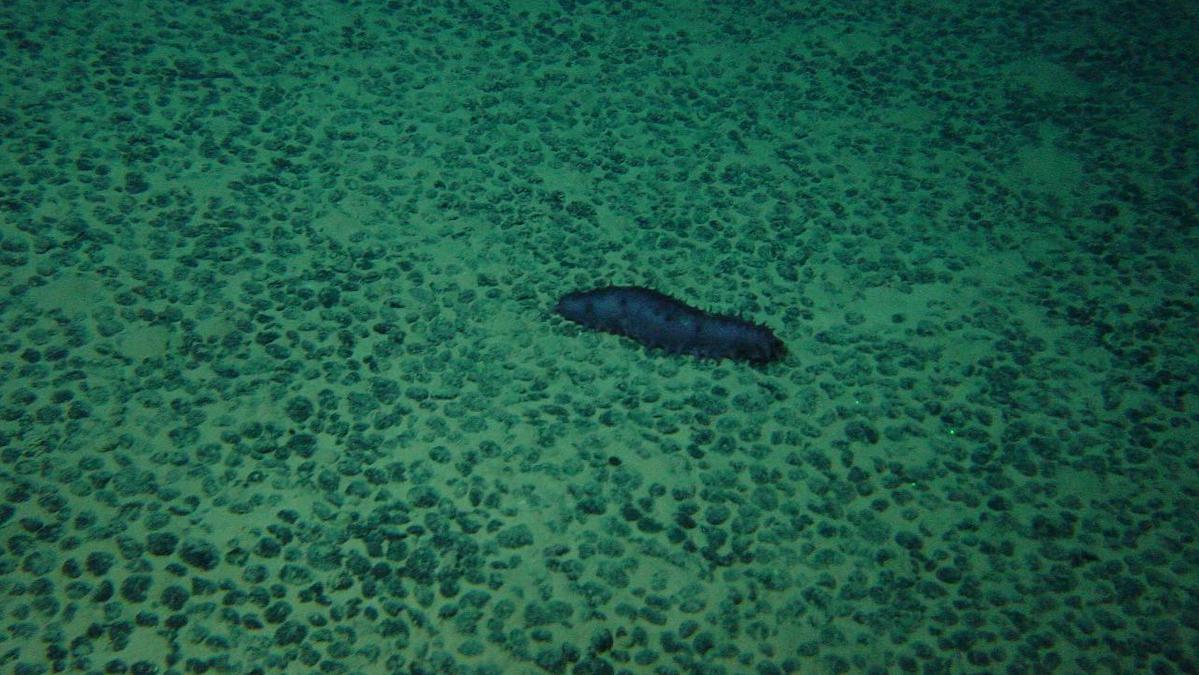
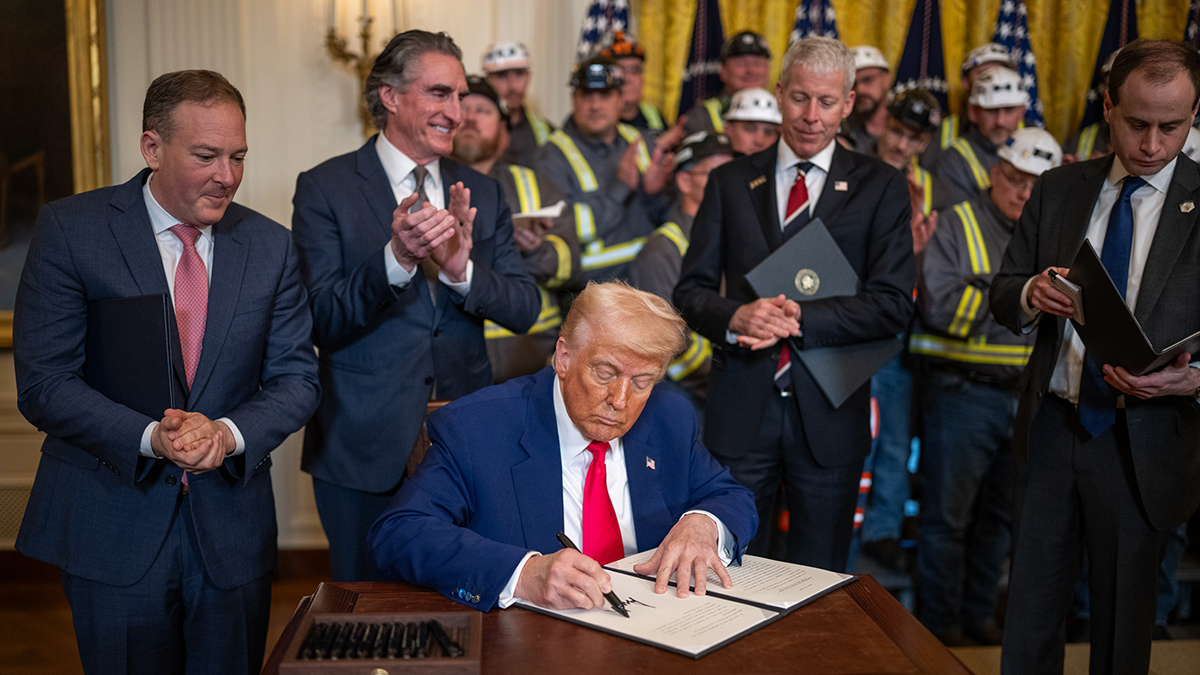
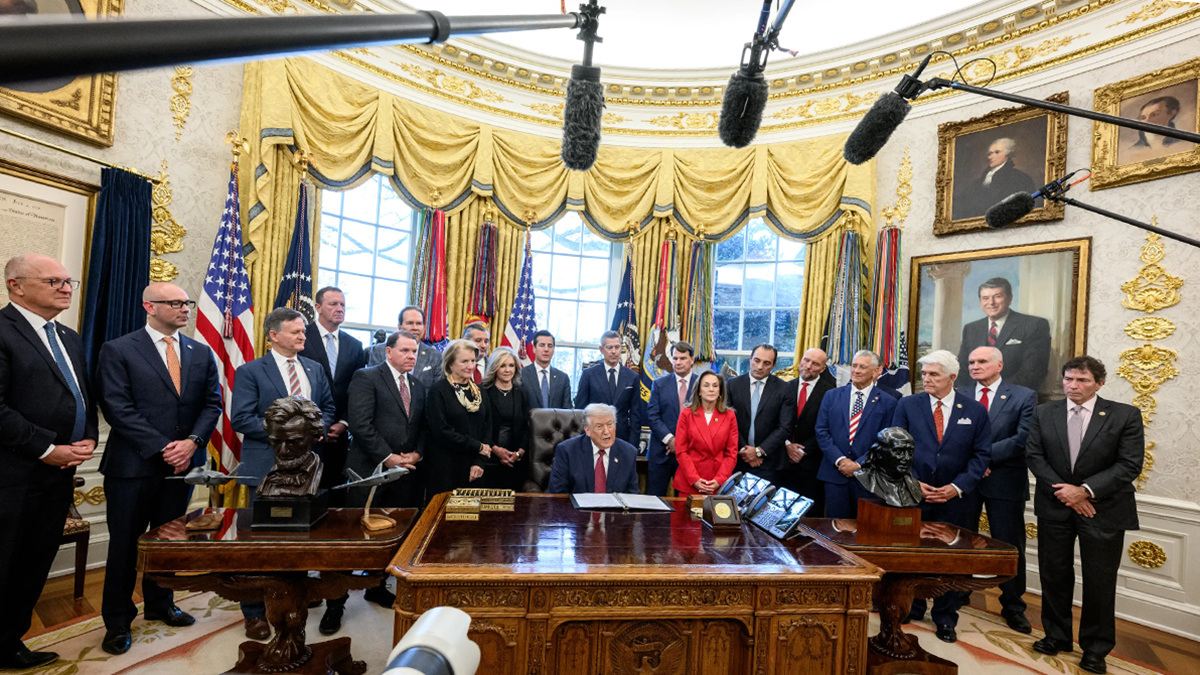
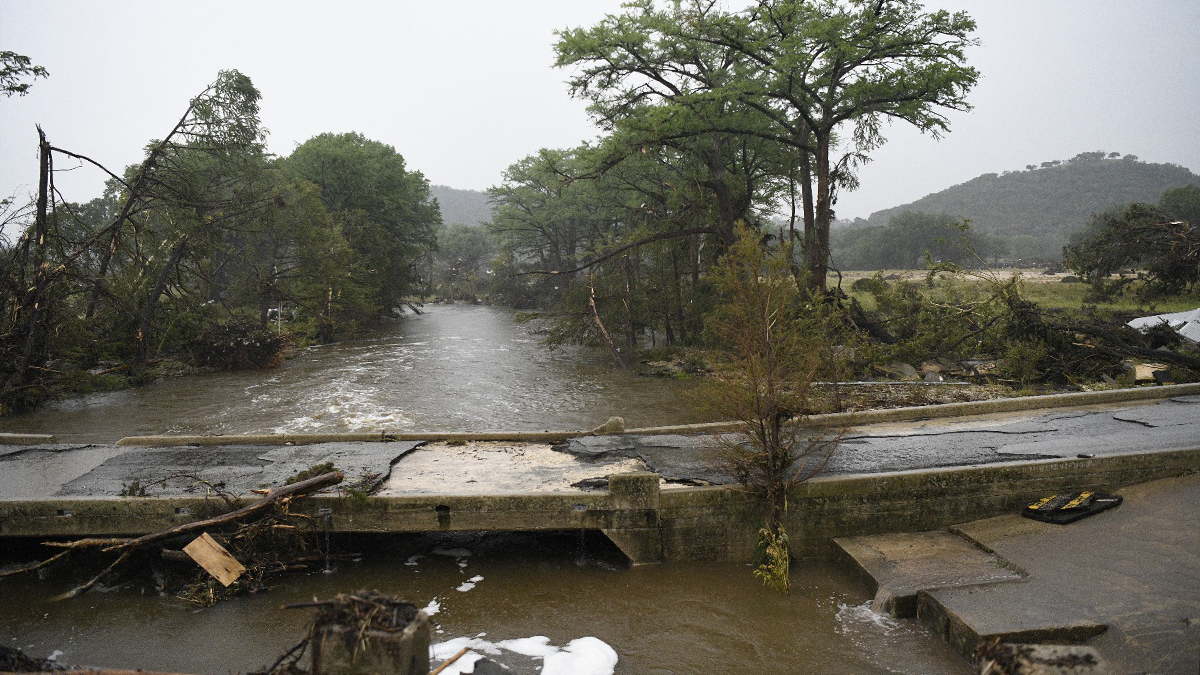
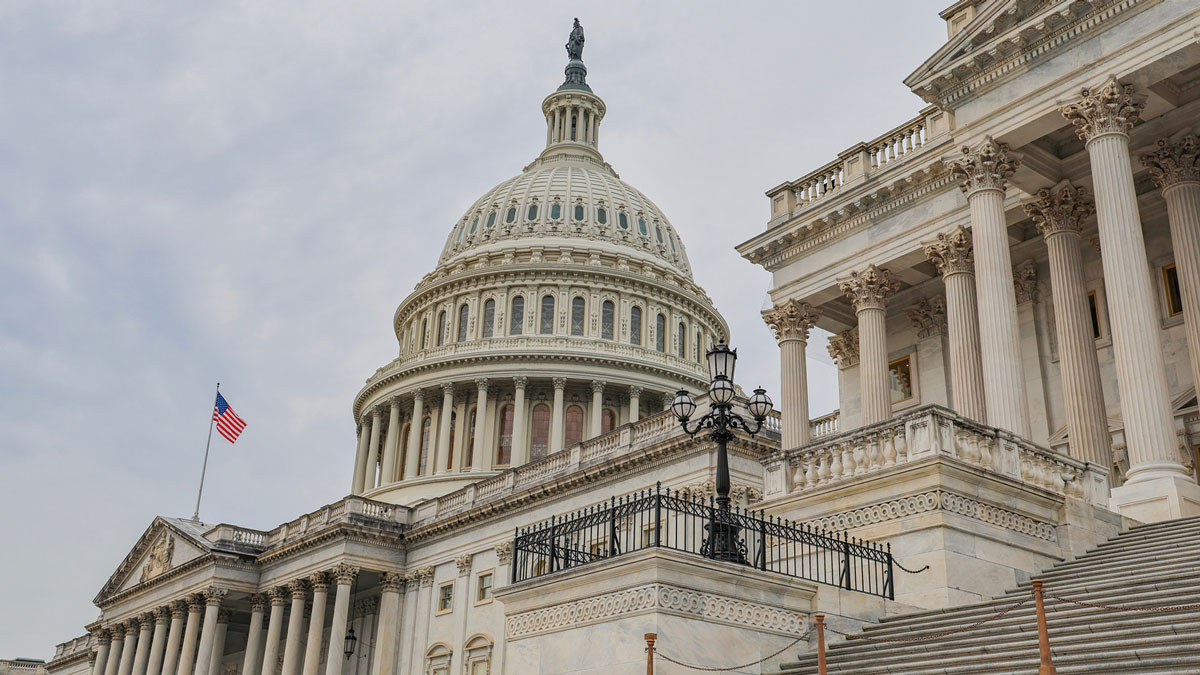
NOAA has finalized a rule that will expedite the permit and license application process for deep seabed mining and allow companies to mine beyond U.S. jurisdictional boundaries.
culture & policy
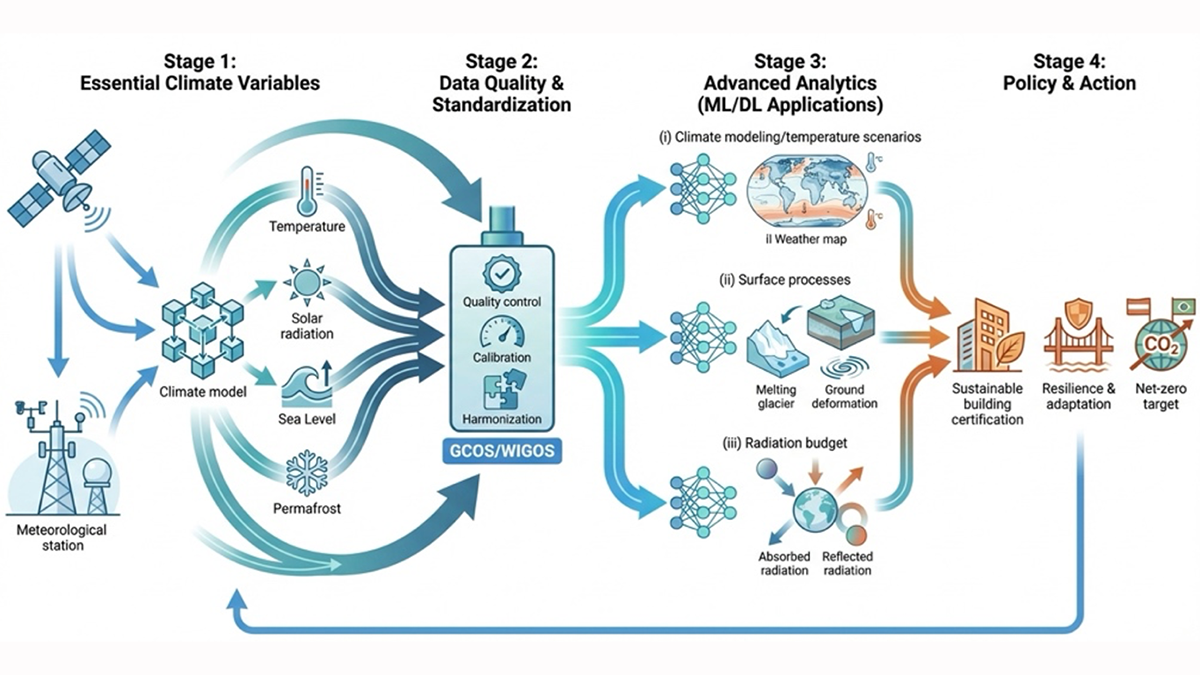
Bridging the Gap: Transforming Reliable Climate Data into Climate Policy
A new special collection welcomes research that bridges the gap between rigorous Essential Climate Variable (ECV) monitoring, AI analytics, and climate policy.
The State of the Science 1 Year On: Climate Change and Energy
Trump’s first year in office has reversed many climate policy decisions and aggressively advanced fossil fuel interests.
The State of the Science 1 Year On: Academia and Research
The past year was a shock to the U.S. higher education system. The coming year may see even more jolts.
The State of the Science 1 Year On: Environment
Administration policies have eliminated funding sources, review processes, and pollution limits designed to protect the nation’s land, water, and air.
The State of the Science 1 Year On: Executive Summary
How the Trump Administration is redefining the way science is practiced and perceived in the United States.
The State of the Science 1 Year On: The Federal Workforce
Thousands have left the federal workforce, and those who remain face significant uncertainty about their professional futures.
The State of the Science 1 Year On: Health and Safety
The Trump administration has holistically reevaluated the government’s relationship—and how it responds to threats— to the health and welfare of its citizens.
The State of the Science 1 Year On: Conclusion
The future of federal career paths, funding, and climate-related legislation likely lies in the courts, not the ballot box.
Plan to End NEPA’s “Regulatory Reign of Terror” Is Finalized
The Trump administration has finalized a plan to roll back regulations outlined by one of our nation’s bedrock environmental laws.