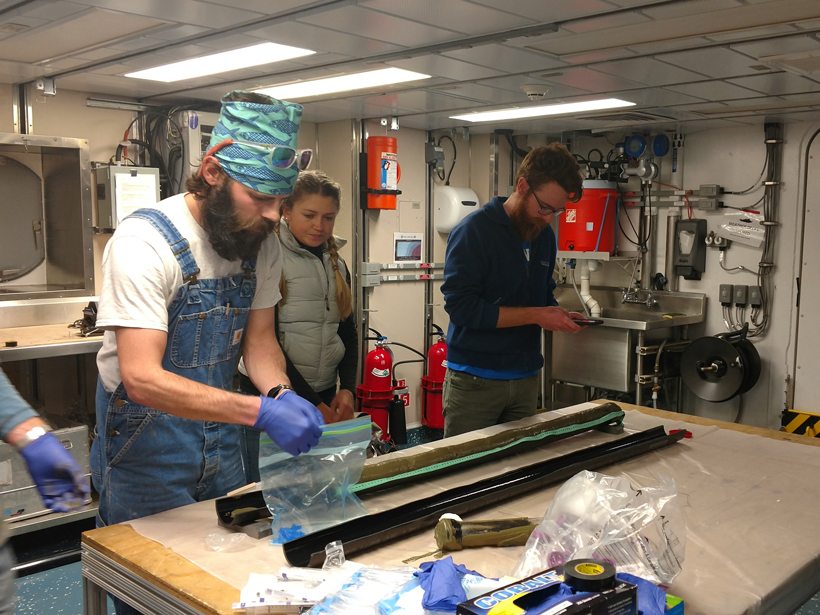
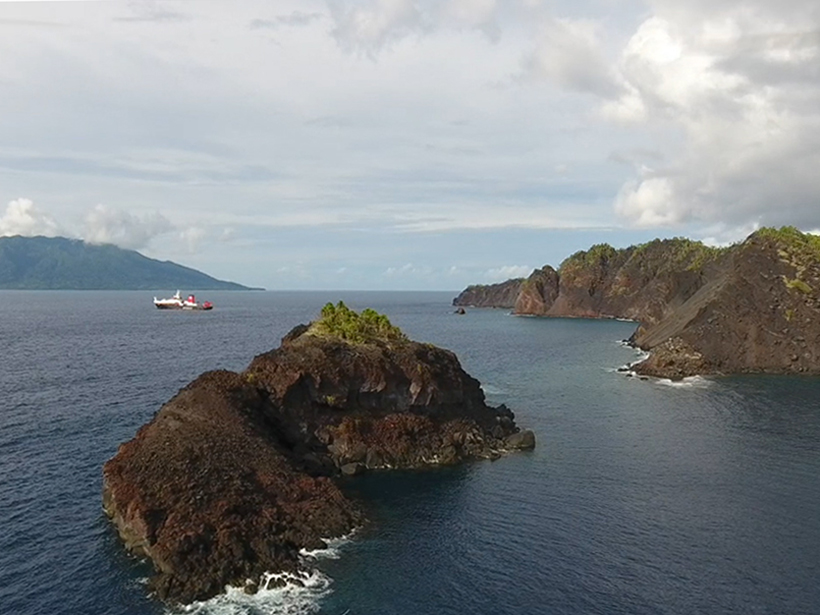
Researchers probe millennia-old deep-ocean sponges for links between ocean nutrients and climate.
Pacific Ocean
Calm Waters off Hawaii Harbor a “Nursery” of Sea Life
Ocean slicks—naturally occurring bands of smooth water—are home to an astounding diversity of fish larvae and other marine life, researchers show.
Plotting the Pliocene Polar Front
Understanding changing conditions in the south polar oceans during the warm late Pliocene period may help predict the impact of contemporary warming.
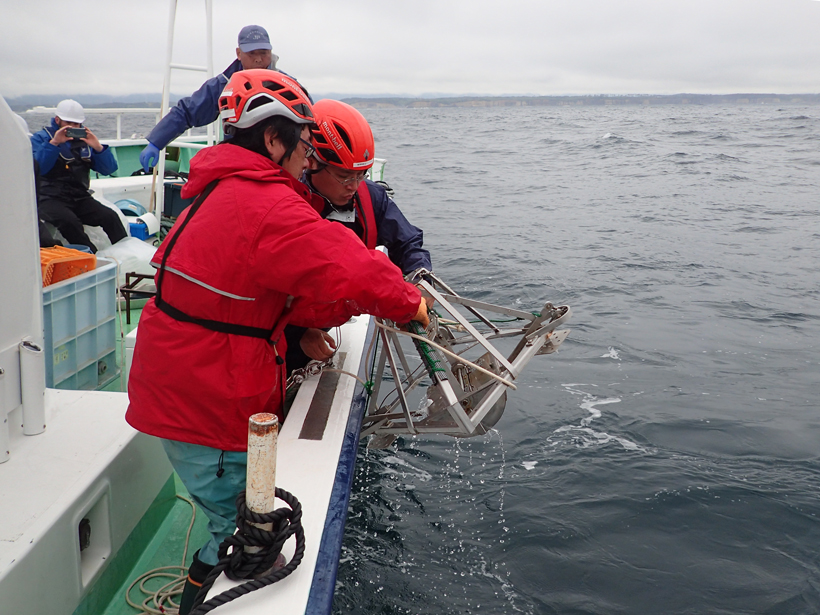
Exploring Methane Gas Seepage in the California Borderlands
Early-career scientists aboard the 2016 UNOLS Chief Scientist Training Cruise explored recently reactivated underwater methane seeps in the San Diego Trough.
Threatened Sea Turtles in Hawaii Losing Ground to Rising Oceans
By midcentury, the Hawaiian green sea turtle could lose nesting beaches of increasing importance on Oahu, the most populous island in the chain.
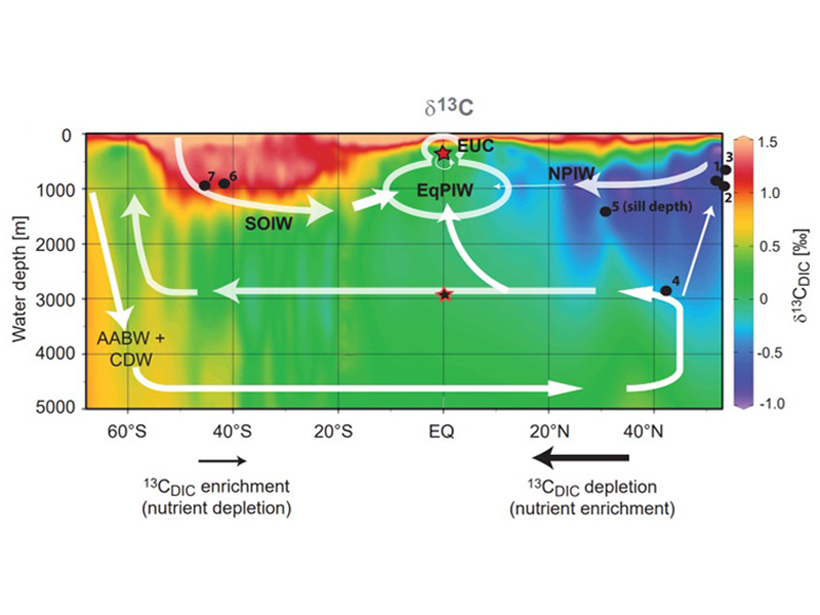
“North Pacific Nutrient Leakage” During Glacials
Carbon isotope data suggest an alternative source of nutrients to the Eastern Equatorial Pacific during glacial periods.
Is Global Warming Suppressing Canonical El Niño?
A study explores the relationship between diverse El Niño events and the background state of the tropical Pacific.
Microfossils Illuminate Ancient Ocean Currents
Researchers use dissolved silicon concentrations to map out how currents may have changed millennia ago in the Pacific.
IAEA Affirms Japan’s Fukushima-Related Radioactivity Monitoring
Laboratories outside Japan have validated the results. Marine radioactivity levels from the nuclear disaster have fallen, but questions remain years after the meltdown.
An 1888 Volcanic Collapse Becomes a Benchmark for Tsunami Models
When volcanic mountains slide into the sea, they trigger tsunamis. How big are these waves, and how far away can they do damage? Ritter Island provides some answers.