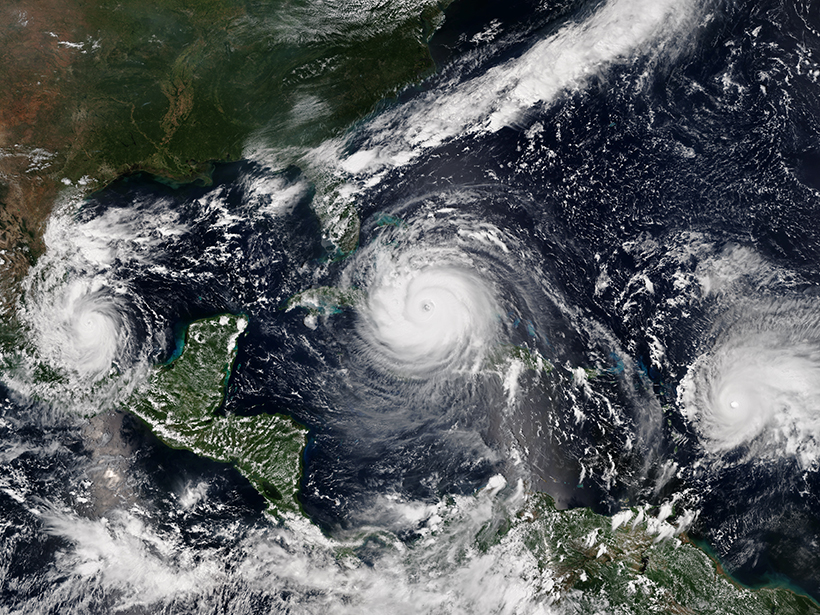
An efficient, low-resolution machine learning model can usefully predict the global atmospheric state as much as 3 days out.
forecasting
NOAA Predicts Busy Hurricane Season
FEMA issued new guidance yesterday advising states to prepare for evacuations during the pandemic.
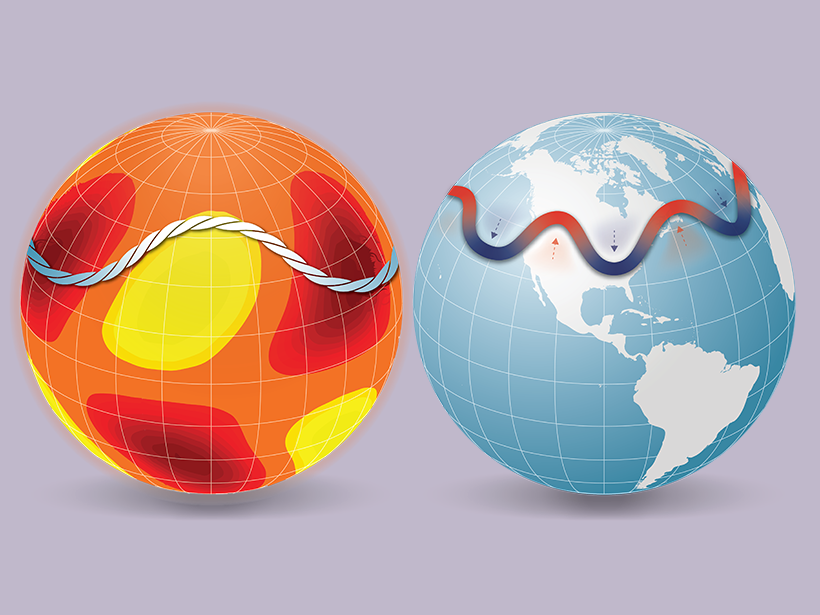
Space Weather Forecasting Takes Inspiration from Meteorology
Solar features analogous to major atmospheric waves on Earth could offer more advanced warning of harmful solar storms.
Tracing the Past Through Layers of Sediment
Signals in layers of sedimentary rock hint at climates and ecosystems come and gone. Understanding this history can help us forecast the future, but challenges abound.
Lightning Research Flashes Forward
A greater understanding of lightning mechanisms is spurring the development of more accurate weather forecasting, increased public health precautions, and a more sophisticated understanding of lightning itself.
Are Cosmic Rays a Key to Forecasting Volcanic Eruptions?
A combination of relativistic particles and artificial intelligence may provide a new way to forecast when a volcano could erupt.
An Element of Randomness in Modeling Arctic Ice Cover
Incorporating random variation of temperature, humidity, and wind offers a computationally cheap alternative to improving resolution in an Earth system model when predicting when Arctic sea ice will disappear.
Machine Learning Improves Weather and Climate Models
New research evaluates the performance of generative adversarial networks for stochastic parameterizations.
Evaluating Cloud Cover Predictions in Climate Models
A new analysis highlights progress in predictions of cloud cover from models that are part of the Coupled Model Intercomparison Project.
Combining AI and Analog Forecasting to Predict Extreme Weather
New deep learning technique brings an obsolete forecasting method “back to life” to predict extreme weather events.