thalia sparling, Heat Spurs Unequal Consumption of Sweet Treats


thalia sparling, Heat Spurs Unequal Consumption of Sweet Treats
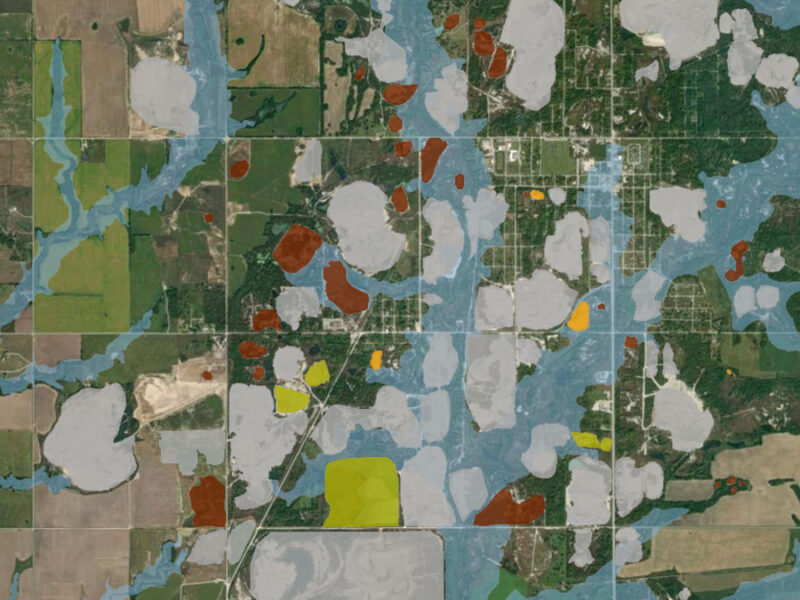
A new study highlights the partnership between scientists and nonscientist community members in building an interactive GIS map to show flooding risk in a Superfund site.
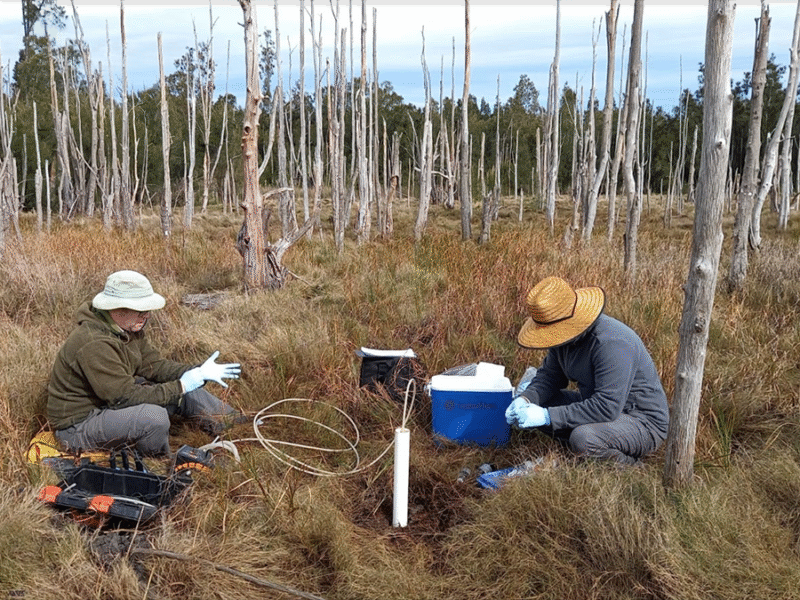

Coastal wetland restoration offers major carbon benefits, and understanding groundwater processes helps explain how these ecosystems store carbon over the long term.
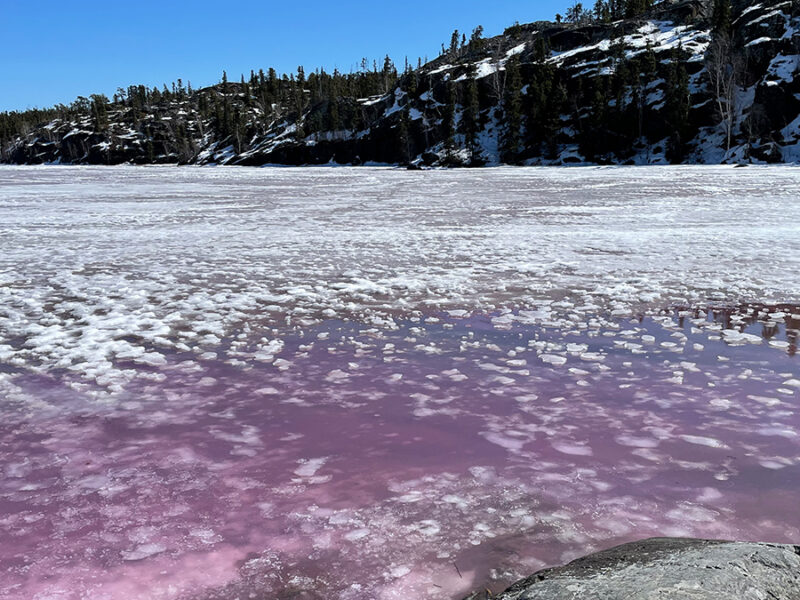

Four lakes near Yellowknife, Canada, show that there’s no one-size-fits-all answer.
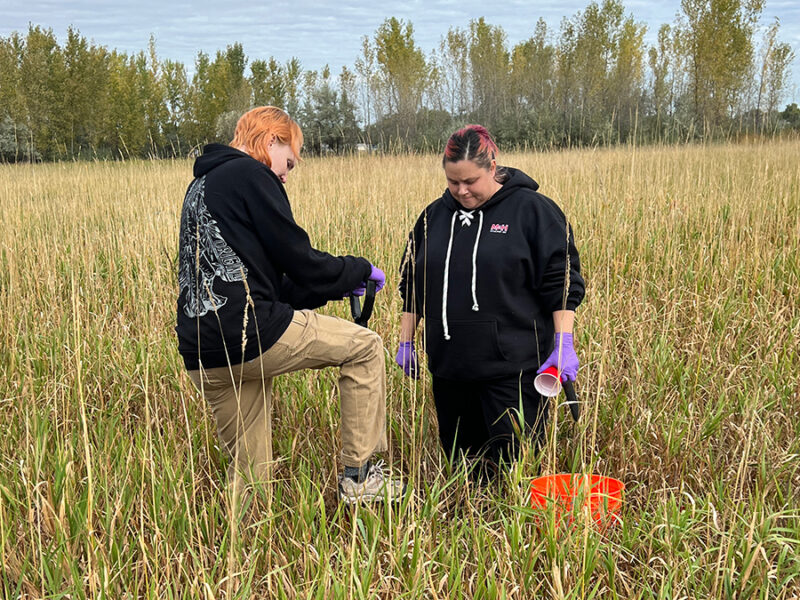

Researchers and students are building a comprehensive picture of the microbial life beneath our feet.
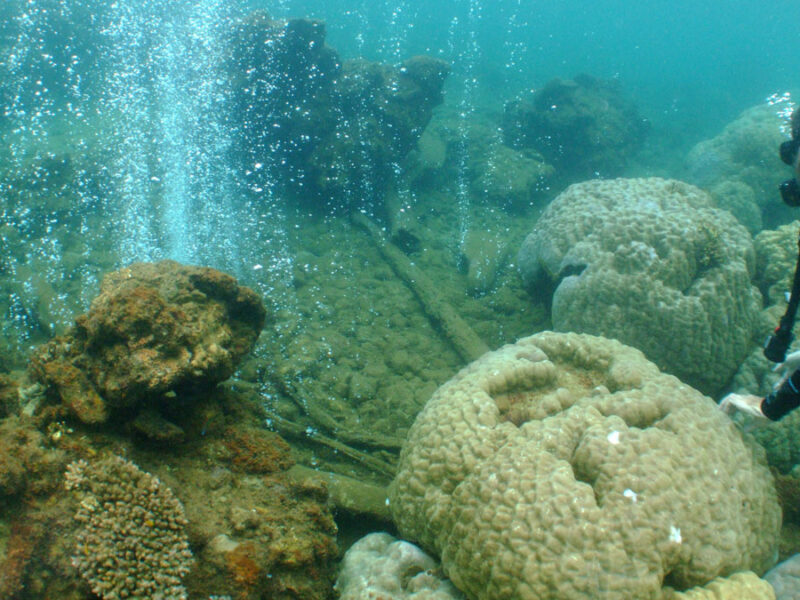

As seawater becomes steadily more acidic, complex branching corals die off and are replaced with hard boulder corals and algae.

The U.S. government entered a partial shutdown Saturday at 12:01 Eastern after the Senate failed to resolve a showdown over funding for DHS and restrictions on ICE.
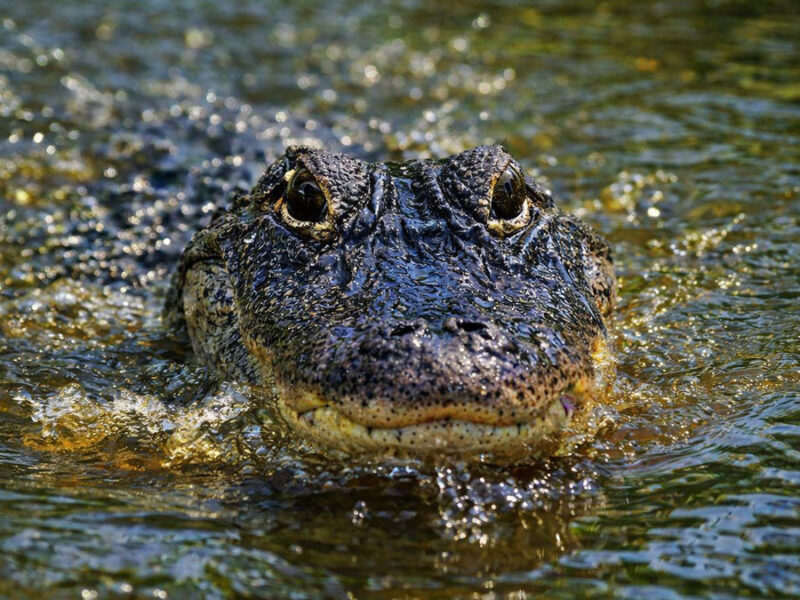

Research suggests that American alligators help coastal wetlands retain more carbon, linking predator recovery in the southeastern United States to ecosystem function and climate processes.
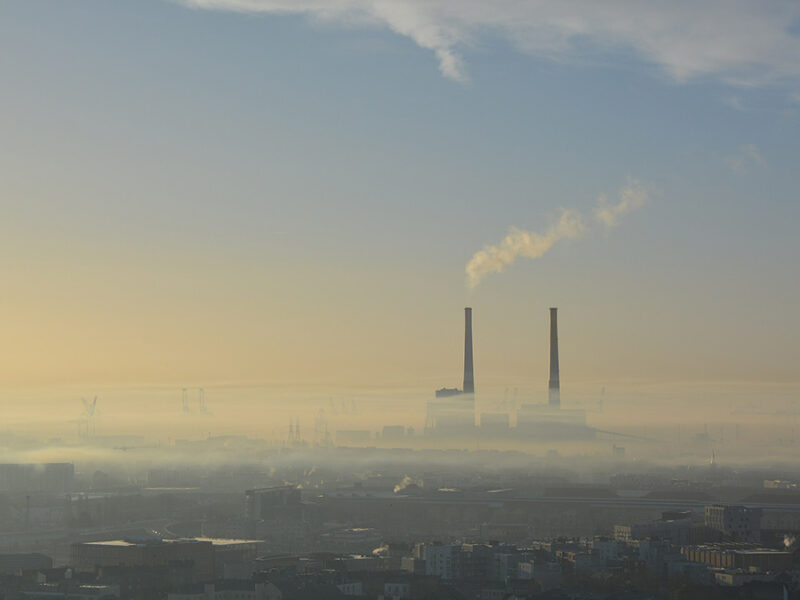

Reducing the effects of air pollution requires estimations of where it costs the most—in both money and lives.
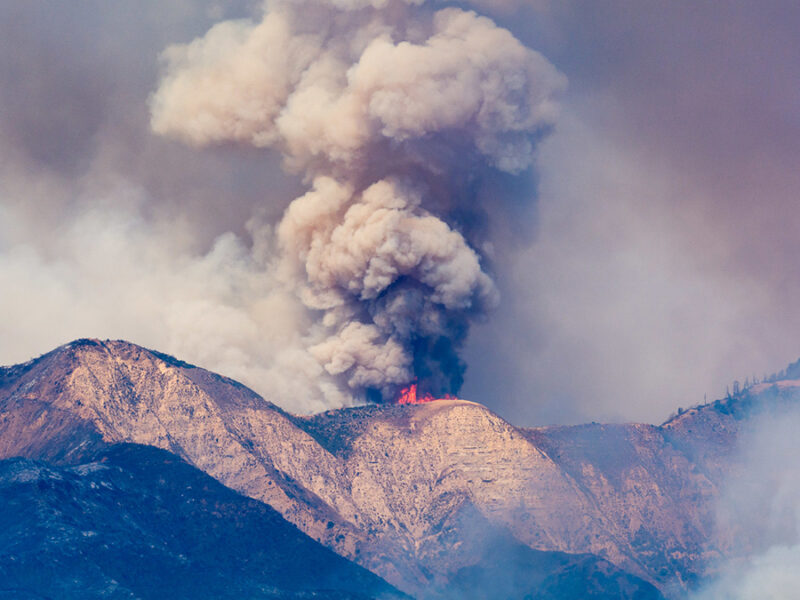

A study of 25 million Medicare participants adds to a body of evidence suggesting that prolonged exposure to wildfire smoke is more harmful to human health than other forms of air pollution.
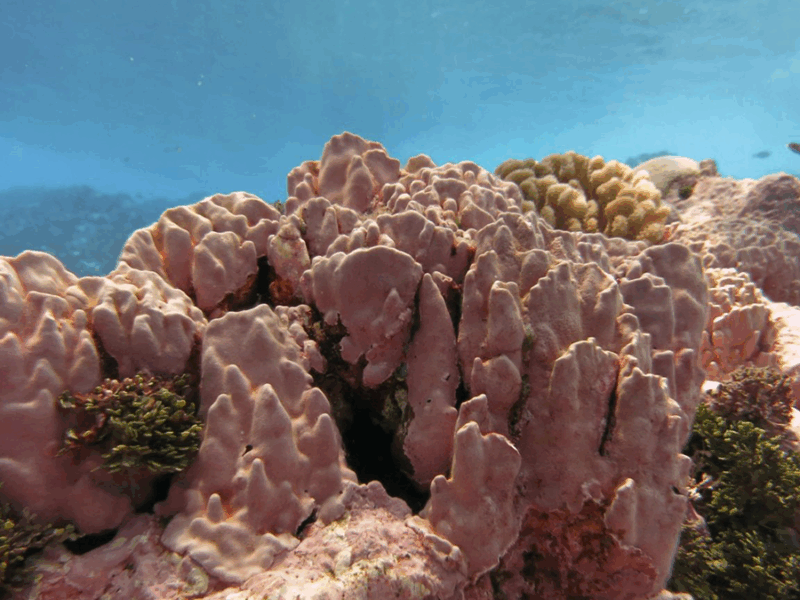

Time-series monitoring shows that a coastal coralline algae reef is naturally exposed to extreme low pH levels, suggesting potential adaptation of this biodiverse habitat to future ocean acidification.
Something went wrong. Please refresh the page and/or try again.