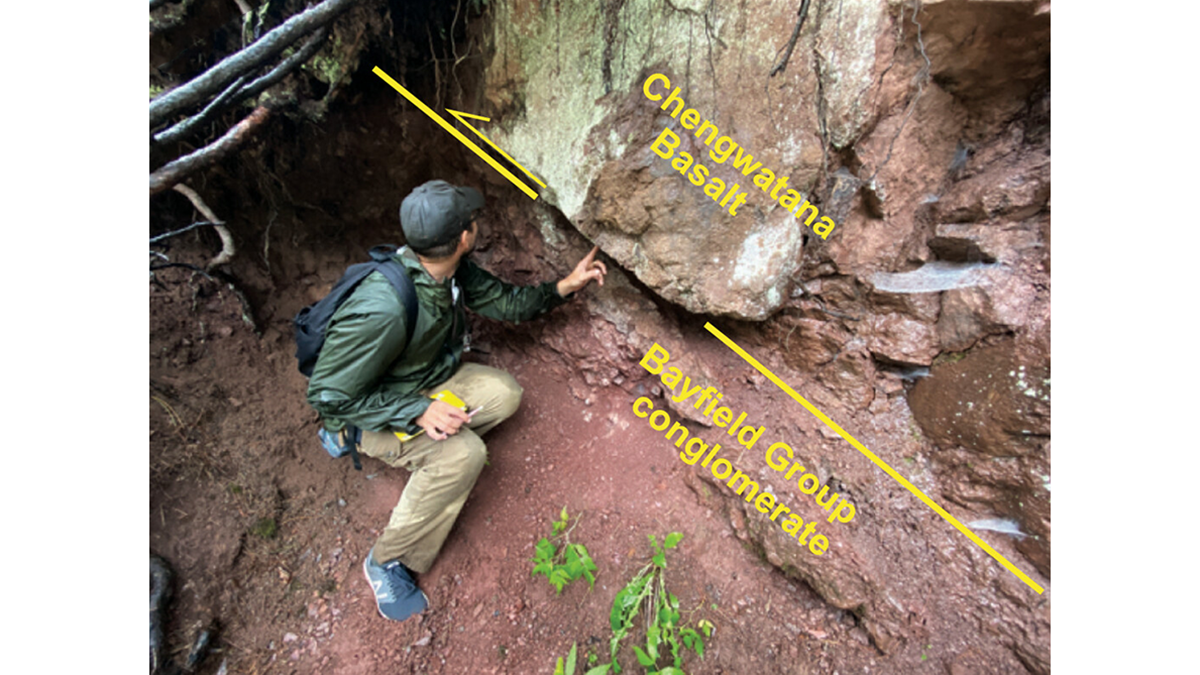
A new study reconstructs how an ancient North American rift system was uplifted in space and time due to subsequent continent-continent collision.
plate tectonics
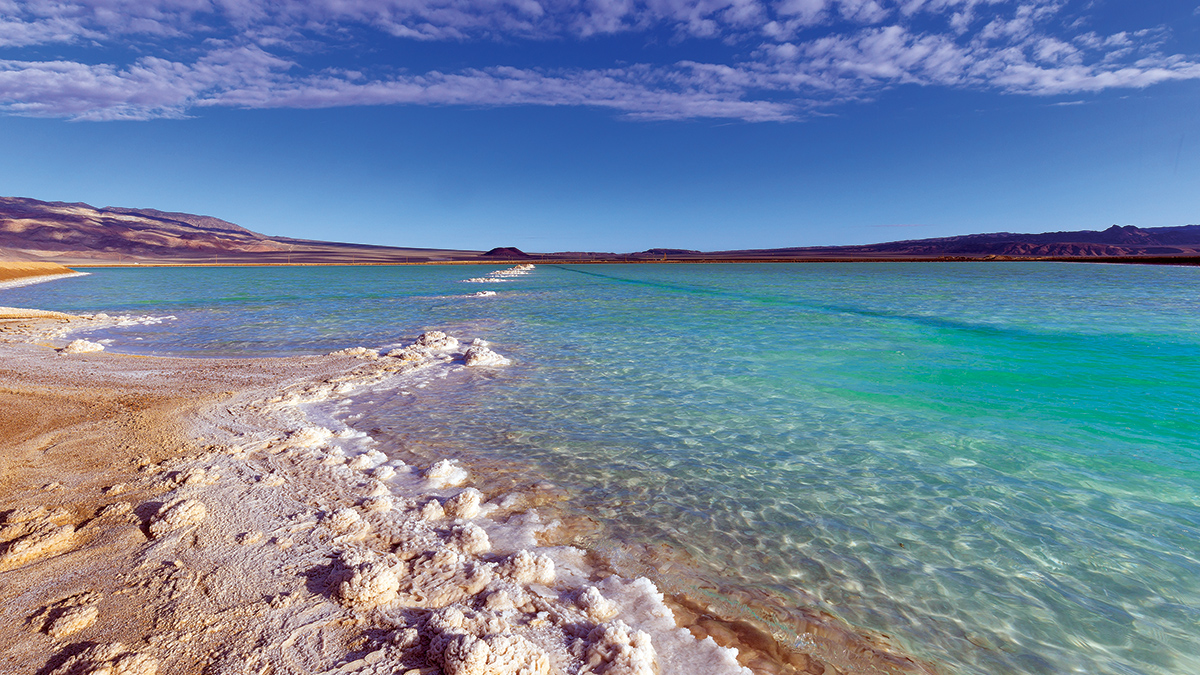
Nevada Has Loads of Lithium. Here’s Why.
Nevada is becoming a major producer of lithium, thanks to topography, climate, and geologic serendipity.
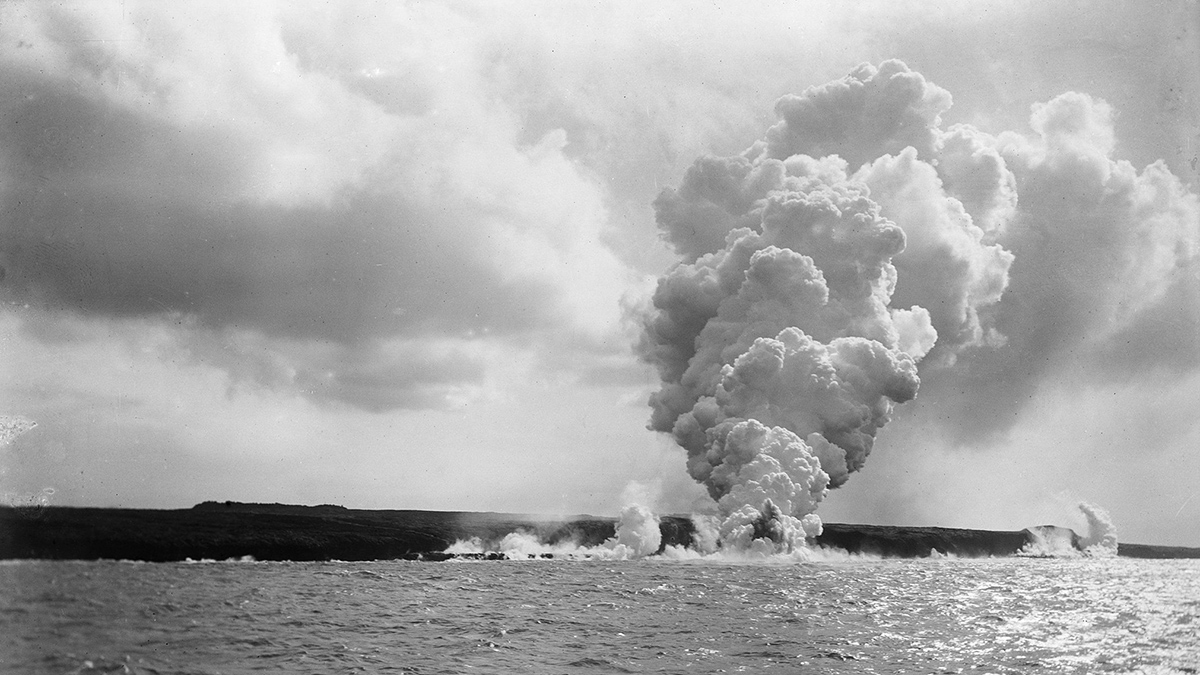
Tracking a Disappearing Mantle Plume in Ancient Samoa
A thick portion of Earth’s crust may have capped the Samoan plume and suppressed volcanism for 30 million years, explaining a curious gap along the Samoan chain.
A Close Asteroid Encounter May Have Once Given Earth a Ring
An unusual concentration of impact craters suggests that they may have been caused by the breakup of an asteroid that created a temporary debris ring around Earth.
Seismotectonic Update of the Philippines-Taiwan Region
Using more than two decades of data, scientists find that the Philippine and Taiwan subduction region is controlled mainly by shallow seismicity and low magnitude earthquakes.
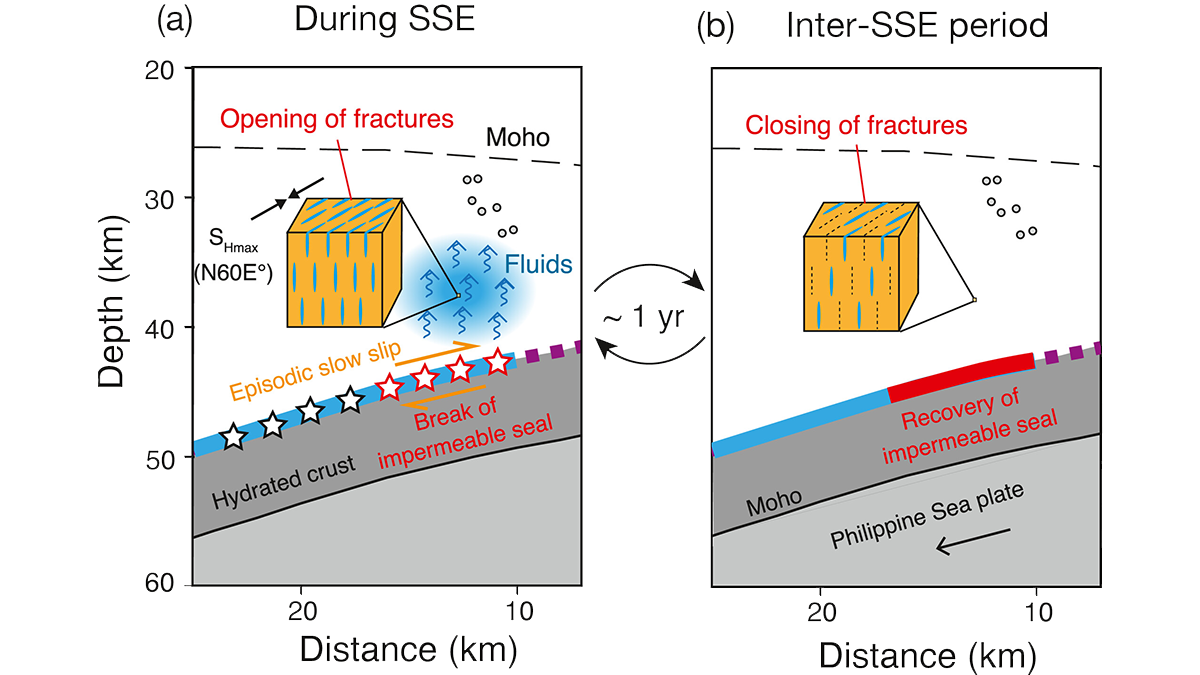
Cyclic Opening of Deep Fractures Regulates Plate Boundary Slip
Seismic anisotropy changes through time suggest that cyclical opening of fluid-filled fractures is synchronized with subduction zone slow slip events.
High-Pressure Reactions Can Turn Nonporous Rocks into Sponges
Mathematical models describe how water moves through rocks in deep Earth.
Sediment Dampens the Impact of Glaciation on Cenozoic Denudation
Rates of continental-scale sediment flux and denudation are similar between glacial and interglacial periods when the aggradation of glacier-eroded sediment inhibits fluvial erosion downstream.
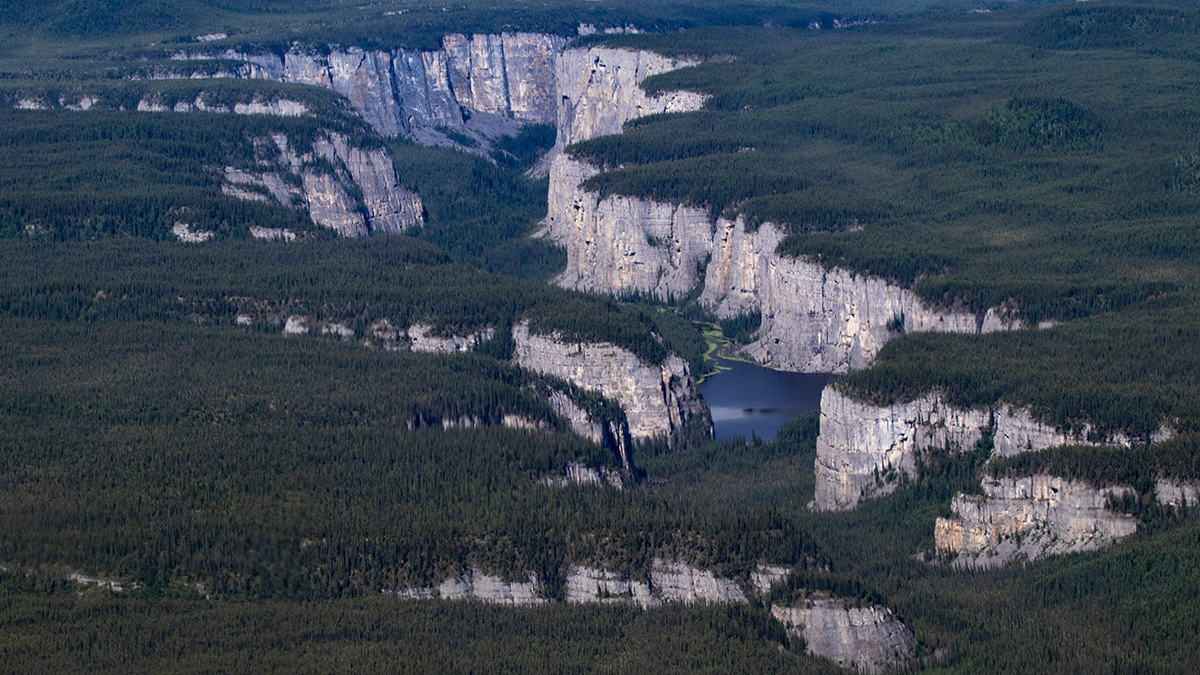
Lithospheric Oddities May Be Sculpting Continental Interiors
Researchers propose a novel explanation for vertical motions of Earth’s surface far from active tectonic plate boundaries.