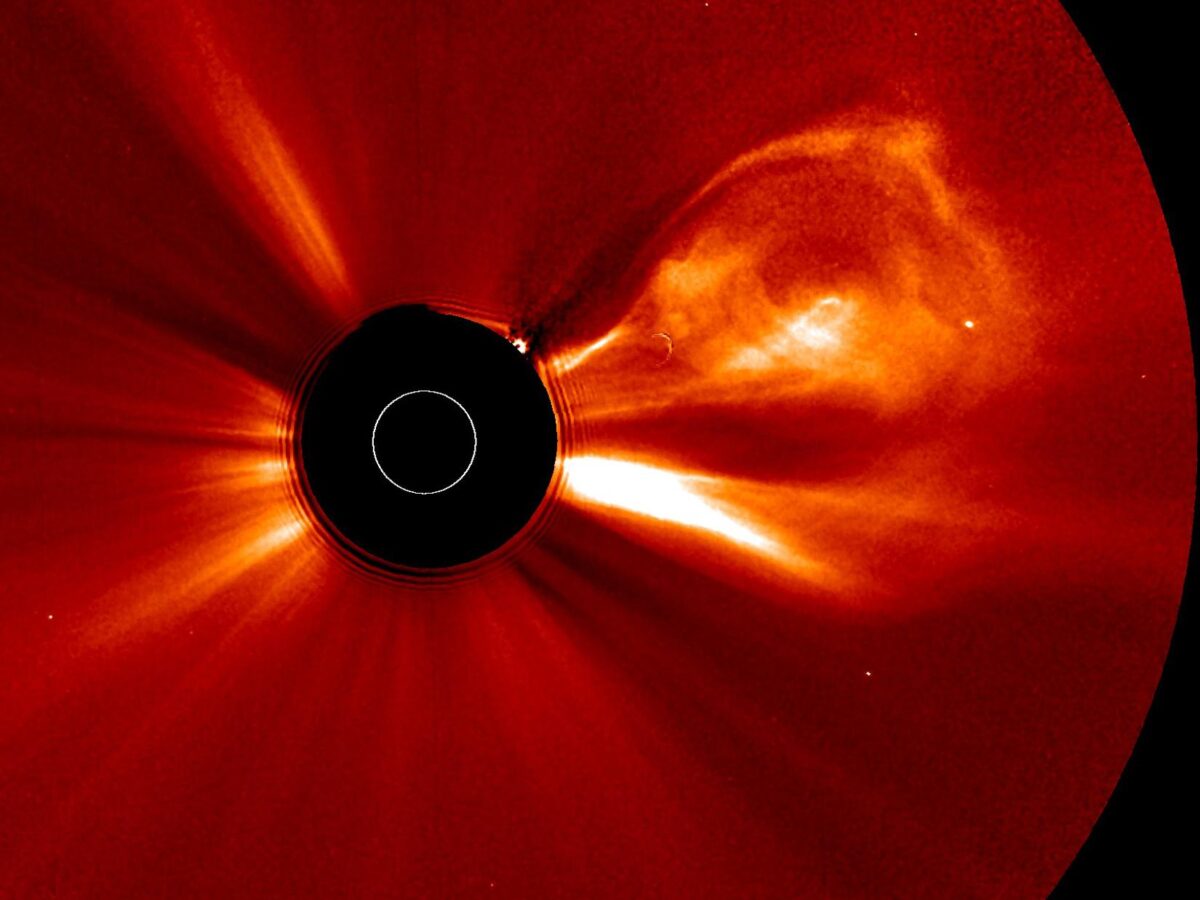
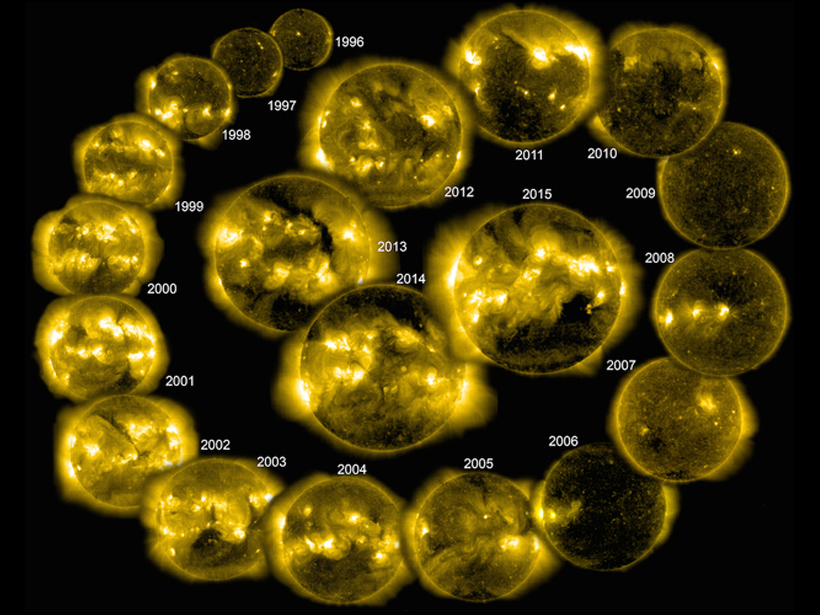
New research suggests that Jupiter's magnetic field replenishes its stock of plasma during lulls in solar activity, creating spectacular displays when a solar storm hits.
solar activity
Tracking Ions at the Edge of the Atmosphere
The first results from a recently launched satellite hold promise for studying solar storms, the very top of Earth's ionosphere, and how the atmosphere is evolving.
Did Solar Flares Cook Up Life on Earth?
Scientists have found that "super" solar flares could have warmed the ancient planet and jump-started life.
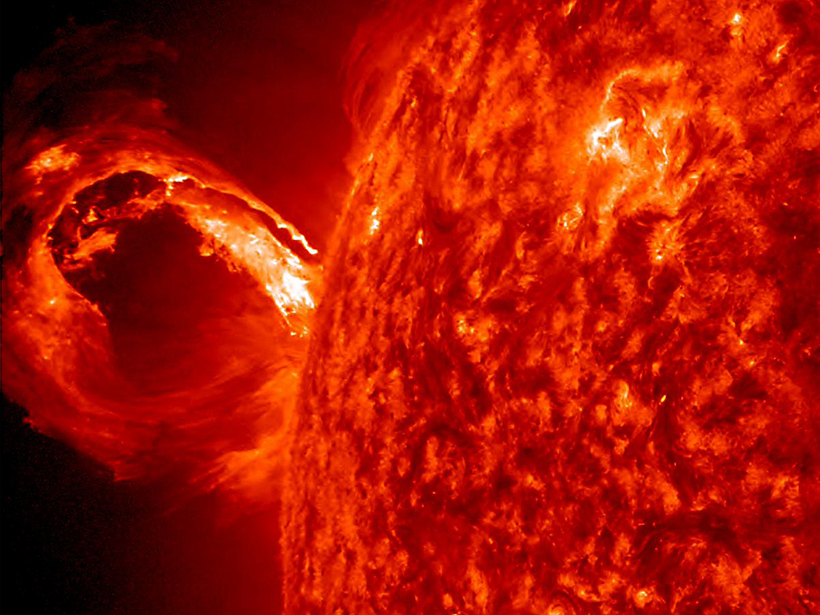
Toward an Understanding of Earth-Affecting Solar Eruptions
Coronal mass ejection forecasting improves with technological developments and increasing availability of data.
Radiation Belt Processes in a Declining Solar Cycle
The Van Allen Probes began an extended mission in November to advance understanding of Earth's radiation belts.
Satellite Shows Earth's Magnetic Field Bent During a Solar Storm
When solar storms strike, they weaken Earth's defenses against harmful radiation. New satellite measurements reveal just how much.
Sun's Magnetic Fields Best at Forecasting Solar Cycle Peaks
Models based on the Sun's polar magnetic fields performed best in simulating the solar cycle and predicting solar behavior.
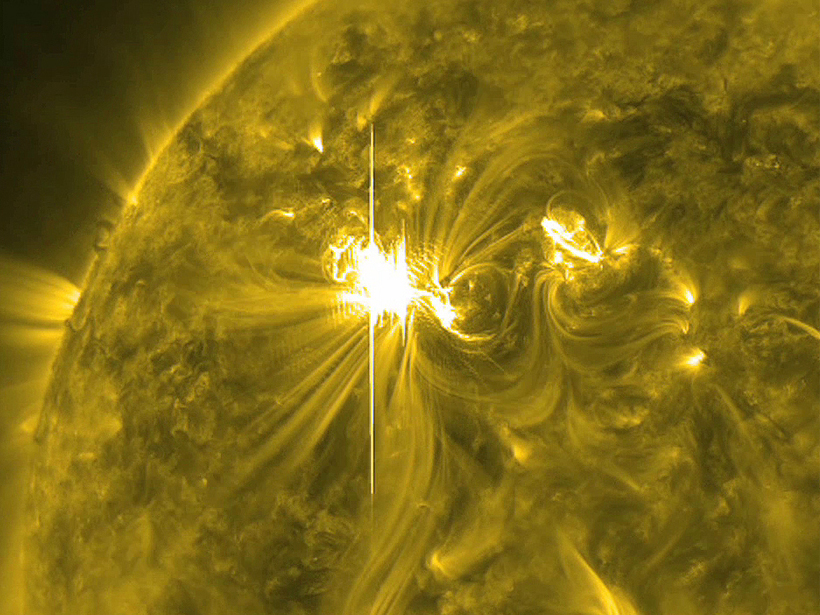
Solar Storms Are More Predictable Than Hurricanes
An encouraging new study finds that solar storms don't propagate chaotically like hurricanes—their arrivals are more predictable, which should make it easier for our planet to prepare for them.
New Space Weather Forecast Technique Fails to Improve Forecasts
For years, scientists have proposed upgrading the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration's solar storm forecasts to account for their tilt as they streak toward Earth. But does it help?
New Model Predicts Big Solar Proton Storms
Forecasts of dangerous solar events could buy time for astronauts en route to the Moon or Mars.