Developing shared cyberinfrastructure can enhance predictions of ecological change and enable improved decisionmaking for resource management and public well-being.
transdisciplinary science
Creating Communities to Help Interdisciplinary Scientists Thrive
Solving complex challenges often requires diverse expertise, but skepticism remains within traditional academic institutions and mindsets regarding interdisciplinary science and scientists.
Las olas de calor marinas lentifican el flujo de carbono de los océanos
Cuando el plancton se encuentra en agua caliente, la materia orgánica se estanca en la superficie e interrumpe el transporte de carbono hacia el fondo océanico.
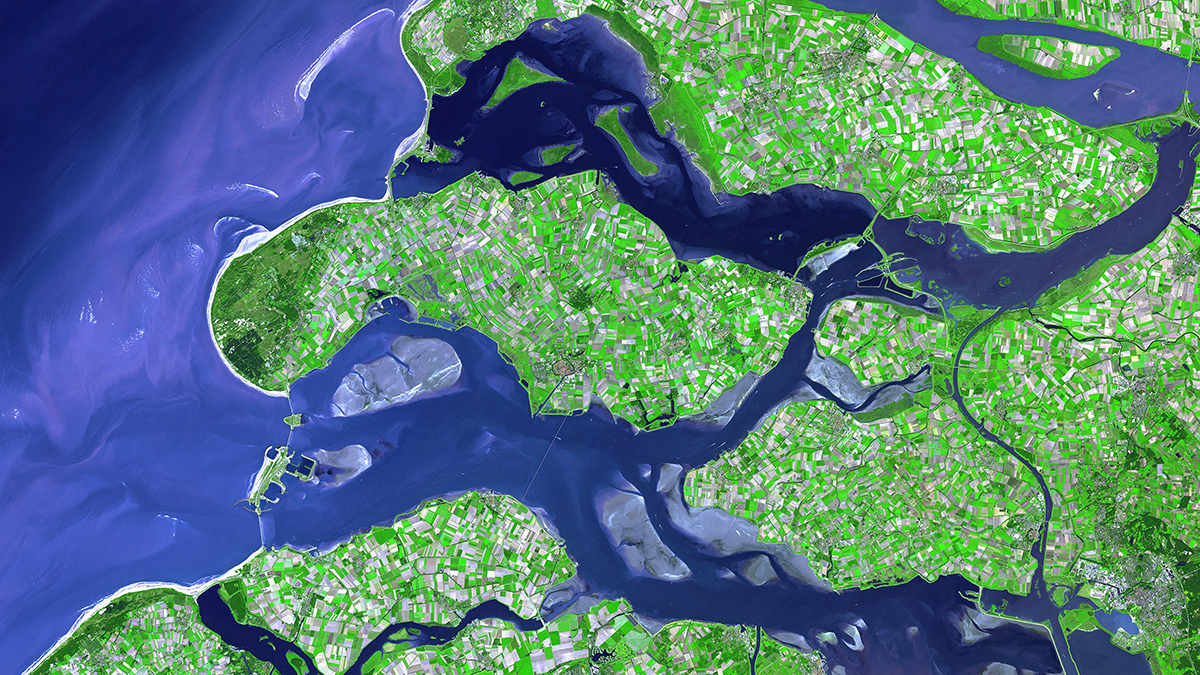
Blending Science and Indigenous Knowledge to Tell an Estuary’s Story
A new study of nutrient levels in soil cores supports oral Indigenous history, informing future estuary restoration efforts.
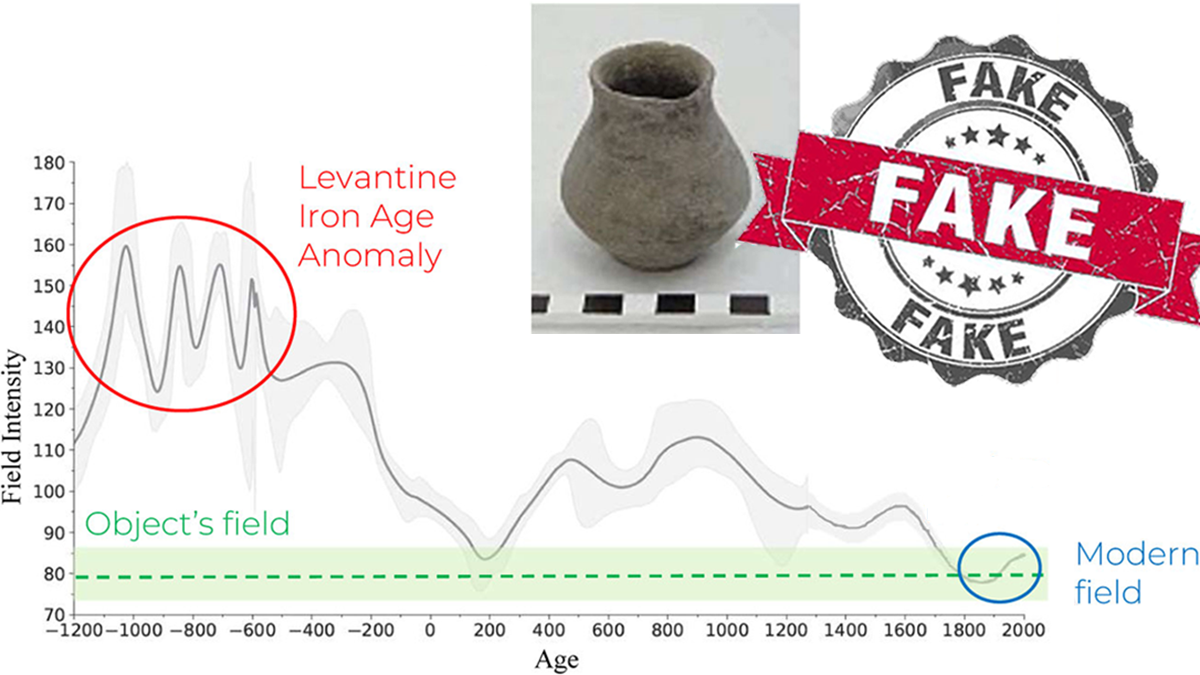
Credible or Counterfeit: How Paleomagnetism Can Help Archaeologists Find Frauds
Duplicating artifacts that preserve records from biblical times is a lucrative business. A method used for both dating artifacts and reconstructing Earth’s history could identify phony pieces.
Celebrating the MacGyver Spirit: Hacking, Tinkering, Scavenging, and Crowdsourcing
The MacGyver sessions allow scientist-tinkerers to have “nerd-on-nerd” discussions about do-it-yourself gadgets and gizmos.
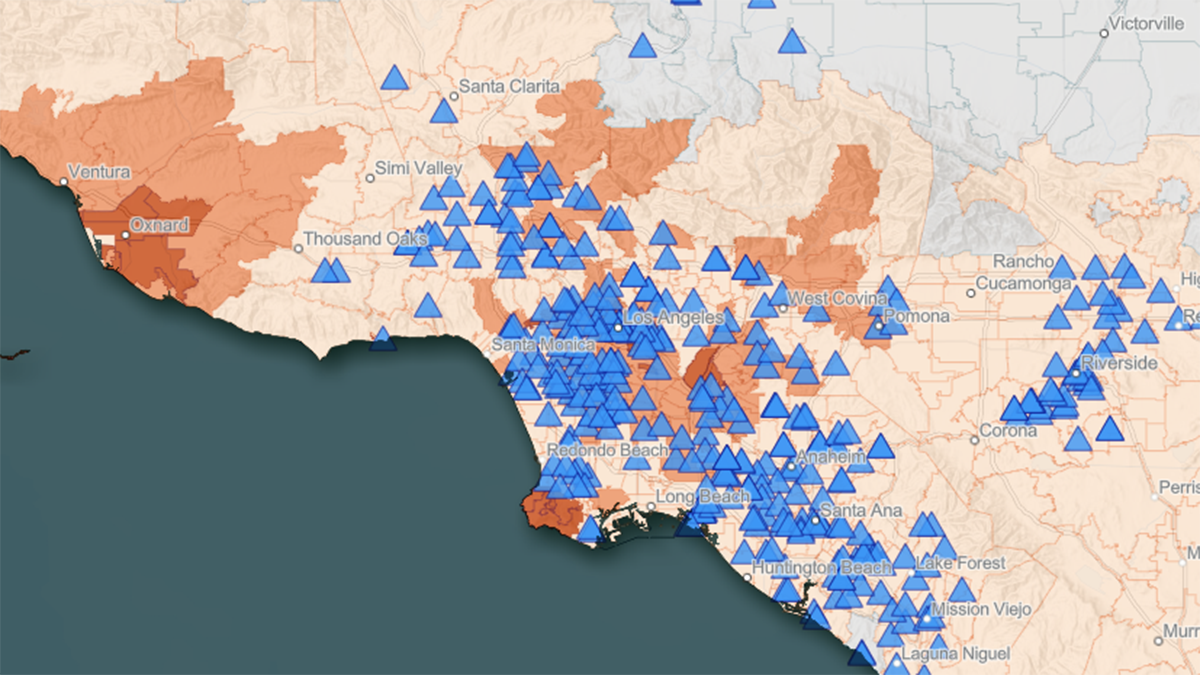
New Tool Maps the Overlap of Heat and Health in California
CalHeatScore creates heat wave warnings for every zip code in California, using temperature data, socioeconomic indicators, and the history of emergency room visits, to predict heat-related health risk.
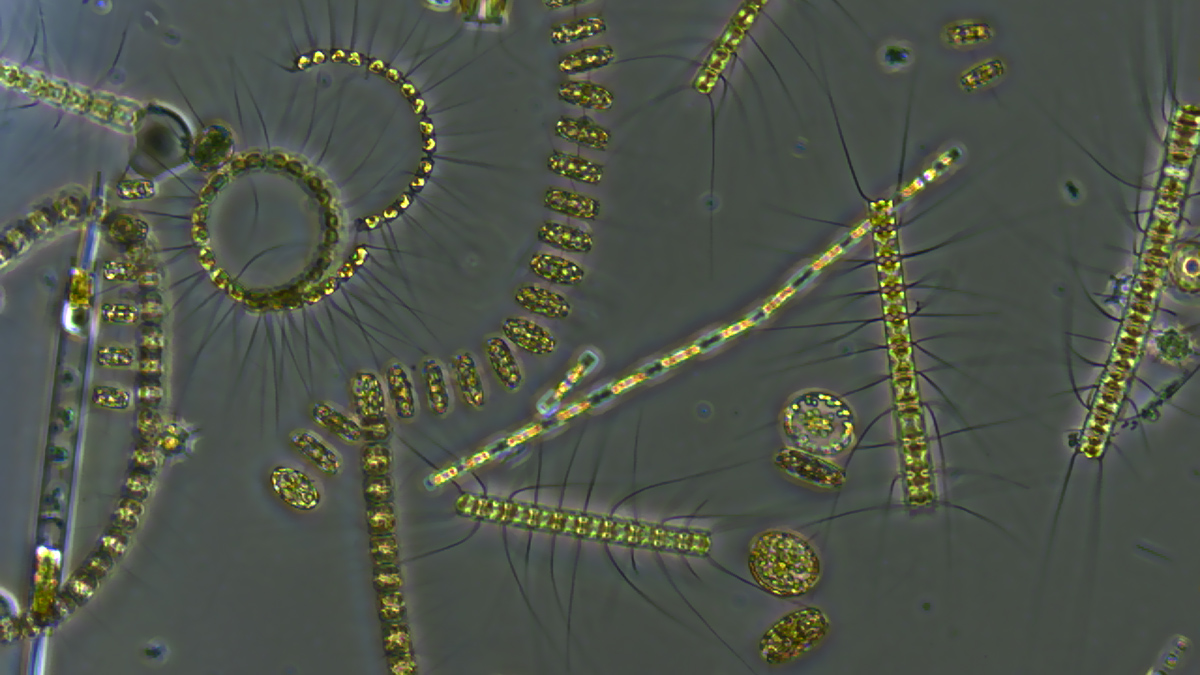
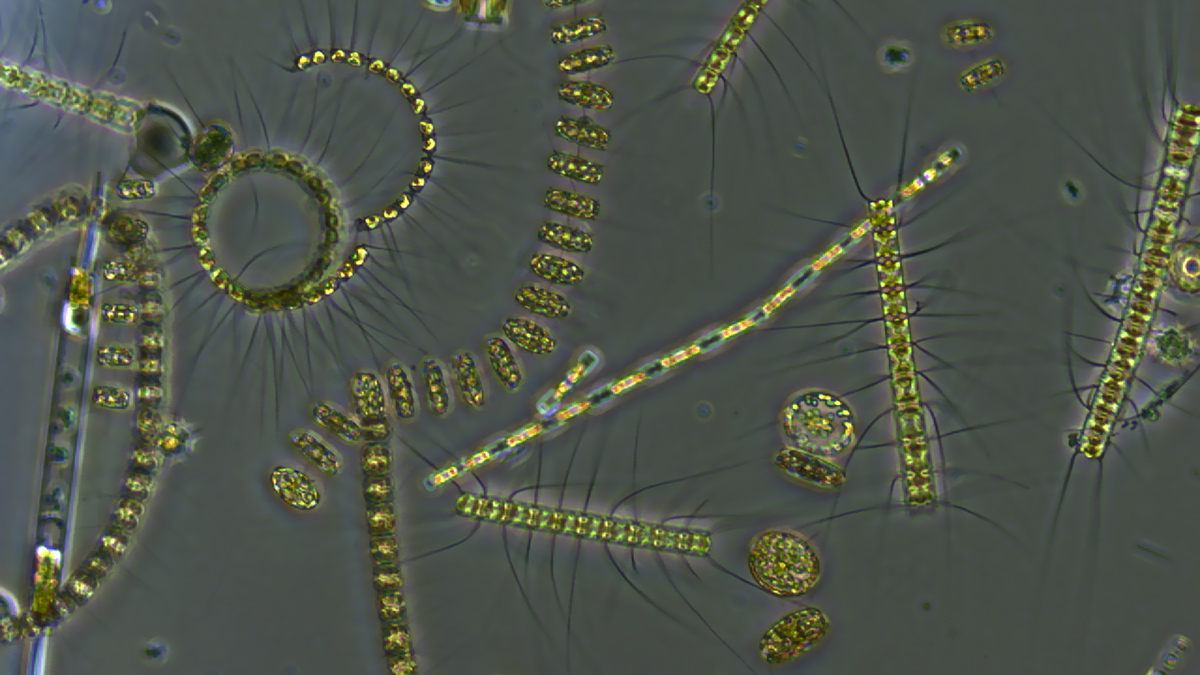
Marine Heat Waves Slow the Ocean’s Carbon Flow
When plankton find themselves in hot water, organic matters stalls at the surface and disrupts transport of carbon to the deep ocean.
The Role of a Ditch in the Matrix
These constructed waterways are often a “no-man’s-land” between terrestrial scientists and limnologists. But ditches’ role in transport, agriculture, biodiversity, greenhouse gas emissions, and even archaeology means it’s time to take a closer look.
Scientists Must Join Forces to Solve Forecasting’s Predictability Desert
To strengthen societal resilience to worsening natural hazards, siloed Earth system science communities must collaborate to understand conditions that favor skillful subseasonal-to-seasonal forecasts.