Earth’s magnetosphere controls ionospheric total electron content modulation via plasma wave-induced electron loss impacting GPS spatial location determination.
satellites
Imaging Magma from Afar
Reservoirs of magma and fluids in the crust create gravity anomalies detectable by altimetry, which can help find submarine volcanoes and provide key insights into their depth, shape and volume.
Climate Change Is Driving Dangerous Bacteria Farther North
Satellite data could help address rising rates of vibriosis infections, often the result of eating undercooked seafood, along the East Coast of the United States.
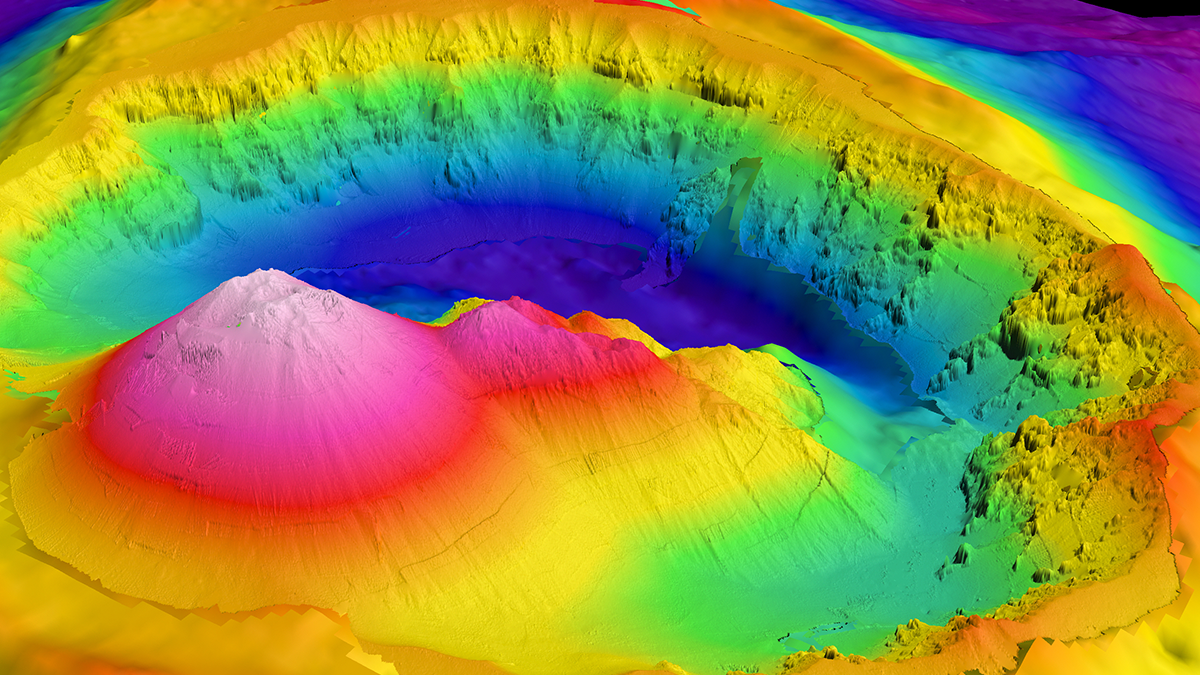
Satellite Measurements Make Major Seafloor Map Improvements
Though ship-based sounding has mapped some areas of the ocean floor in higher resolution, researchers have used SWOT data to create a detailed new map of the seafloor, including thousands of previously undetected small seamounts.
The Survival of Arctic Sea Ice May Depend on Its Travel Routes
Researchers find that the motions of ice parcels determine which ones survive the annual summer melt.
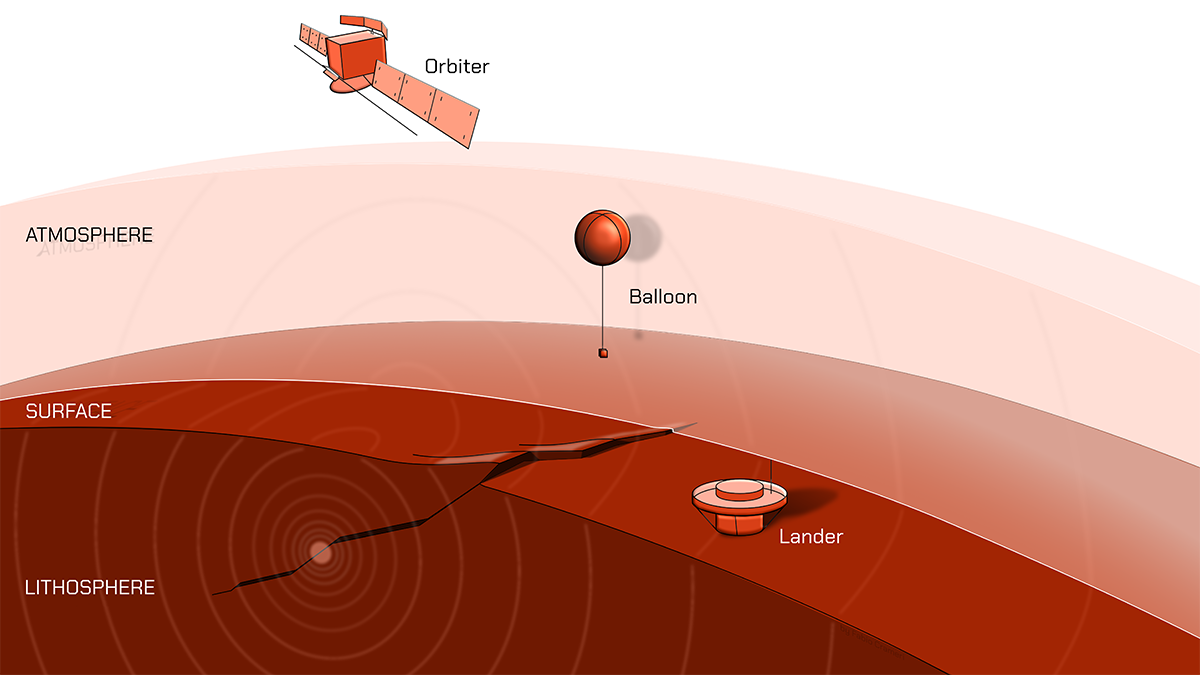
Three Ways to Track Venusquakes, from Balloons to Satellites
The planet’s harsh conditions make studying seismicity challenging, but it is likely possible.
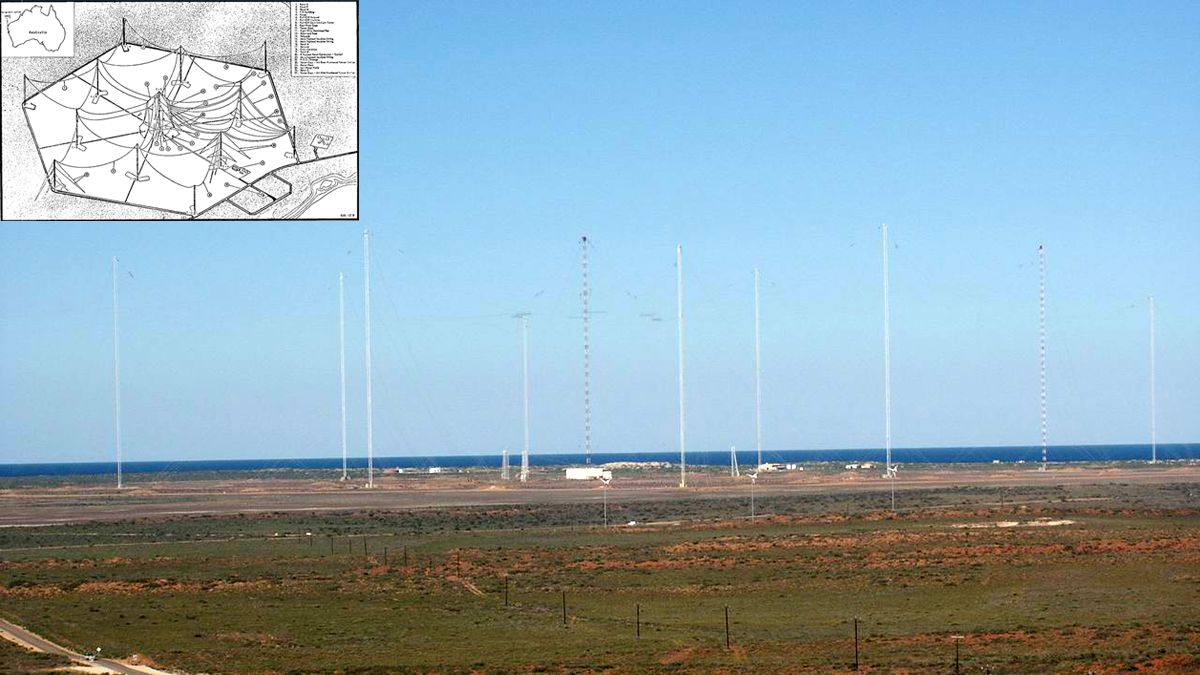
Ground-based Transmitters Cause Radiation Belt Electron Loss
A U.S. Navy transmitter in Australia produces wisps of electron loss as observed by the Colorado Inner Radiation Belt Experiment (CIRBE) CubeSat in Low Earth Orbit.
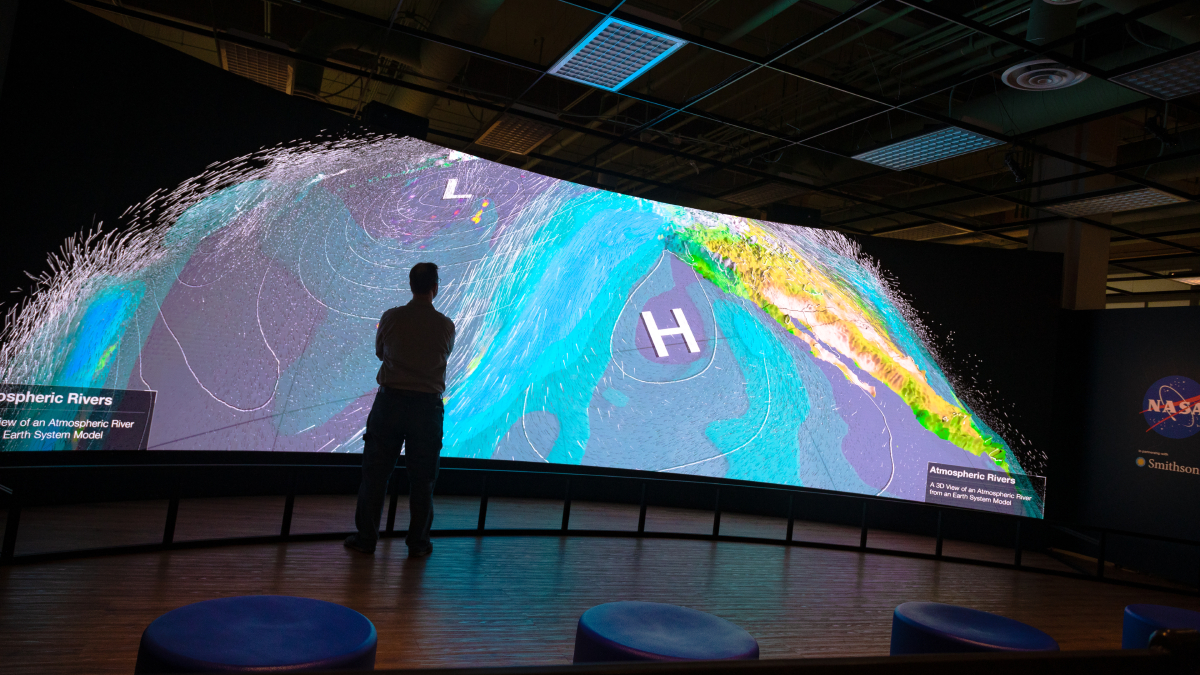
Smithsonian Exhibit Connects Sky-High Views with Down-Home Impacts
“Preserve and cherish the pale blue dot, the only home we’ve ever known.”
Improvements to Measuring the Ups and Downs of the Landscape
If you are a jazz fan, you may be familiar with Ella Fitzgerald singing ‘How deep is the ocean, how high is the sky’. Using data from the Shuttle Radar Topography Mission we now know how high the land really is.
Unlocking the Power of Synthetic Aperture Radar for Geosciences
Due to its unique ability to monitor Earth’s surface, Synthetic Aperture Radar plays a pivotal role in revolutionizing the geosciences.