A new model deploys a neural network to spot beavers’ engineering exploits in aerial and satellite imagery, an approach that should aid studies of ecosystem and landscape change.
Modeling
Simulating Clouds on Arbitrary Grids in Any Spatial Direction
A new non-column based spectral element implementation of cloud microphysics enables full 3D flexibility in computing clouds and improves computational efficiency.
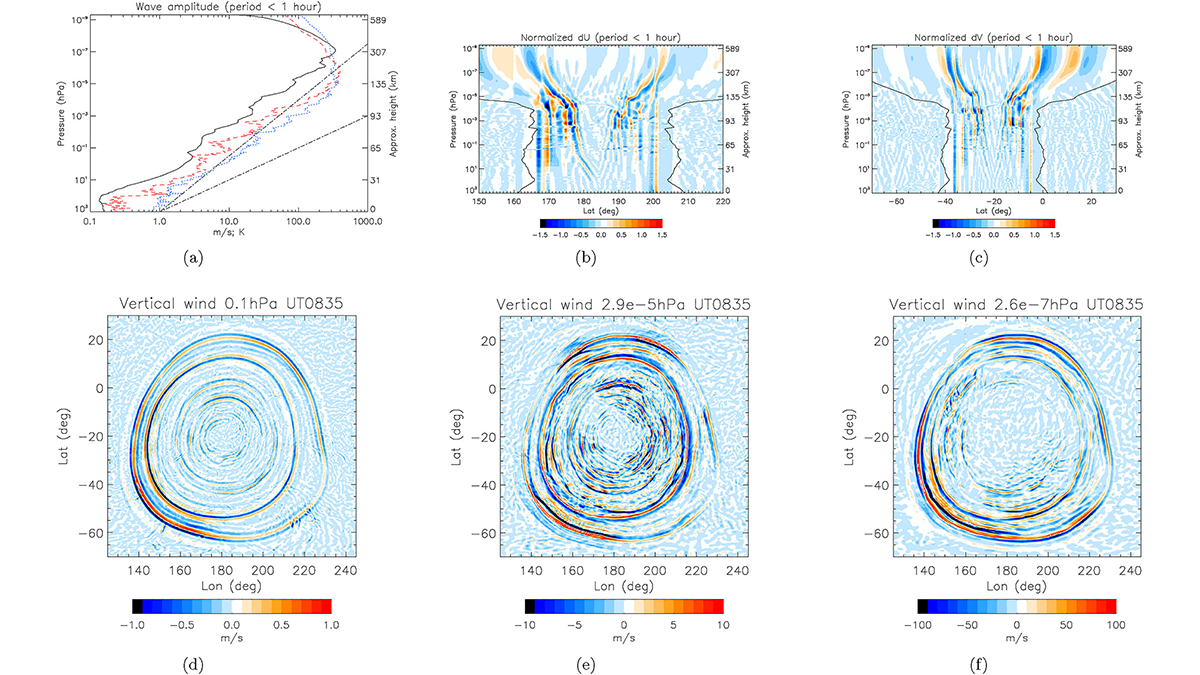
Modeling Whole Atmosphere Responses to the Hunga-Tonga Eruption
A high-resolution whole atmosphere simulation captures the strong, global responses up to the thermosphere and ionosphere following the Hunga-Tonga volcano eruption.
Reducing Aerosol Climate-Forcing Uncertainty: A Three-Way Street
To reduce persistent aerosol-climate-forcing uncertainty, new in situ aerosol and cloud measurement programs are needed, plus much better integration of satellite and suborbital measurements with models.
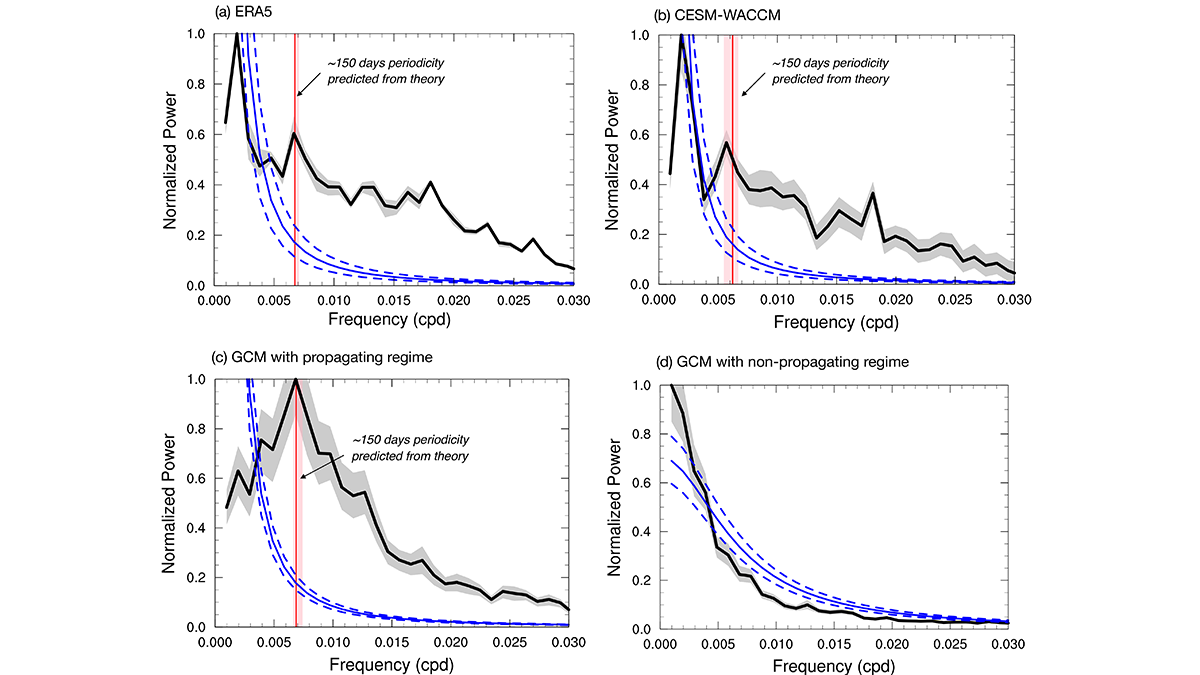
A 150-Day Periodicity is Revealed in the Southern Extratropics
An internally generated 150-day periodicity is newly identified in the Southern Hemisphere extratropical large-scale atmospheric circulation, which arises from the annular mode’s propagating regime.
Climate Change Is Drying Out Earth’s Soils
Earth’s land is drying as it warms, but it is not clear how dry is too dry.
Danger in the Dust! The Hazards of Windblown Dust
Airborne dust not only causes disease, it also menaces transportation on land, sea, and air; disrupts renewable energy systems; transports pathogens and toxic substances; and poses many other hazards.
A New Look at the Changing Water Cycle Over Land
Whether warming increases or decreases, rain over land depends on the relationship of soil moisture, evaporation, and aridity which shape rain regimes.
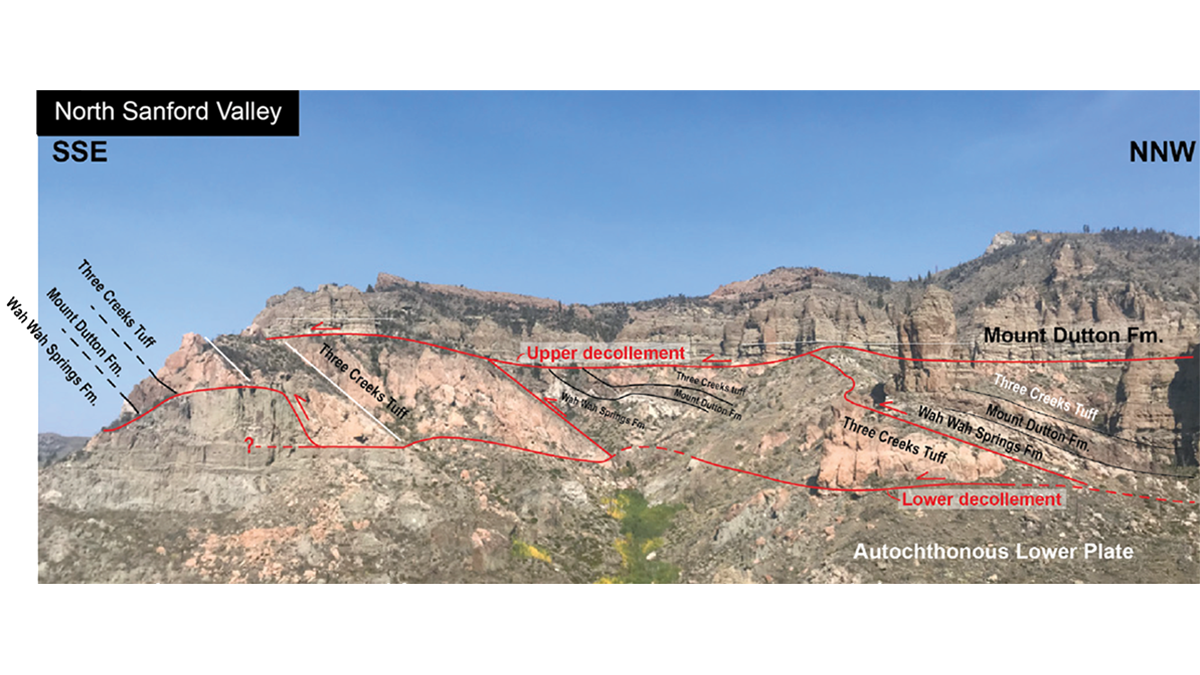
A Giant Rockslide on a Bed of Steam
Detailed observations of the giant Sevier gravity slide in Utah show that the exceedingly low basal friction required for its rapid emplacement was developed by trapped thermally pressurized fluids.
Fine-Tuning Air Pollution Models
InMAP estimates air pollution within cities, but its predictions are flawed for specific chemicals. Now, scientists are addressing that shortcoming.