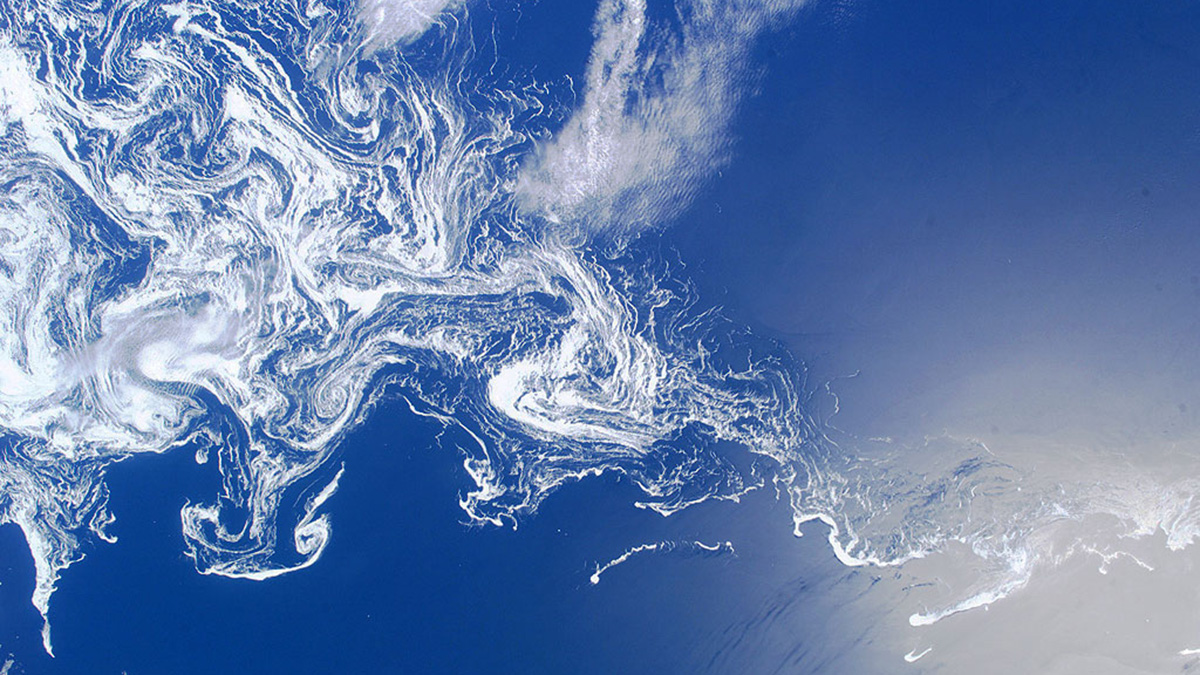
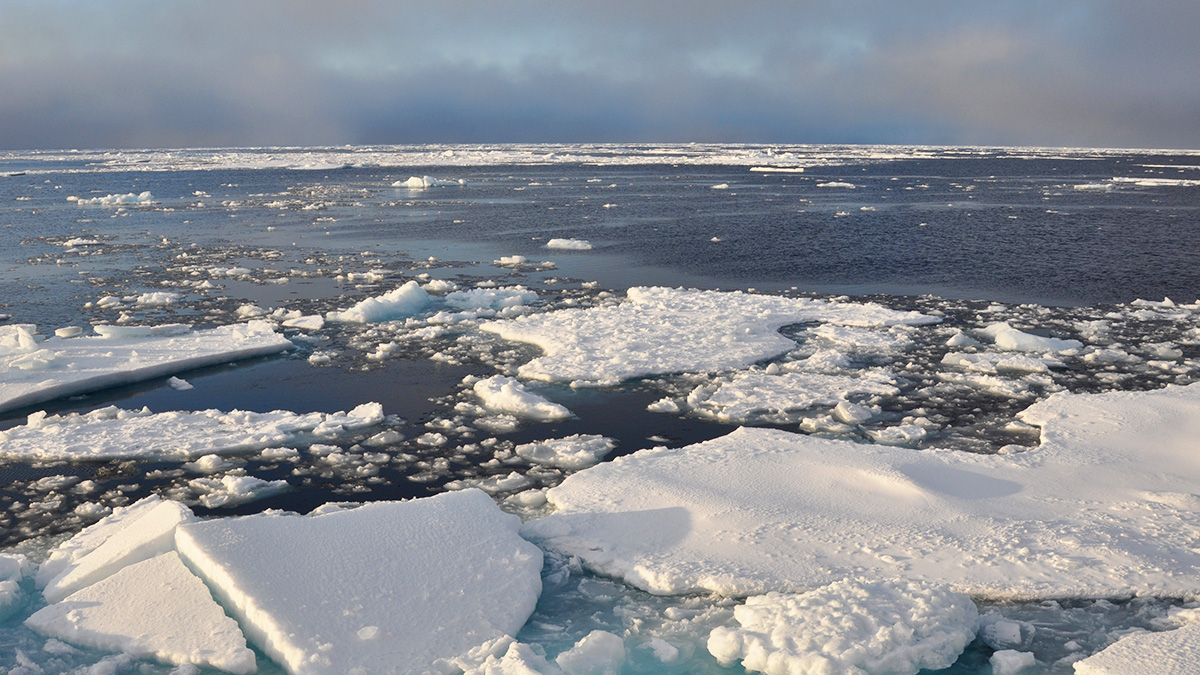
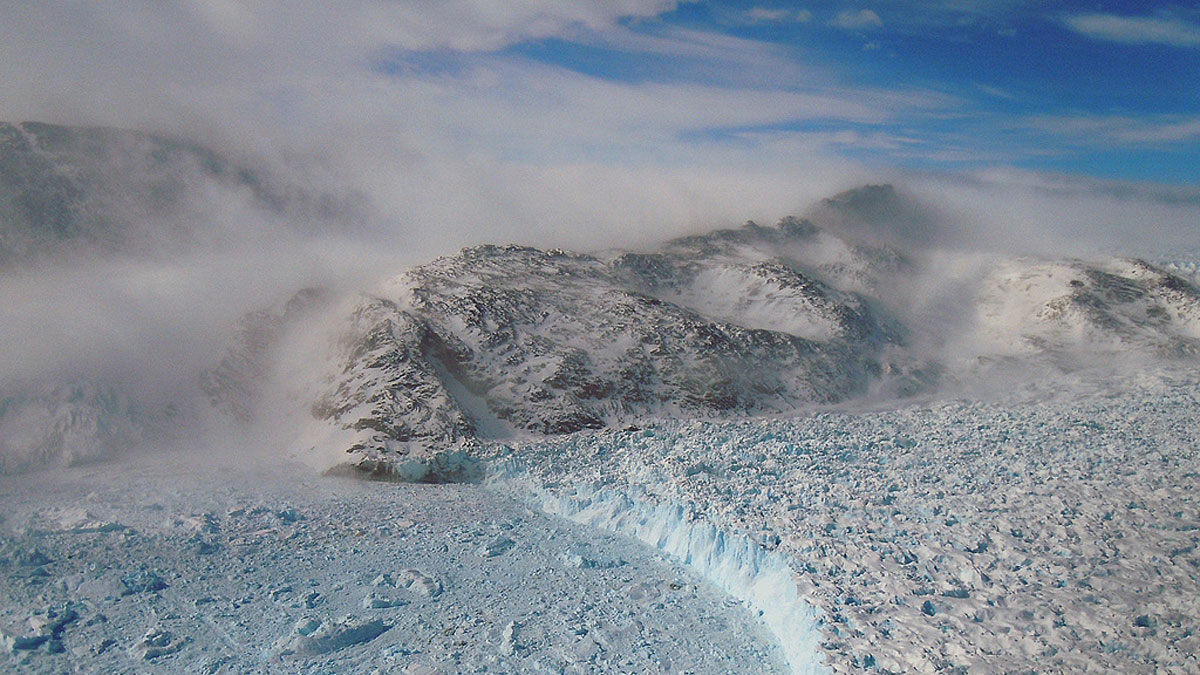
The Labrador Sea “inhales” oxygen and supplies it to deep-sea life across the world. But its breath could be threatened by climate change.
Atlantic Ocean
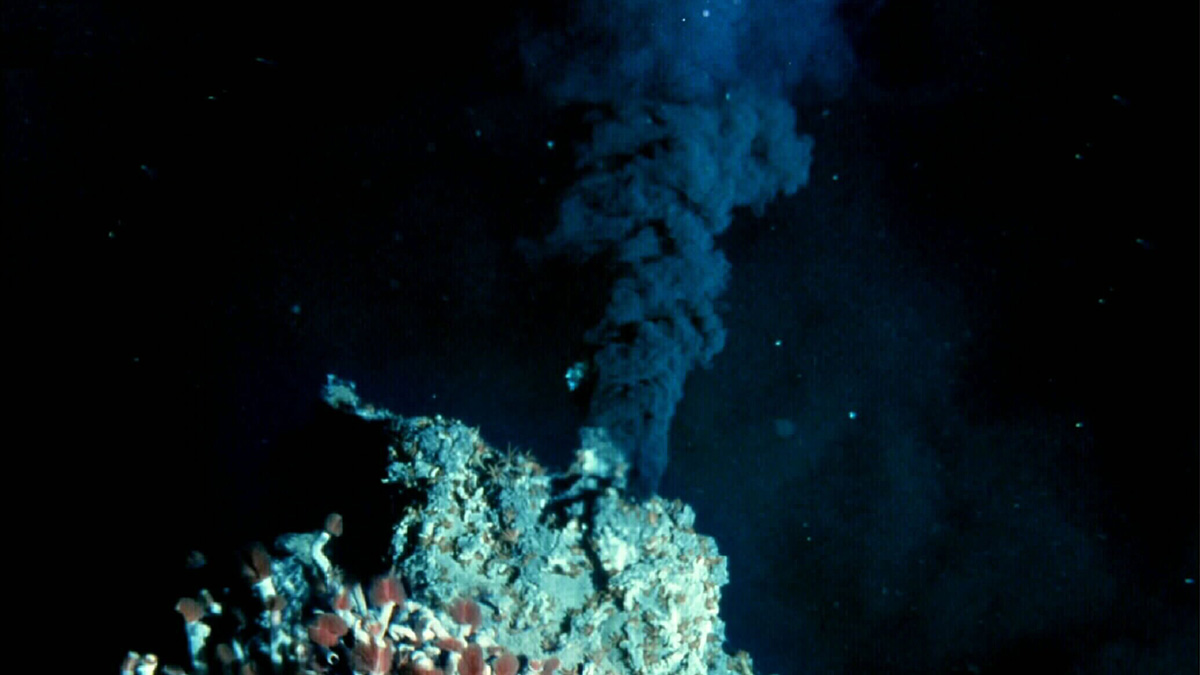
Exploration and Evaluation of Deep-Sea Mining Sites
Two studies chart new territory for the fledgling deep-sea mining industry through advances in the identification and analysis of seafloor hydrothermal mounds.
Tracking Heat Gains and Losses in the Nordic Seas
The Nordic Seas experience influxes of warm water and losses of heat to the atmosphere with knock-on effects on sea ice, glacier retreat, and carbon dioxide uptake.
Mapping a River Beneath the Sea
A recent expedition mapped one of the world’s longest submarine channels, revealing previously undiscovered physical features and raising questions about its unusual origin and shape.
The Role of Magma in the Birth of the Atlantic Ocean
High-resolution seismic models of the Nova Scotia margin reveal a role for magmatism in continental breakup, even at magma-poor sections of the eastern North American margin.
Nonlinear Effects of Wind on Atlantic Ocean Circulation
Simulations reveal the influence of reduced and enhanced wind stress on the Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation.
“Sticky” Ice Sheets May Have Led to More Intense Glacial Cycles
New research attributes a shift to longer, stronger glacial cycles to increased friction between ice sheets and bedrock in the Northern Hemisphere 1 million years ago.
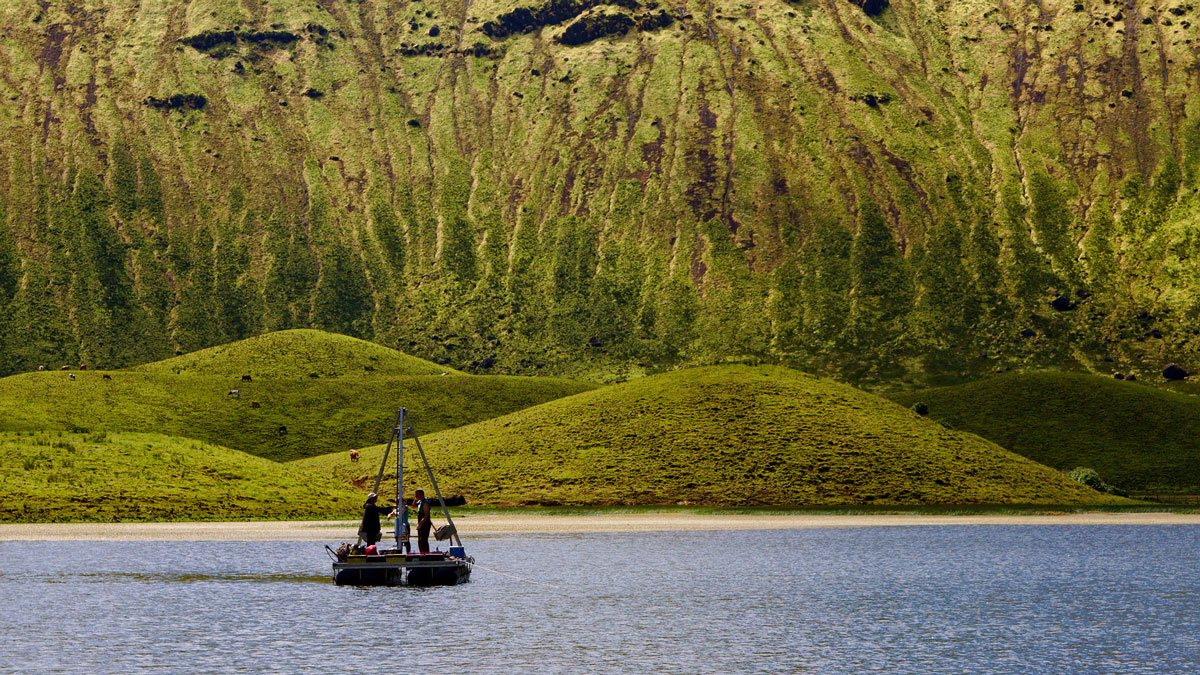
Sediments Suggest Vikings May Have Been the First to Settle the Azores
A multidisciplinary team studying lake sediments and climate change found evidence that the archipelago was inhabited 700 years earlier than historical sources claim.
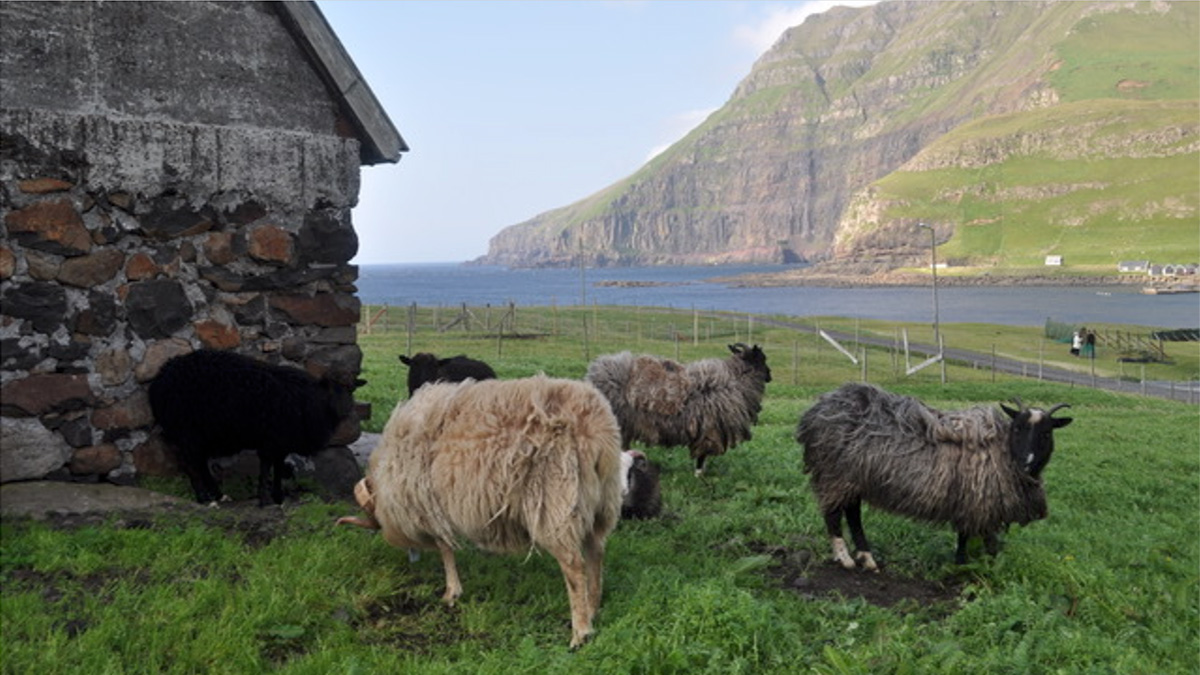
Ancient Eruptions Reveal Earliest Settlers on the Faroe Islands
Lake sediment is helping scientists resolve a decades-long historical mystery.
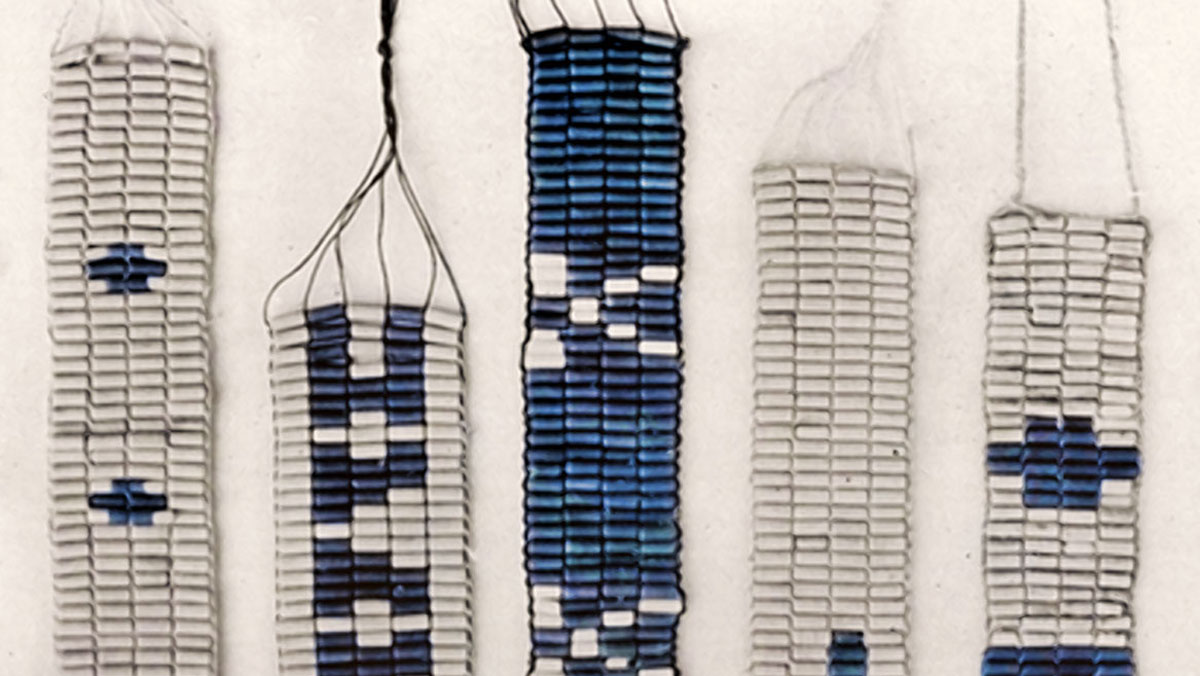
WAMPUM: An Indigenous-Designed Path to Sea Level Rise Adaptation
Northeastern and mid-Atlantic tribal nations lived sustainably on the coastline for centuries before colonization. How can their experiences inform strategies for sea level rise adaptation?