New detection of millimeter-scale subsidence along vulnerable coastlines means flood risk predictions may be inaccurate.
satellites
A Cloud-Based Solution to a Radar Data Deluge
An open-science tool built to support NASA missions is making synthetic aperture radar, once the domain only of subject matter experts, more accessible for nonspecialists and real-world applications.
An All-Community Push to “Close the Loops” on Southern Ocean Dynamics
A new study highlights the connected nature of the Southern Ocean dynamic system, the research priorities needed to understand its influence on climate change, the importance of cross-disciplinary collaborations.
Data to Decisions: Changing Priorities for Earth Observations
NASA is updating how it designs and implements Earth science missions to ensure their data and science reach users and decisionmakers faster and more effectively.
Fixing Pollution from Space Needs Global Coordination
Remote sensing is a tool of choice for monitoring regions for air pollution, but the scale of the problem requires extending geostationary soundings globally.
From Sun to Earth: A New Network for Comprehensive Space Weather Monitoring
The Chinese Meridian Project combines hundreds of instruments for a detailed, three-dimensional view of the solar-terrestrial environment.
Using Satellite Data to Estimate Atmospheric CO2 Growth Rates
A new method improves growth rate estimates of carbon dioxide increase in the atmosphere by combining the standard NOAA approach with satellite data.
New Method Reveals Hidden Structures in Clear-Sky Vertical Motion
High-resolution satellite data reveal unexpected, highly heterogeneous vertical motions in the clear-sky atmosphere, with a new method proposed for measuring these motions.
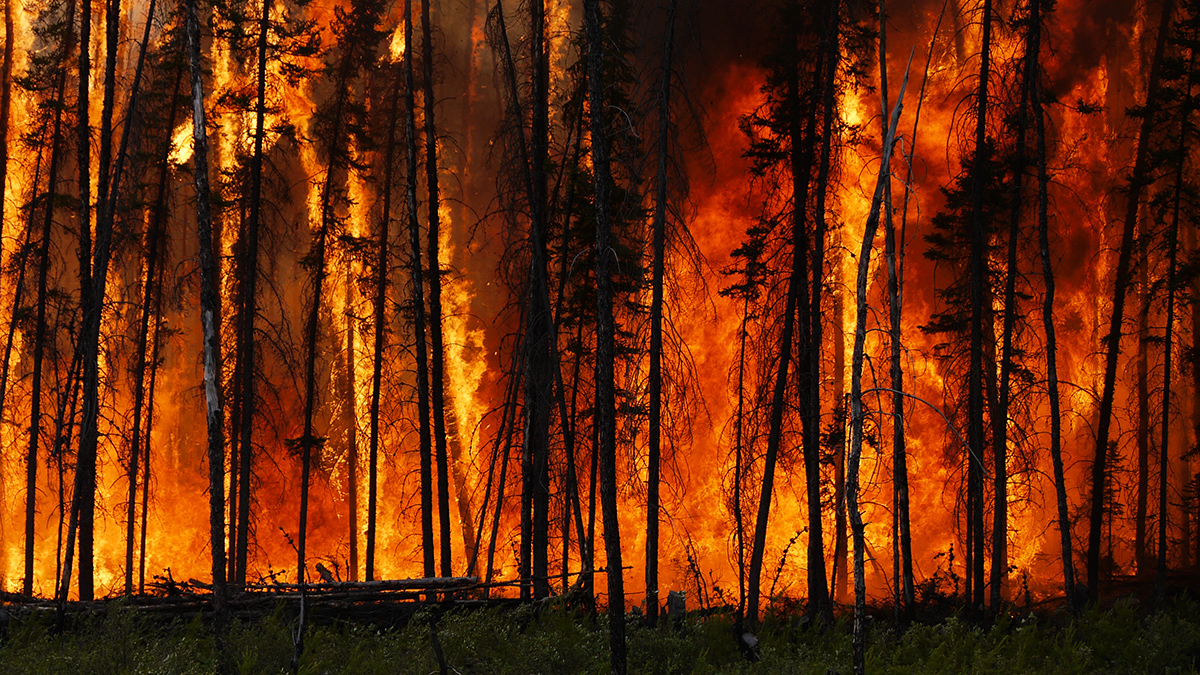
Extreme Wildfires Are Getting More Extreme and Occurring More Often
The world’s most energetic wildfires have doubled in intensity and number over the past 2 decades, with climate change and land management likely to blame.
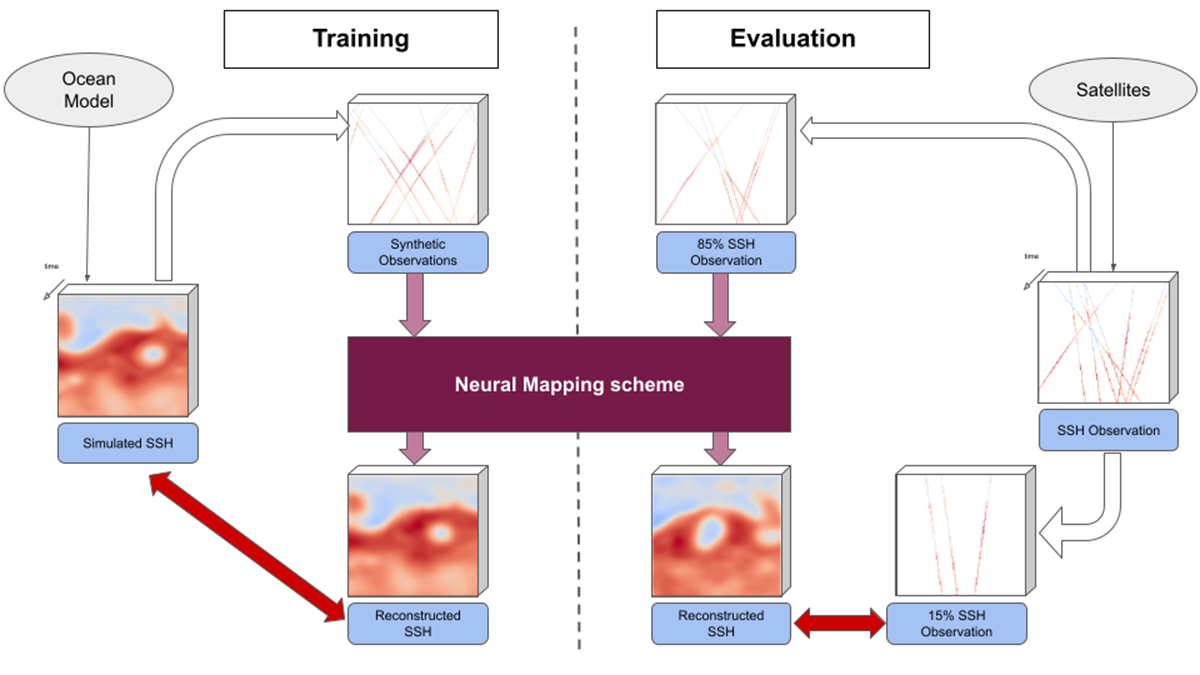
Physics + Machine Learning Provide a Better Map of Ocean Measurements
A new study offers a compelling example where the merger of dynamical modeling, machine learning, and ocean measurements enhances oceanographic understanding, monitoring, and mapping.