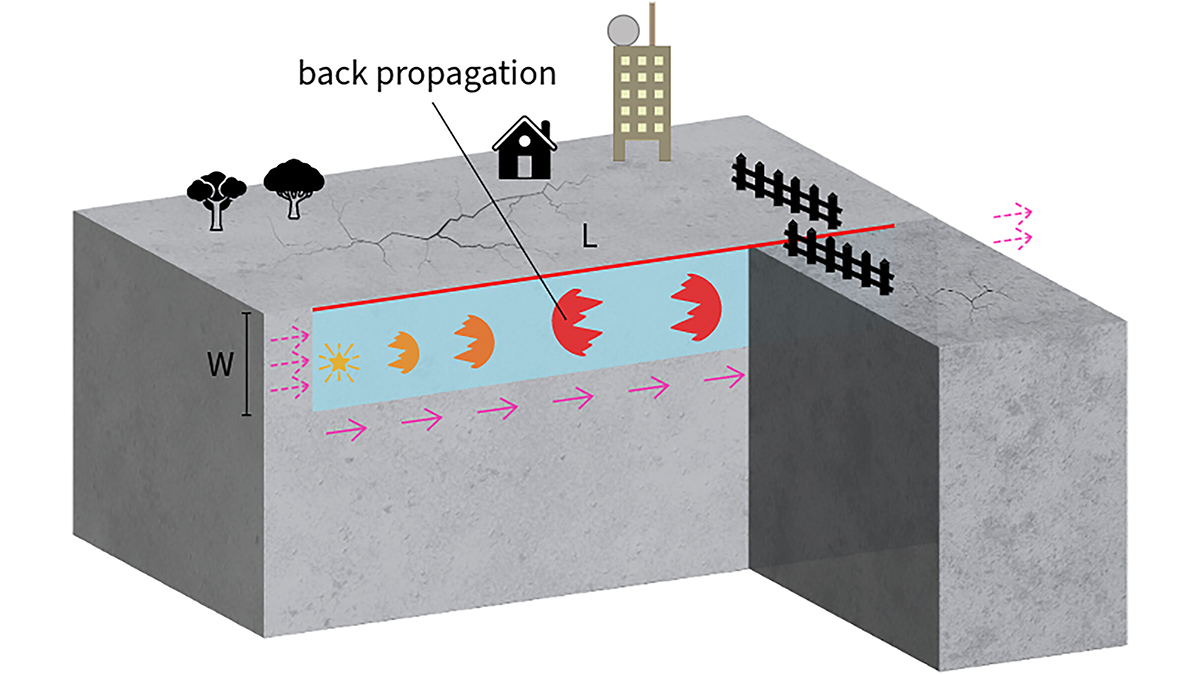
New simulations show earthquakes can reverse direction within seconds on simple, uniform faults, suggesting back-propagating subevents are more common than previously thought.
Natural hazards
The State of the Science 1 Year On: Health and Safety
The Trump administration has holistically reevaluated the government’s relationship—and how it responds to threats— to the health and welfare of its citizens.
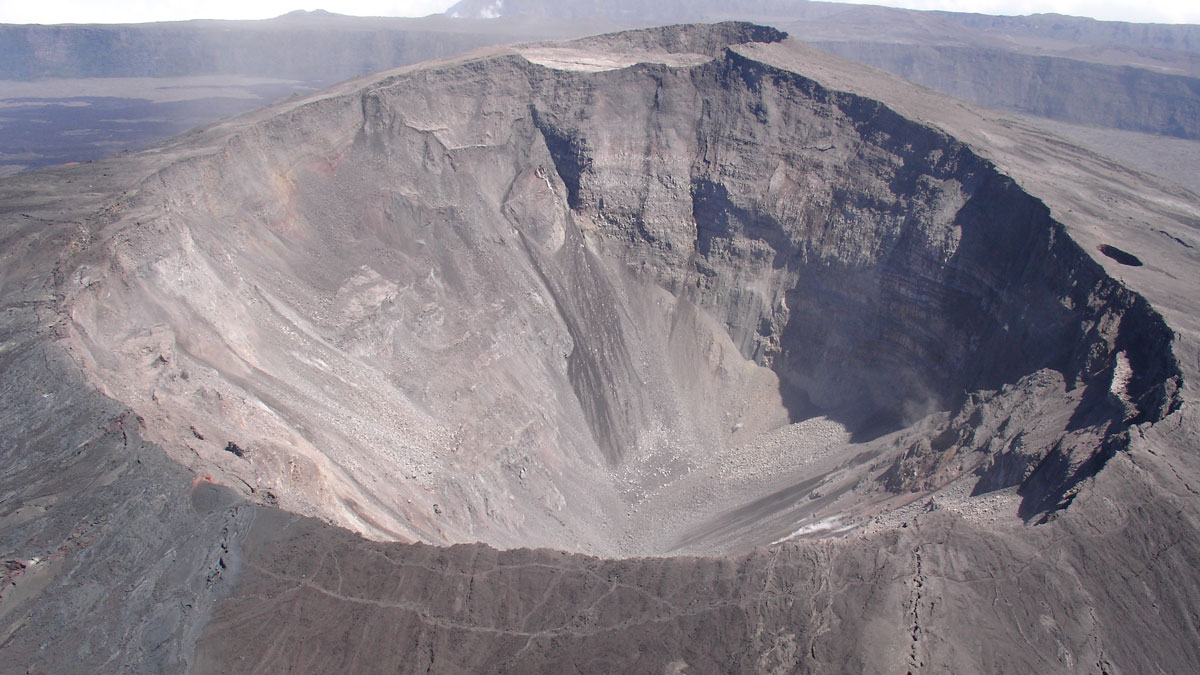
Lessons and Lingering Questions from Collapsing Basaltic Calderas
Research into the hazardous collapses of basaltic volcanoes has revealed common physical processes, but addressing remaining questions requires learning more from historical events.
2025 State of the Climate Report: Our Planet’s Vital Signs are Crashing
A yearly analysis of climate change’s progress and effects shows a “planet on the brink” of ecological breakdown and widespread crisis and suggests that only rapid climate mitigation able to avoid the worst consequences.
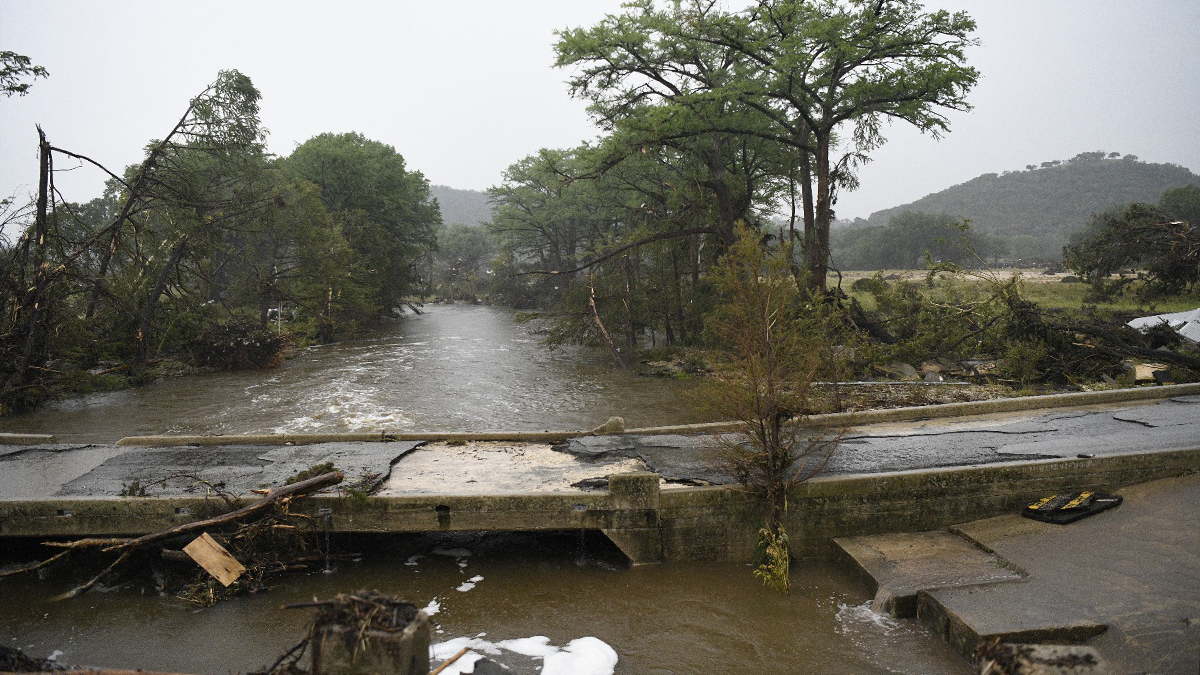
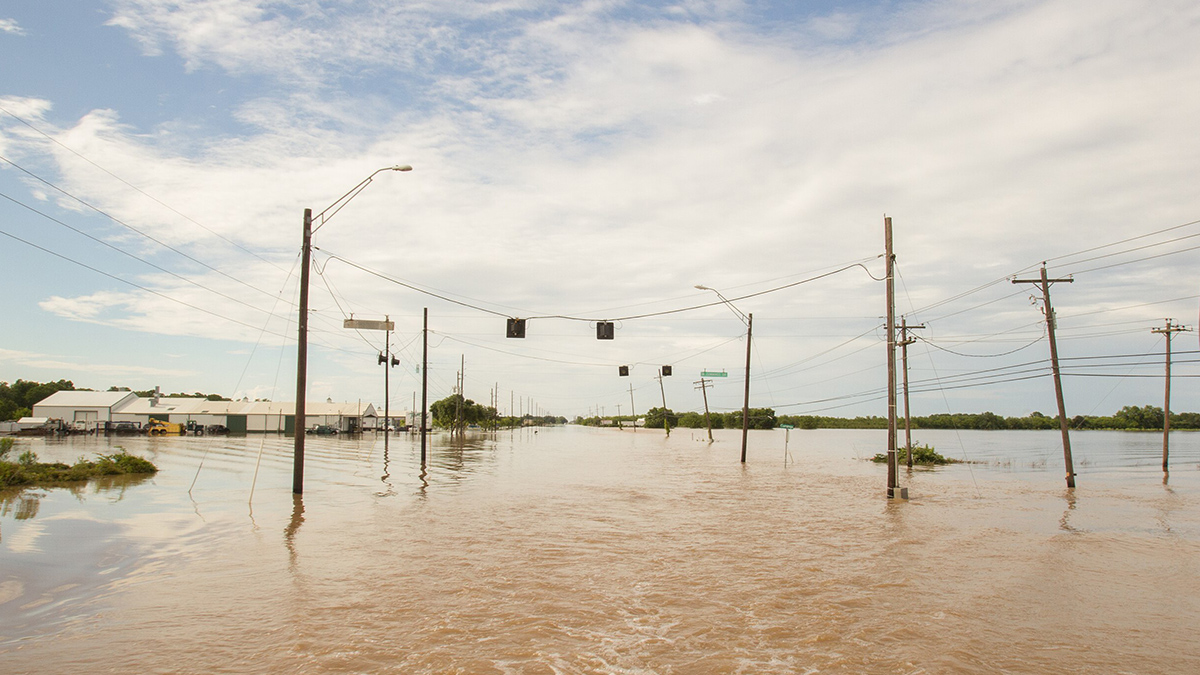
Alaska Awaits Response from FEMA in the Aftermath of Major Floods
Major floods in Alaska have caused the death of at least one person and displaced thousands more over the course of the last two weeks. Many of the displaced may not be able to return home for 18 months or longer, according to Alaska Gov. Mike Dunleavy.
When the Earth Moves: 25 Years of Probabilistic Fault Displacement Hazards
Surface ruptures causing earthquakes pose risks to infrastructure and human lives, but advances in models and data in the last few decades have improved our ability to mitigate their effects.
New 3D Model Reveals Geophysical Structures Beneath Britain
Using magnetotelluric data to identify subsurface electrically conductive and resistive areas, scientists can identify underground features and predict how space weather may affect infrastructure.
Científicos revelan los peligros ocultos del calor y las inundaciones en Texas
Una parte más amplia del “Estado de la Estrella Solitaria” podría verse afectada por más olas de calor e inundaciones de lo que sugieren registros previos.
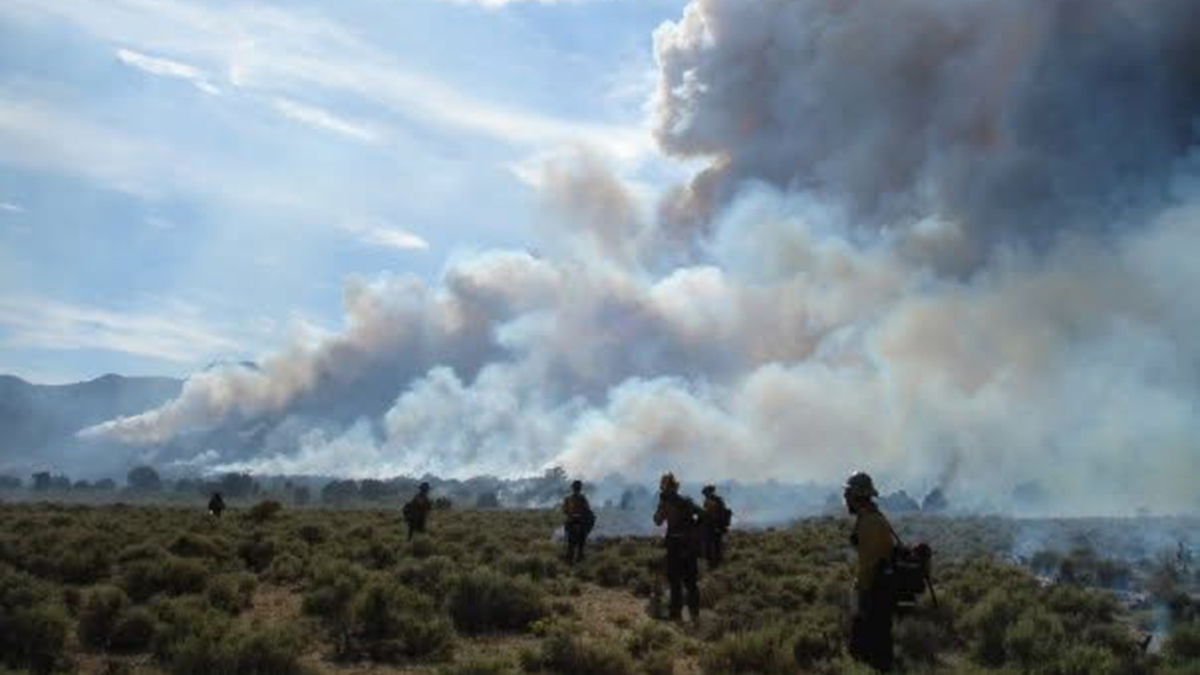
The Goldilocks Conditions for Wildfires
Twenty years of data from around the world show that areas that are not too dry and not too wet are most conducive to wildfire burning.
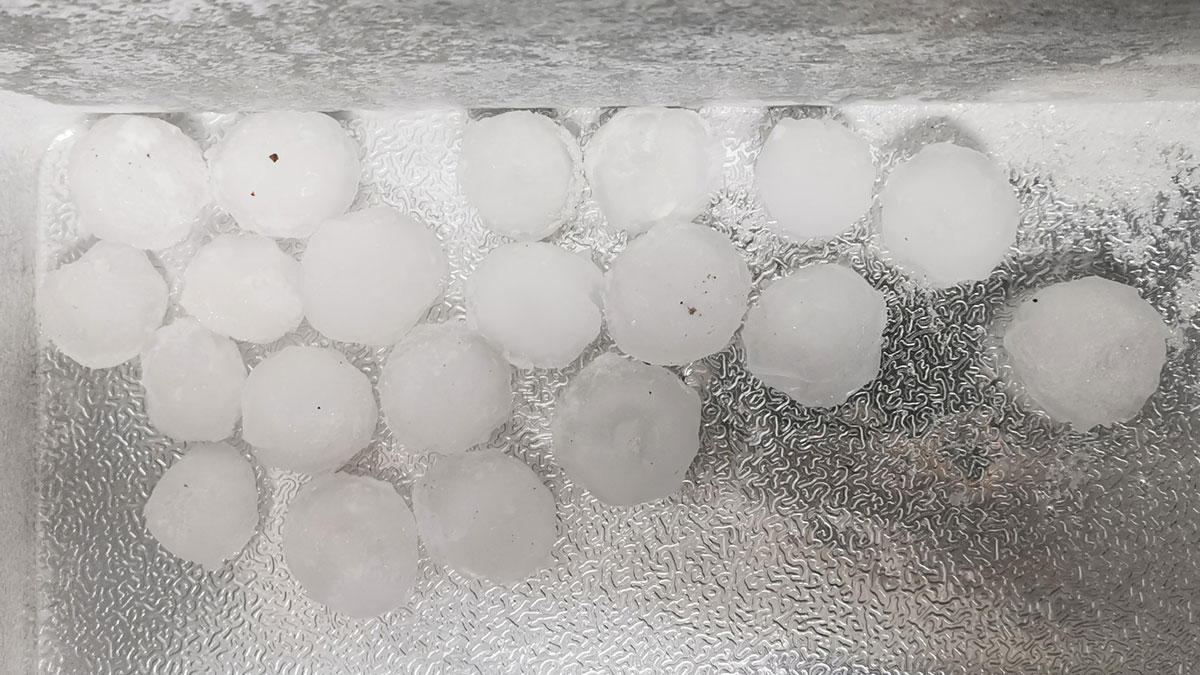
Isotopes Map Hailstones’ Paths Through Clouds
Hailstones have been said to bounce up and down through clouds as they grow. A new study found that many stones take much simpler paths.