A recent update to an algorithm for processing satellite data could improve understanding of the variable climate effects of clouds composed of different amounts of ice and liquid.
Research Spotlights
Research spotlights are plain-language summaries of recent articles published in AGU’s suite of 24 journals.
What Led to the Largest Volcanic Eruption in Human History?
A mineral-dating project at the Toba caldera in Indonesia sheds light on the science of supereruptions.
How "Godzilla" El Niño Affected Tropical Fish in Low-Oxygen Zone
A warm period unexpectedly boosted some species of fish larvae off the coast of Mexico.
Mysterious Intraseasonal Oscillations in Monsoons
The unpredictable cycles of rainfall during India's summerlong monsoon have stymied scientists for decades.
Mushrooms Could Provide a Record of Grassland History
Scientists measured carbon isotopes in certain types of fungi to assess whether the organisms can track how climate change is affecting grasses.
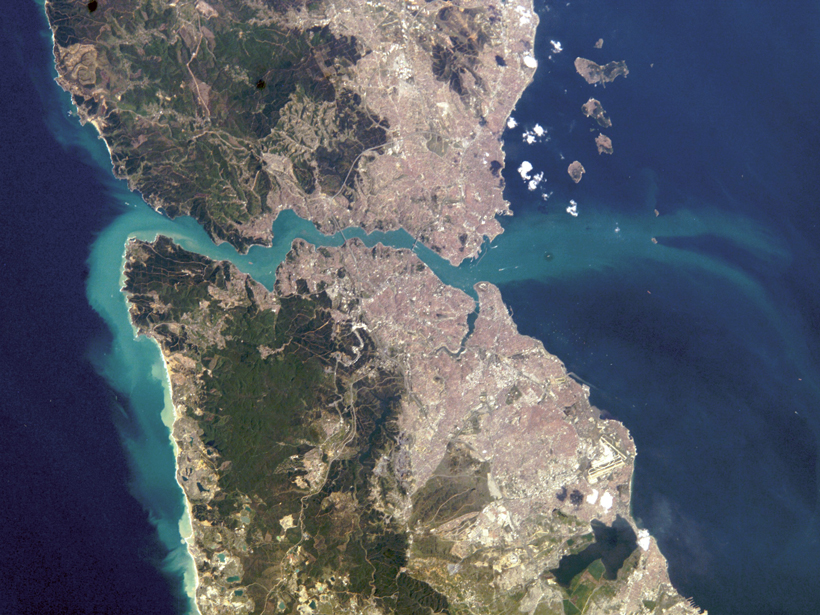
Big Storms Pump Mediterranean Water Far into the Black Sea
For the first time, scientists provide a sea-wide view of what happens to Mediterranean waters that flow into the Black Sea through the Bosporus Strait.
For Magnetic Reconnection Energy, O—not X—Might Mark the Spot
A new analysis of satellite data could upend conventional wisdom about how solar storms produce their dangerous radiation—not from X-shaped mergers of magnetic field lines but from swirling vortices.
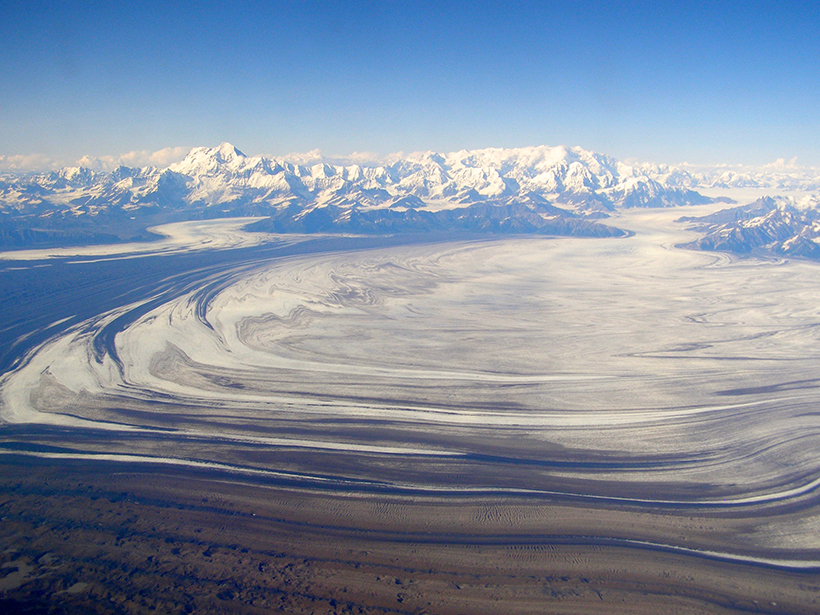
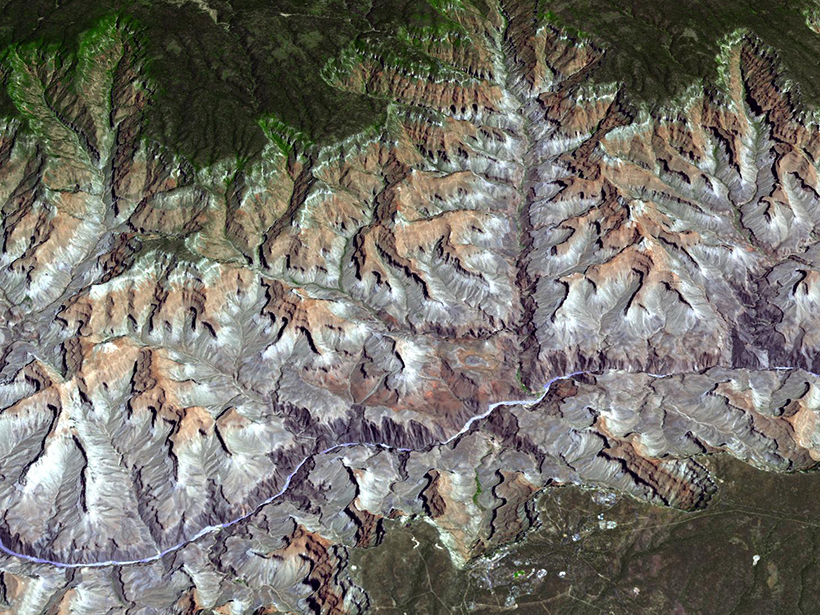
A Mountain Range's History Preserved in Ocean Sediments
Fission track dating core samples from the Gulf of Alaska demonstrates that offshore sediments can be used to reconstruct a mountain range's changing exhumation patterns.
Stream Network Geometry Correlates with Climate
A "big data" analysis of nearly 1 million river junctions in the contiguous United States shows that branching angles in dendritic drainages vary systematically between humid and arid regions.
High Arctic Emissions of a Strong Greenhouse Gas
Isotope data bring scientists one step closer to revealing the microbial processes behind nitrous oxide emission in the tundra.