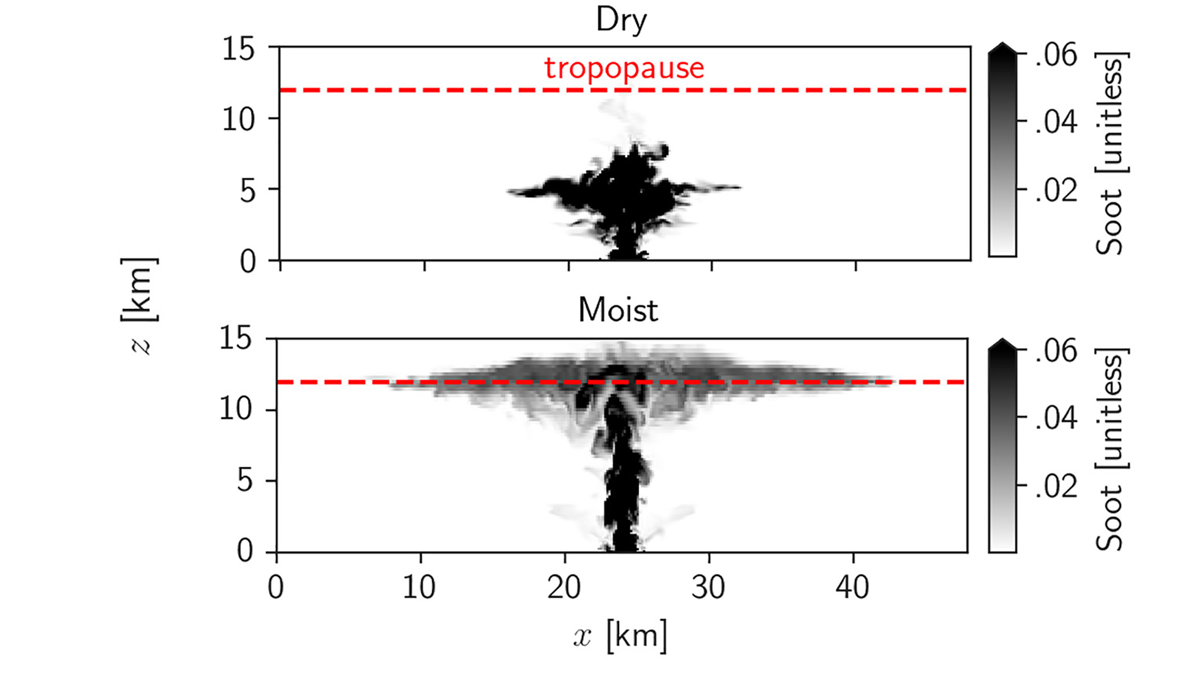
How Can Nuclear Plumes Reach the Stratosphere?
A new study shows how moist convection can lift sooty air from firestorms to the stratosphere, potentially leading to a nuclear winter.
A Really Big (Global) Splash at Chicxulub
What caused a tsunami 30,000 times more powerful than the December 26, 2004 Indian Ocean tsunami? A new modeling study says this was one of the results from the Cretaceous Chicxulub asteroid impact.
Two Kinds of Warm Core Rings Emanate From the Gulf Stream
A new study reveals that long-lived warm core rings found in the “Ring Corridor”, a narrow path north of the Gulf Stream, have two different formation mechanisms.
New Cloud and Precipitation Data Over the Southern Ocean
New measurements show the macro- and microphysical characteristics of the clouds and precipitation over the data-space regions of the Southern Ocean.
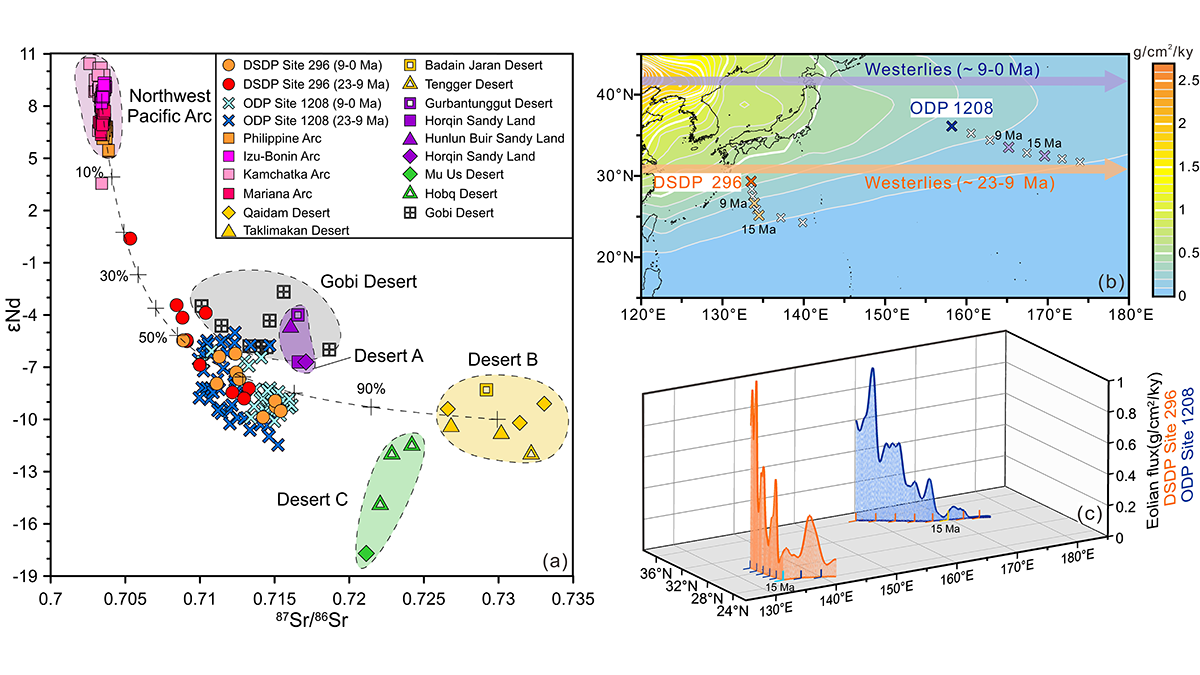
Asian Dust Flux into Philippine Sea Increased During Miocene
A new deep sea dust record from the Philippine Sea, when added to evidence from the NW Pacific, suggests how dust may record a change in dustiness or the position of wind transport.